TCAP Review 2013 – Page 9 – Electromagnetism
... Draw the figure of the Earth’s magnetic poles on p. 429. ...
... Draw the figure of the Earth’s magnetic poles on p. 429. ...
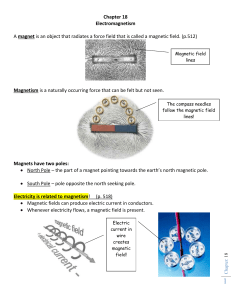
Lesson 1: Magnets have 2 poles. Like poles attract, unlike poles
... Lesson 1: Magnets have 2 poles. Like poles attract, unlike poles repel. Magnets attract iron. Magnetic force is strongest around the poles of a magnet. Vocab: magnet Magnetism Magnetic pole Magnetic force Lesson 2: Magnetic fields spread out from one pole to the other. They are curves lines that nev ...
... Lesson 1: Magnets have 2 poles. Like poles attract, unlike poles repel. Magnets attract iron. Magnetic force is strongest around the poles of a magnet. Vocab: magnet Magnetism Magnetic pole Magnetic force Lesson 2: Magnetic fields spread out from one pole to the other. They are curves lines that nev ...
922
... from the element to the point P, and r^ is a unit vector pointing from d S s toward point P. We find the total field at P by integrating this expression over the entire current ...
... from the element to the point P, and r^ is a unit vector pointing from d S s toward point P. We find the total field at P by integrating this expression over the entire current ...
ELECTRIC MOTOR
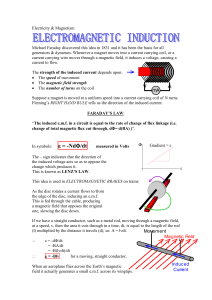
... This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. The direction of induced current can be found using Fleming’s right-hand rule. Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of right hand so that they are perpendicular to each other ,if the forefinger indicates the direction of magnetic fiel ...
... This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. The direction of induced current can be found using Fleming’s right-hand rule. Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of right hand so that they are perpendicular to each other ,if the forefinger indicates the direction of magnetic fiel ...
Magnetism 4 Electromagnets
... Discovered that an electric current causes a magnetic field How? Connected a series circuit and turned on the power. A nearby compass moved! ...
... Discovered that an electric current causes a magnetic field How? Connected a series circuit and turned on the power. A nearby compass moved! ...
Dynamical Petschek Reconnection
... stable in a system with spatially uniform resistivity. Some mechanism such as anomalous resistivity or kinetic physics is needed to sustain the localized diffusion region. It is, therefor, not clear yet how fast reconnection realizes in the actual parameter of the solar corona. In order to answer to ...
... stable in a system with spatially uniform resistivity. Some mechanism such as anomalous resistivity or kinetic physics is needed to sustain the localized diffusion region. It is, therefor, not clear yet how fast reconnection realizes in the actual parameter of the solar corona. In order to answer to ...
Simulations and radiative diagnostics of turbulence and waves in
... G-band diagnostics From thermodynamic and magnetic parameters in the simulation we compute this: ...
... G-band diagnostics From thermodynamic and magnetic parameters in the simulation we compute this: ...
PHY-ZS-004 Electromagnetic Induction
... oxide of iron). They discovered that the stone always pointed in the same direction. Later, stones of magnetite called “lodestones” were used in navigation. ...
... oxide of iron). They discovered that the stone always pointed in the same direction. Later, stones of magnetite called “lodestones” were used in navigation. ...
Anticipation Guide: Electricity from Magnetism
... Anticipation Guide: Electricity from Magnetism Before Reading: In the space to the left of each statement, place a check mark () if you agree or think the statement is true or an (X) if you disagree or think the statement is false. During or After Reading: Add new check marks or cross-through the X ...
... Anticipation Guide: Electricity from Magnetism Before Reading: In the space to the left of each statement, place a check mark () if you agree or think the statement is true or an (X) if you disagree or think the statement is false. During or After Reading: Add new check marks or cross-through the X ...
Cosmic Structure Formation via Gravitational Radiation
... modes of oscillation in the plasma field like a crystal is excited by sound waves. • What are the results of these excited modes? What part did they play in the evolution of the universe? • Can these excited modes contribute to the formation of structures in the early universe? ...
... modes of oscillation in the plasma field like a crystal is excited by sound waves. • What are the results of these excited modes? What part did they play in the evolution of the universe? • Can these excited modes contribute to the formation of structures in the early universe? ...
Magnetohydrodynamics

Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) (magneto fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magneto-fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes. The word magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is derived from magneto- meaning magnetic field, hydro- meaning water, and -dynamics meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970.The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically.