Open file - PebblePad
... Natural magnets derived from magnetite were discovered by Greeks in ~600 BC. They were then widely used in navigation due to their property to orient themselves to the north and south poles. Having found their wide use in navigation; magnets generated a great amount of ...
... Natural magnets derived from magnetite were discovered by Greeks in ~600 BC. They were then widely used in navigation due to their property to orient themselves to the north and south poles. Having found their wide use in navigation; magnets generated a great amount of ...
Magnetism - District 196
... Similar, yet DIFFERENT than electric charges. Similarities 1. Can attract and repel without touching 2. The amount of attracting or repelling depends on distance 3. Like poles repel, opposite poles attract. Difference Magnetic poles can NOT be separated. They always occur in pairs. ...
... Similar, yet DIFFERENT than electric charges. Similarities 1. Can attract and repel without touching 2. The amount of attracting or repelling depends on distance 3. Like poles repel, opposite poles attract. Difference Magnetic poles can NOT be separated. They always occur in pairs. ...
Name Section 18-1 “Magnets and Magnetism” pages 510
... Write either magnetic forces or magnetic fields in the space provided. _______________________ 7. come from spinning electric charges in the magnets _______________________ 8. can push magnets apart or pull them together _______________________ 9. depend on how two magnets’ poles line up ___________ ...
... Write either magnetic forces or magnetic fields in the space provided. _______________________ 7. come from spinning electric charges in the magnets _______________________ 8. can push magnets apart or pull them together _______________________ 9. depend on how two magnets’ poles line up ___________ ...
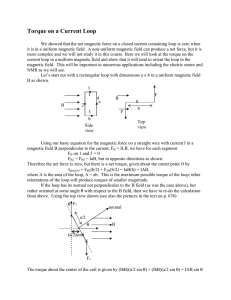
Torque on a Current Loop
... for the energy of a magnetic dipole in a B field, U = − µ ⋅ B , so that the difference between a spin up and down nucleus has an energy ∆U = 2µ B B . The RF signal must match this energy difference to be absorbed – a condition known as a resonance (hence the R in NMR). A spin flip to a higher energy ...
... for the energy of a magnetic dipole in a B field, U = − µ ⋅ B , so that the difference between a spin up and down nucleus has an energy ∆U = 2µ B B . The RF signal must match this energy difference to be absorbed – a condition known as a resonance (hence the R in NMR). A spin flip to a higher energy ...
Magnetic Induction
... When an electric current flows in a circuit it produces a magnetic field. Another way of saying that is “a moving charge generates a magnetic field”. Michael Faraday reversed the process. By passing a magnet through a coil, he produced a voltage. Another way of saying that is “a moving magnetic fiel ...
... When an electric current flows in a circuit it produces a magnetic field. Another way of saying that is “a moving charge generates a magnetic field”. Michael Faraday reversed the process. By passing a magnet through a coil, he produced a voltage. Another way of saying that is “a moving magnetic fiel ...
Magnetic Polarity - Ms. Chelsea Gaudet
... Students, before this experiment, will write a prediction in their science journal. After completing the experiment 3 times, will compare their findings with another group. Students will then record their observations. Did the needle always point in the same direction? What direction did it point in ...
... Students, before this experiment, will write a prediction in their science journal. After completing the experiment 3 times, will compare their findings with another group. Students will then record their observations. Did the needle always point in the same direction? What direction did it point in ...
Magnets
... 5 Earth has two magnetic poles. 6 Earth’s geographic north pole is _____. 7 Electrons are tiny _______. 8 In the atoms of most materials, pairs of electrons spin in a way that cancels the magnetic field. 9 A clump of magnetic atoms is called a _____. 10 If you cut a magnet into small pieces, the sma ...
... 5 Earth has two magnetic poles. 6 Earth’s geographic north pole is _____. 7 Electrons are tiny _______. 8 In the atoms of most materials, pairs of electrons spin in a way that cancels the magnetic field. 9 A clump of magnetic atoms is called a _____. 10 If you cut a magnet into small pieces, the sma ...
Force between magnets
Magnets exert forces and torques on each other due to the complex rules of electromagnetism. The forces of attraction field of magnets are due to microscopic currents of electrically charged electrons orbiting nuclei and the intrinsic magnetism of fundamental particles (such as electrons) that make up the material. Both of these are modeled quite well as tiny loops of current called magnetic dipoles that produce their own magnetic field and are affected by external magnetic fields. The most elementary force between magnets, therefore, is the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction. If all of the magnetic dipoles that make up two magnets are known then the net force on both magnets can be determined by summing up all these interactions between the dipoles of the first magnet and that of the second.It is always more convenient to model the force between two magnets as being due to forces between magnetic poles having magnetic charges 'smeared' over them. Such a model fails to account for many important properties of magnetism such as the relationship between angular momentum and magnetic dipoles. Further, magnetic charge does not exist. This model works quite well, though, in predicting the forces between simple magnets where good models of how the 'magnetic charge' is distributed is available.