Electrical System Overview The Electrical System (An Overview)
... device, which automatically switches the headlights from high beam to low in response to light from an approaching vehicle or light from the taillight of a vehicle being overtaken. The dimmer switch in the automatic headlamp dimming system is a special override type. It is located in the steering co ...
... device, which automatically switches the headlights from high beam to low in response to light from an approaching vehicle or light from the taillight of a vehicle being overtaken. The dimmer switch in the automatic headlamp dimming system is a special override type. It is located in the steering co ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... If charges are not constrained to move within a wire, or other conductor, then the force on the charge as it passes through a magnetic field will change its direction of travel. As the force is perpendicular to the velocity (current direction) it alters the direction, but not the speed, of the parti ...
... If charges are not constrained to move within a wire, or other conductor, then the force on the charge as it passes through a magnetic field will change its direction of travel. As the force is perpendicular to the velocity (current direction) it alters the direction, but not the speed, of the parti ...
File
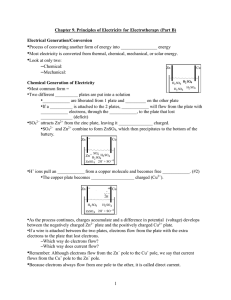
... are rubbed together, charge is transferred from one to the other and the objects become oppositely charged. • This is called charging by friction. • Objects charged by this method will attract each other. ...
... are rubbed together, charge is transferred from one to the other and the objects become oppositely charged. • This is called charging by friction. • Objects charged by this method will attract each other. ...
File
... _______into a coil and attaching the ends of the wire to the terminals of a battery cell. This magnet is called a(n)______________________. The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the number of ______ in the wire. The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the amount of electrical _ ...
... _______into a coil and attaching the ends of the wire to the terminals of a battery cell. This magnet is called a(n)______________________. The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the number of ______ in the wire. The strength of an electromagnet is affected by the amount of electrical _ ...
What`s This Thing Called “Current”?
... Figure 2 illustrates this point. We are all familiar with this desktop toy. The falling ball at the front hits the first ball and transfers its energy to it, which then transfers energy to the second ball, and so on. The last ball in the string pops out (in the absence of friction) as far as the fi ...
... Figure 2 illustrates this point. We are all familiar with this desktop toy. The falling ball at the front hits the first ball and transfers its energy to it, which then transfers energy to the second ball, and so on. The last ball in the string pops out (in the absence of friction) as far as the fi ...
File
... in it is called a solenoid and the ends of the solenoid act like poles in a bar magnet. The magnetic field around a solenoid is the same as a magnetic field around a bar magnet with the two poles: • North Pole • South Pole ...
... in it is called a solenoid and the ends of the solenoid act like poles in a bar magnet. The magnetic field around a solenoid is the same as a magnetic field around a bar magnet with the two poles: • North Pole • South Pole ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.