Electricity and Magnetism Vocabulary Pearson
... Electric current – an electric charge in motion Circuit – a current in which electric charges flow in a loop Power source – the place from which the power comes Conductor – a material through which an electric charge can move through easily (most metals) Insulators – a material through which an elec ...
... Electric current – an electric charge in motion Circuit – a current in which electric charges flow in a loop Power source – the place from which the power comes Conductor – a material through which an electric charge can move through easily (most metals) Insulators – a material through which an elec ...
Guided Reading Chapter 22 Section 2 Also do: 539 #1
... 5. What are two other useful ways electromagnets are used in everyday life? ...
... 5. What are two other useful ways electromagnets are used in everyday life? ...
NOT
... ___________________________ a small magnet that can turn freely. How could you use a compass? ...
... ___________________________ a small magnet that can turn freely. How could you use a compass? ...
Learning Objectives
... A dynamo is a particular type of generator which is often used on bikes to power lights. Here the magnet is rotated instead of the coil. They dynamo is attached to a wheel so as you turn the wheels, your turning inside the dynamo. ...
... A dynamo is a particular type of generator which is often used on bikes to power lights. Here the magnet is rotated instead of the coil. They dynamo is attached to a wheel so as you turn the wheels, your turning inside the dynamo. ...
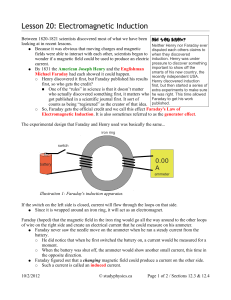
Faraday`s Law of Induction
... If the switch on the left side is closed, current will flow through the loops on that side. ● Since it is wrapped around an iron ring, it will act as an electromagnet. Faraday (hoped) that the magnetic field in the iron ring would go all the way around to the other loops of wire on the right side an ...
... If the switch on the left side is closed, current will flow through the loops on that side. ● Since it is wrapped around an iron ring, it will act as an electromagnet. Faraday (hoped) that the magnetic field in the iron ring would go all the way around to the other loops of wire on the right side an ...
Department of Natural Sciences
... In the figure, a uniform electric field is shown passing through a flat area A. In (a), the surface of area A is perpendicular to the electric field. In (b), the surface is tilted by an angle θ with respect to the electric field. In (c), the surface is parallel to the electric field. In which orient ...
... In the figure, a uniform electric field is shown passing through a flat area A. In (a), the surface of area A is perpendicular to the electric field. In (b), the surface is tilted by an angle θ with respect to the electric field. In (c), the surface is parallel to the electric field. In which orient ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.