Key words
... The pattern of attraction around a magnet. This can be seen by using iron filings. ...
... The pattern of attraction around a magnet. This can be seen by using iron filings. ...
Magnetism - Reocities
... have north and south poles. Each domain is a magnet in itself. In an ordinary piece of iron, domains are oriented randomly. The magnetic effect is absent. But in a magnet, those domains are properly oriented. Therefore there is a net magnetic effect on one end i.e., north pole and the other, south p ...
... have north and south poles. Each domain is a magnet in itself. In an ordinary piece of iron, domains are oriented randomly. The magnetic effect is absent. But in a magnet, those domains are properly oriented. Therefore there is a net magnetic effect on one end i.e., north pole and the other, south p ...
PHYS 1442-004, Dr. Brandt
... • People knew some 60 years before Maxwell that light behaves like a wave, but … – They did not know what kind of waves they are. • Most importantly what is it that oscillates in light? ...
... • People knew some 60 years before Maxwell that light behaves like a wave, but … – They did not know what kind of waves they are. • Most importantly what is it that oscillates in light? ...
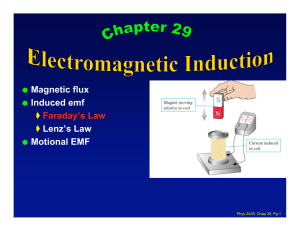
induced current
... As the coil begins to rotate, the induced back emf opposes the applied voltage The current in the coil is reduced The power requirements for starting a motor and for running it under heavy loads are greater than those for running the motor under average loads ...
... As the coil begins to rotate, the induced back emf opposes the applied voltage The current in the coil is reduced The power requirements for starting a motor and for running it under heavy loads are greater than those for running the motor under average loads ...
B.Sc. PHYSICS GE Syllabus Under CHOICE BASED CREDIT
... Vector Analysis: Scalar and Vector product, gradient, divergence, Curl and their significance, Vector Integration, Line, surface and volume integrals of Vector fields, Gaussdivergence theorem and Stoke's theorem of vectors (statement only). (8 Lectures) Electrostatics: Electrostatic Field, electric ...
... Vector Analysis: Scalar and Vector product, gradient, divergence, Curl and their significance, Vector Integration, Line, surface and volume integrals of Vector fields, Gaussdivergence theorem and Stoke's theorem of vectors (statement only). (8 Lectures) Electrostatics: Electrostatic Field, electric ...
Chapter 1 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 General overview The Time
... The third factor proves to be the most difficult – accurately solving Maxwell’s equations. These equations can only be solved analytically for a few very simple geometrical models and only if assumptions regarding homogeneity, isotropy, frequency dependence, and frequency and conductivity ranges are ...
... The third factor proves to be the most difficult – accurately solving Maxwell’s equations. These equations can only be solved analytically for a few very simple geometrical models and only if assumptions regarding homogeneity, isotropy, frequency dependence, and frequency and conductivity ranges are ...
Heat, Force, Motion, Electricity, Magnetism, sound, light
... Often missed question…, but you’re gonna ace it next week! ...
... Often missed question…, but you’re gonna ace it next week! ...