mass number - KCPE-KCSE
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of neutrons. ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of neutrons. ...
Atomic Structure Guided Notes
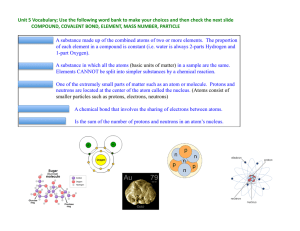
... Protons, neutrons and electrons are __________evenly distributed in an atom. Drawing of an Atom The protons and neutrons exist in a _________________ core at the center of the atom. This is called the ___________________. The nucleus has a _______________________ charge because the protons have a po ...
... Protons, neutrons and electrons are __________evenly distributed in an atom. Drawing of an Atom The protons and neutrons exist in a _________________ core at the center of the atom. This is called the ___________________. The nucleus has a _______________________ charge because the protons have a po ...
Unit Review III
... __ 14) Which of the following particles has the smallest mass? a) proton b) neutron c) alpha particle d) electron __ 15) A pure substance whose atoms have all the same atomic number is a) a compound b) an element c) a radical d) a mixture __ 16) An atom containing 9 protons, 10 neutrons and 9 elect ...
... __ 14) Which of the following particles has the smallest mass? a) proton b) neutron c) alpha particle d) electron __ 15) A pure substance whose atoms have all the same atomic number is a) a compound b) an element c) a radical d) a mixture __ 16) An atom containing 9 protons, 10 neutrons and 9 elect ...
03 Atoms – Nuclides
... a positively charged alpha particle (α), which is the same as a helium nuclei consisting of two neutrons and two protons a negatively charged beta minus particle (β-), which is the same as an electron a positively charged beta plus particle (β+), which is the same as a positron, a particle of equal ...
... a positively charged alpha particle (α), which is the same as a helium nuclei consisting of two neutrons and two protons a negatively charged beta minus particle (β-), which is the same as an electron a positively charged beta plus particle (β+), which is the same as a positron, a particle of equal ...
Review Unit 5
... Whenever a chemical reac=on occurs, the mass of the reactants always equals the mass of the products. (Some=mes some products are released to the environment, but they are never destroyed and they ...
... Whenever a chemical reac=on occurs, the mass of the reactants always equals the mass of the products. (Some=mes some products are released to the environment, but they are never destroyed and they ...
Chemical Periodicity
... the amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron, the valence electron, of an isolated gaseous atom to form a cation. 5 How does the ionization energy vary as you move left to right across the periodic table? Why? It increases, because it is more difficult to remove an elect ...
... the amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron, the valence electron, of an isolated gaseous atom to form a cation. 5 How does the ionization energy vary as you move left to right across the periodic table? Why? It increases, because it is more difficult to remove an elect ...
atomic number - Cloudfront.net
... – If 2 or more different compounds are composed of the same 2 elements, then the ratio of the masses of the 2nd element combined with a certain mass of the 1st element is always a ratio of small whole numbers ...
... – If 2 or more different compounds are composed of the same 2 elements, then the ratio of the masses of the 2nd element combined with a certain mass of the 1st element is always a ratio of small whole numbers ...
Webquest: Atomic Theories and Models * an Historical Work in
... 5. he developed the plum pudding model and also was the first to discover the ...
... 5. he developed the plum pudding model and also was the first to discover the ...
Atom Basics
... 6. The region in an atom that contains the protons and neutrons is called the _____. a. Nucleus b. Electron cloud c. Atom d. Cell 7. Which of the following are the subatomic particles that make up an atom? a. neutrons, electrons, and atomic mass b. neutrons, electrons, and protons c. electrons and p ...
... 6. The region in an atom that contains the protons and neutrons is called the _____. a. Nucleus b. Electron cloud c. Atom d. Cell 7. Which of the following are the subatomic particles that make up an atom? a. neutrons, electrons, and atomic mass b. neutrons, electrons, and protons c. electrons and p ...
Atomic
... • Atomic # = # Protons = # Electrons • Because the number of positive charges equals the number of negative charges, the atom is neutral (no charge) ...
... • Atomic # = # Protons = # Electrons • Because the number of positive charges equals the number of negative charges, the atom is neutral (no charge) ...
The atom: Ionisation energy and the periodic table
... An atom is made up of a central nucleus (containing protons and neutrons), surrounded by electrons. The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in an atom. The atomic mass number (A) is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The standard notation that is used to write an el ...
... An atom is made up of a central nucleus (containing protons and neutrons), surrounded by electrons. The atomic number (Z) is the number of protons in an atom. The atomic mass number (A) is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The standard notation that is used to write an el ...
Classification of Matter slides
... Atomic Number Resulting Charge Mass number (number of protons plus neutrons) ...
... Atomic Number Resulting Charge Mass number (number of protons plus neutrons) ...
Chemistry Note PowerPoint
... • An atom’s valance electrons are those that have the highest energy levels and are held most loosely. • The number of valance electrons determine many properties of that element, including the ways in which the atom combines with other atoms ...
... • An atom’s valance electrons are those that have the highest energy levels and are held most loosely. • The number of valance electrons determine many properties of that element, including the ways in which the atom combines with other atoms ...
Ch. 5.1 History of the periodic table ppt.
... Warm Up: November 7th 1. Using the periodic table, determine the number of protons and electrons in a chlorine atom. 2. Identify which group and period chlorine is located on the periodic table. 3. Is chlorine considered a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid? Explain your choice. 4. What is the mass of on ...
... Warm Up: November 7th 1. Using the periodic table, determine the number of protons and electrons in a chlorine atom. 2. Identify which group and period chlorine is located on the periodic table. 3. Is chlorine considered a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid? Explain your choice. 4. What is the mass of on ...
The Modern Periodic Table (cont.)
... when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and ...
... when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and ...
3.1 Early History of Atomic Theories
... charge) analogy. The Rutherford model of the atom (1911) included electrons orbiting a positively charged nucleus. There may have been a hypothesis about the nucleus being composed of positively charged particles, but it was not until 1914 that evidence was gathered to support such a hypothesis. Rut ...
... charge) analogy. The Rutherford model of the atom (1911) included electrons orbiting a positively charged nucleus. There may have been a hypothesis about the nucleus being composed of positively charged particles, but it was not until 1914 that evidence was gathered to support such a hypothesis. Rut ...
Lecture 10
... Brief history: (not examinable) – BC Greeks, found when amber is rubbed, it attracted bits of straw. Electron is Greek for “amber” – Ben Franklin postulated idea of “electric fluid” : If matter has excess electric fluid, it is “positively charged” and if it is deficient, it is “negatively charged”. ...
... Brief history: (not examinable) – BC Greeks, found when amber is rubbed, it attracted bits of straw. Electron is Greek for “amber” – Ben Franklin postulated idea of “electric fluid” : If matter has excess electric fluid, it is “positively charged” and if it is deficient, it is “negatively charged”. ...
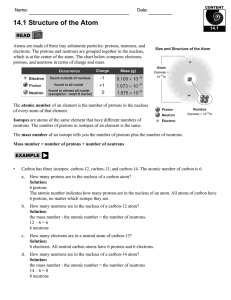
14.1 Structure of the Atom
... In 1917, Rutherford made another discovery. He bombarded nitrogen gas with alpha particles and found that occasionally an oxygen atom was produced. He concluded that the alpha particles must have knocked a positively charged particle (which he named the proton) from the nucleus. He called this “play ...
... In 1917, Rutherford made another discovery. He bombarded nitrogen gas with alpha particles and found that occasionally an oxygen atom was produced. He concluded that the alpha particles must have knocked a positively charged particle (which he named the proton) from the nucleus. He called this “play ...
UNIT 1 Atomic Structure
... Note electrons are usually shown as far apart as possible -they have the same charge and therefore repel each other. 3. The Noble gases (Group 0) have a stable electron configuration (s2p6) with 8 electrons filling the outer s and p orbitals. This stability comes from the low energy state of this c ...
... Note electrons are usually shown as far apart as possible -they have the same charge and therefore repel each other. 3. The Noble gases (Group 0) have a stable electron configuration (s2p6) with 8 electrons filling the outer s and p orbitals. This stability comes from the low energy state of this c ...