6th grade Force and Motion lp
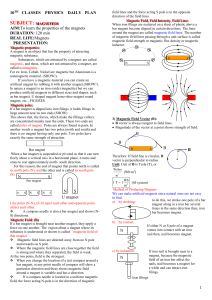
... What do students need to learn to be able to answer the Essential Question? Assessment Prompt 1: What effects gravitational force? Assessment Prompt 2: How does magnetism produce an electrical force? Activating Strategy: (Hook and Link; Anticipatory Set; Vocabulary) ...
... What do students need to learn to be able to answer the Essential Question? Assessment Prompt 1: What effects gravitational force? Assessment Prompt 2: How does magnetism produce an electrical force? Activating Strategy: (Hook and Link; Anticipatory Set; Vocabulary) ...
7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
... d) By the means of earth’s magnetic field If you place an iron bar at an angle with the horizontal and strike bar with a hammer several times. Then the iron bar becomes a magnet. Because, sudden motions of the domains in the iron bar are aligned in the direction in the earth’s magnetic field PPrroo ...
... d) By the means of earth’s magnetic field If you place an iron bar at an angle with the horizontal and strike bar with a hammer several times. Then the iron bar becomes a magnet. Because, sudden motions of the domains in the iron bar are aligned in the direction in the earth’s magnetic field PPrroo ...
Chapter 22 Gauss*s Law
... An electric dipole consists of two charges Q, equal in magnitude and opposite in sign, separated by a distance .The dipole moment, pp= Q , points from the negative to the positive charge. ...
... An electric dipole consists of two charges Q, equal in magnitude and opposite in sign, separated by a distance .The dipole moment, pp= Q , points from the negative to the positive charge. ...
Skeleton
... a) Turn on the calculator and start the EasyData application with the magnetometer probe plugged into the interface. For this portion of the experiment, select “0.3 mT” as the range on the probe (small black switch). b) On a non-metallic flat surface, turn the detector surface until it gives the max ...
... a) Turn on the calculator and start the EasyData application with the magnetometer probe plugged into the interface. For this portion of the experiment, select “0.3 mT” as the range on the probe (small black switch). b) On a non-metallic flat surface, turn the detector surface until it gives the max ...
File
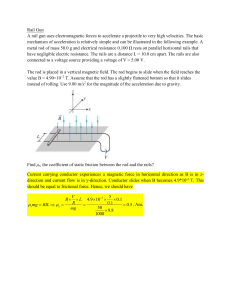
... magnetic field strength due to a long wire that carries a current of 6.0 A at a point 1.0 cm away from the wire? [1.2 x 10-4 T] ...
... magnetic field strength due to a long wire that carries a current of 6.0 A at a point 1.0 cm away from the wire? [1.2 x 10-4 T] ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.