Faraday`s Law and the Rotationg Coil File
... ε is the e.m.f. Induced (V) N is the number of turns on the coil ∆Φ is the change in flux though each turn of the coil. (Wb) ∆t is the time taken for the flux change.(s) Note that in this equation the total change in flux linkage in the coil is N∆Φ. Sometimes you may see this written as ∆NΦ. It foll ...
... ε is the e.m.f. Induced (V) N is the number of turns on the coil ∆Φ is the change in flux though each turn of the coil. (Wb) ∆t is the time taken for the flux change.(s) Note that in this equation the total change in flux linkage in the coil is N∆Φ. Sometimes you may see this written as ∆NΦ. It foll ...
lecture19
... cannot change a charged particle’s potential energy or electric potential. But electric fields can do work. This equation shows that a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, which can change a charged particle’s potential energy. This induced electric field is responsible for induced emf. ...
... cannot change a charged particle’s potential energy or electric potential. But electric fields can do work. This equation shows that a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, which can change a charged particle’s potential energy. This induced electric field is responsible for induced emf. ...
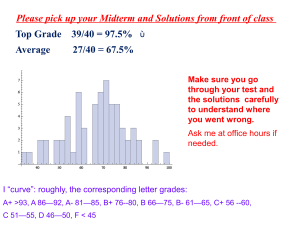
Top Grade 39/40 = 97.5% Average 27/40 = 67.5%
... Current on one side of the loop flows in the opposite direction to the current on the other side of loop. So, the two sides gets deflected in opposite directions, as shown; hence it turns. After a half turn, the sides have reversed, so deflection is in the opposite direction – makes coil turns back. ...
... Current on one side of the loop flows in the opposite direction to the current on the other side of loop. So, the two sides gets deflected in opposite directions, as shown; hence it turns. After a half turn, the sides have reversed, so deflection is in the opposite direction – makes coil turns back. ...
Answers 6
... If it were non-zero for some reason, charges would move within the conductor. The separation of positive and negative charge would set up an internal electric field which would oppose the original field. In equilibrium the two fields would be equal and opposite, making the total field zero. ...
... If it were non-zero for some reason, charges would move within the conductor. The separation of positive and negative charge would set up an internal electric field which would oppose the original field. In equilibrium the two fields would be equal and opposite, making the total field zero. ...
Electric Motors
... (A generator takes a manual force (a person turning a crankshaft) and moves a conductor through a magnetic field to produce an electric current.) ...
... (A generator takes a manual force (a person turning a crankshaft) and moves a conductor through a magnetic field to produce an electric current.) ...
Homework 7 Solutions Ch. 28: #28 à 28)
... acceleration and therefore the net force must be just above zero we ' ll call the direction of the static friction force x and the direction of the normal force z Fnet x = i L B cos θ − µs N Fnetz = i L B sin θ + N − m g since there is no acceleration upwards or downwards Fnetz = 0 ⇒ N = mg − i L B ...
... acceleration and therefore the net force must be just above zero we ' ll call the direction of the static friction force x and the direction of the normal force z Fnet x = i L B cos θ − µs N Fnetz = i L B sin θ + N − m g since there is no acceleration upwards or downwards Fnetz = 0 ⇒ N = mg − i L B ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.