Motor Fundamentals - Clark Science Center
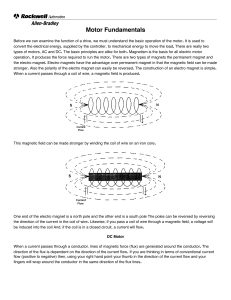
... magnet. The permanent magnet is free to rotate and is therefore called the rotor. The electro magnets are stationary and are therefore called the stator. Initially if the north and south poles are aligned in the motor and, because like poles repel and unlike poles attract, the rotor will be pushed b ...
... magnet. The permanent magnet is free to rotate and is therefore called the rotor. The electro magnets are stationary and are therefore called the stator. Initially if the north and south poles are aligned in the motor and, because like poles repel and unlike poles attract, the rotor will be pushed b ...
Non-KAM dynamical chaos in semiconductor superlattices Arkadii Krokhin, UNT
... superlattices in the presence of non-parallel electric and magnetic field. In this geometry the electrons in the superlattice miniband turn out to form a non-KAM dynamical system that exhibits a non-traditional chaotic behavior (PRL 87, 046803 (2001). Due to the resonant coupling between the Bloch o ...
... superlattices in the presence of non-parallel electric and magnetic field. In this geometry the electrons in the superlattice miniband turn out to form a non-KAM dynamical system that exhibits a non-traditional chaotic behavior (PRL 87, 046803 (2001). Due to the resonant coupling between the Bloch o ...
Lab 08: Electromagnetic Induction
... the electrostatic force...). We also know that the magnetic force is an action-atdistance force (which is why we can slide one or two sheets of paper between the magnet and the fridge, but not an entire notebook). We may be less aware, however, of the relationship between electricity and magnetism. ...
... the electrostatic force...). We also know that the magnetic force is an action-atdistance force (which is why we can slide one or two sheets of paper between the magnet and the fridge, but not an entire notebook). We may be less aware, however, of the relationship between electricity and magnetism. ...
File - electro science club
... electric current is called “Magnetic Effect” of electric current. In this unit we will learn about Magnetism, Magnet, Magnetic effect of electric current and its applications. Magnetism: The magnetism is the property possessed by certain bodies of attracting or repelling other bodies of magnetic sub ...
... electric current is called “Magnetic Effect” of electric current. In this unit we will learn about Magnetism, Magnet, Magnetic effect of electric current and its applications. Magnetism: The magnetism is the property possessed by certain bodies of attracting or repelling other bodies of magnetic sub ...
video slide
... magnetic field induces an emf • To learn how Faraday’s law relates the induced emf to the change in flux • To determine the direction of an induced emf • To calculate the emf induced by a moving conductor • To learn how a changing magnetic flux generates an electric field ...
... magnetic field induces an emf • To learn how Faraday’s law relates the induced emf to the change in flux • To determine the direction of an induced emf • To calculate the emf induced by a moving conductor • To learn how a changing magnetic flux generates an electric field ...
PHYS219 Fall semester 2014 - Purdue Physics
... The Lorentz Force • The Lorentz Force - the force on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field ...
... The Lorentz Force • The Lorentz Force - the force on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.