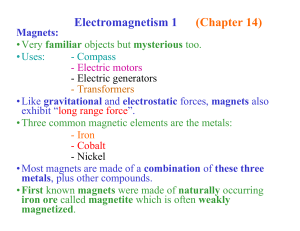
Magnetism Notes
... Unlike electrical charges, can’t have __________ N or S pole; always have both Like electrical charges, opposite poles _____________, like poles ___________ Forces between poles are ____________ proportional to strength of the poles, ________________ proportional to the square of distance between th ...
... Unlike electrical charges, can’t have __________ N or S pole; always have both Like electrical charges, opposite poles _____________, like poles ___________ Forces between poles are ____________ proportional to strength of the poles, ________________ proportional to the square of distance between th ...
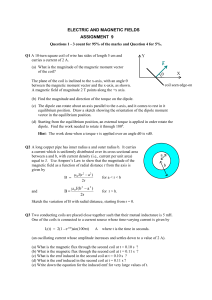
Magnetism I Name: A proton moves with a speed of 1.00 x 105 m/s
... moves eastward? (c) Calculate the gravitational force on the proton and compare it with the magnetic force. Compare it also with the electric force if there were an electric field with a magnitude equal to E = 1.50 x 102 N/C at the location, a common value at Earth’s surface. Note that the mass of t ...
... moves eastward? (c) Calculate the gravitational force on the proton and compare it with the magnetic force. Compare it also with the electric force if there were an electric field with a magnitude equal to E = 1.50 x 102 N/C at the location, a common value at Earth’s surface. Note that the mass of t ...
1 - Flipped Physics
... 1) A proton moving at 2.5X104 m/s horizontally enters a region where a magnetic field of 0.6 T is present, directed vertically downward. What force acts on the proton? a) zero b) 2.4X10-16 N c) 4.8X10-16 N d) 9.6X10-16 N 2) As the current increases in a wire placed perpendicular to a magnetic field, ...
... 1) A proton moving at 2.5X104 m/s horizontally enters a region where a magnetic field of 0.6 T is present, directed vertically downward. What force acts on the proton? a) zero b) 2.4X10-16 N c) 4.8X10-16 N d) 9.6X10-16 N 2) As the current increases in a wire placed perpendicular to a magnetic field, ...
Electromagnetism Unit 2014
... • Static discharge is the movement of charges from one object to another. – Think of this like shocking yourself when you drag your feet on the carpet and touch a door handle. – You feel the “shock.” – What you really experienced is static discharge. – Lightning is also a discharge of static electri ...
... • Static discharge is the movement of charges from one object to another. – Think of this like shocking yourself when you drag your feet on the carpet and touch a door handle. – You feel the “shock.” – What you really experienced is static discharge. – Lightning is also a discharge of static electri ...
Magnetism purple sheet ANSWERS
... field. The north pole of Earth’s magnetic field is located near (but not at) the south geographic pole. 35. The north pole of a compass points north because it aligns with the magnetic field of Earth whose south pole is located close to the north geographic pole of Earth. The north pole is at ...
... field. The north pole of Earth’s magnetic field is located near (but not at) the south geographic pole. 35. The north pole of a compass points north because it aligns with the magnetic field of Earth whose south pole is located close to the north geographic pole of Earth. The north pole is at ...
Force between magnets
Magnets exert forces and torques on each other due to the complex rules of electromagnetism. The forces of attraction field of magnets are due to microscopic currents of electrically charged electrons orbiting nuclei and the intrinsic magnetism of fundamental particles (such as electrons) that make up the material. Both of these are modeled quite well as tiny loops of current called magnetic dipoles that produce their own magnetic field and are affected by external magnetic fields. The most elementary force between magnets, therefore, is the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction. If all of the magnetic dipoles that make up two magnets are known then the net force on both magnets can be determined by summing up all these interactions between the dipoles of the first magnet and that of the second.It is always more convenient to model the force between two magnets as being due to forces between magnetic poles having magnetic charges 'smeared' over them. Such a model fails to account for many important properties of magnetism such as the relationship between angular momentum and magnetic dipoles. Further, magnetic charge does not exist. This model works quite well, though, in predicting the forces between simple magnets where good models of how the 'magnetic charge' is distributed is available.