
Magnets Notes
... Draw a picture modelling the behavior of magnetic poles when they are brought together. Like poles _______________ ...
... Draw a picture modelling the behavior of magnetic poles when they are brought together. Like poles _______________ ...
Teacher Notes PDF
... be found on the CD that accompanies this book. See Appendix A for more information. 2. Demonstrate magnetic field lines by placing a bar magnet on an overhead. Position clear compasses around the magnet and discuss the position of the needles. Another alternative is to provide small compasses for ea ...
... be found on the CD that accompanies this book. See Appendix A for more information. 2. Demonstrate magnetic field lines by placing a bar magnet on an overhead. Position clear compasses around the magnet and discuss the position of the needles. Another alternative is to provide small compasses for ea ...
Guided Reading Chapter 22 Section 2 Also do: 539 #1
... 3. A great advantage of an electromagnet is that you can change the ____________ of the magnet. 4. How does a toaster work? ...
... 3. A great advantage of an electromagnet is that you can change the ____________ of the magnet. 4. How does a toaster work? ...
Physics 12 Magnetic Force
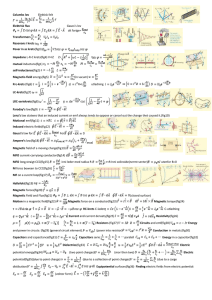
... Physics 12 Magnetic Force. Understanding Concept. 1) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on a proton moving horizontally northward at 8.6 x 104 m/s, as it enters a magnetic field of 1.2 T directed vertically upward. (The mass of a proton is 1.67x 10–27 kg.) 1.7 x 10–14 N [E] ...
... Physics 12 Magnetic Force. Understanding Concept. 1) Determine the magnitude and direction of the magnetic force on a proton moving horizontally northward at 8.6 x 104 m/s, as it enters a magnetic field of 1.2 T directed vertically upward. (The mass of a proton is 1.67x 10–27 kg.) 1.7 x 10–14 N [E] ...
Slide 1
... Electrons spinning around atoms are moving electric charges. Usually, opposite direction spinning electrons pair up, and cancel the magnetic field. ...
... Electrons spinning around atoms are moving electric charges. Usually, opposite direction spinning electrons pair up, and cancel the magnetic field. ...
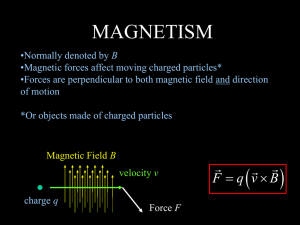
A Magnet is an object with a magnetic force or field that attracts or
... near Earth’s surface. Thousands of years ago, people discovered that when lodestone was hung by a string, one end always pointed north. This was used by Chinese sailors to tell what direction they were sailing. Today a compass is based on the same idea. A compass uses a magnetized needle which is al ...
... near Earth’s surface. Thousands of years ago, people discovered that when lodestone was hung by a string, one end always pointed north. This was used by Chinese sailors to tell what direction they were sailing. Today a compass is based on the same idea. A compass uses a magnetized needle which is al ...
Magnetism PowerPoint
... strongest. These are called “poles.” Each magnet has 2 poles – 1 north, 1 south. ...
... strongest. These are called “poles.” Each magnet has 2 poles – 1 north, 1 south. ...
magnetismintrowebquest8word
... information about the source and properties of magnetism http://www.ndted.org/EducationResources/CommunityCollege/MagParticle/Physics/Magnetism.htm 1) What causes magnetism inside the atom? 2) Why are unpaired electrons more significant than paired electrons in terms of magnetic properties? 3) 3) Wh ...
... information about the source and properties of magnetism http://www.ndted.org/EducationResources/CommunityCollege/MagParticle/Physics/Magnetism.htm 1) What causes magnetism inside the atom? 2) Why are unpaired electrons more significant than paired electrons in terms of magnetic properties? 3) 3) Wh ...
Magnetism PPT
... –Hard – easily magnetized but looses magnetic properties easily. –Soft – difficult to magnetize but does not loose its magnetic properties. ...
... –Hard – easily magnetized but looses magnetic properties easily. –Soft – difficult to magnetize but does not loose its magnetic properties. ...
SPH 3U(G) TEST
... Which statement about the magnetic north pole of Earth is true? a. Its location never changes. b. It corresponds to the N-pole of a bar magnet. c. It is at the same location as the geographic north pole of Earth. d. It corresponds to the S-pole of a bar magnet. e. both A and D ...
... Which statement about the magnetic north pole of Earth is true? a. Its location never changes. b. It corresponds to the N-pole of a bar magnet. c. It is at the same location as the geographic north pole of Earth. d. It corresponds to the S-pole of a bar magnet. e. both A and D ...
Force between magnets
Magnets exert forces and torques on each other due to the complex rules of electromagnetism. The forces of attraction field of magnets are due to microscopic currents of electrically charged electrons orbiting nuclei and the intrinsic magnetism of fundamental particles (such as electrons) that make up the material. Both of these are modeled quite well as tiny loops of current called magnetic dipoles that produce their own magnetic field and are affected by external magnetic fields. The most elementary force between magnets, therefore, is the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction. If all of the magnetic dipoles that make up two magnets are known then the net force on both magnets can be determined by summing up all these interactions between the dipoles of the first magnet and that of the second.It is always more convenient to model the force between two magnets as being due to forces between magnetic poles having magnetic charges 'smeared' over them. Such a model fails to account for many important properties of magnetism such as the relationship between angular momentum and magnetic dipoles. Further, magnetic charge does not exist. This model works quite well, though, in predicting the forces between simple magnets where good models of how the 'magnetic charge' is distributed is available.

















![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001000968_1-9cbbc8bdff99f3eeba0051a7227b6c89-300x300.png)



