2/1: Atomic Structure
... explosion has just started; surplus ships moored nearby can still be seen. ...
... explosion has just started; surplus ships moored nearby can still be seen. ...
The Structure of the Atom
... Subatomic particles composed of fast moving points of energy called quarks Quark Calculations (for protons and neutrons) Each proton is 2 up quarks and 1 down quark 2(2/3) – 1(1/3) = 4/3 – 1/3 = 3/3 or +1 Each neutron is 2 down quarks and 1 up quark ...
... Subatomic particles composed of fast moving points of energy called quarks Quark Calculations (for protons and neutrons) Each proton is 2 up quarks and 1 down quark 2(2/3) – 1(1/3) = 4/3 – 1/3 = 3/3 or +1 Each neutron is 2 down quarks and 1 up quark ...
AP Chemistry-Chapter 6 MC Questions
... a. The effective nuclear charge experienced by an electron in an outer shell is less than the actual nuclear charge. b. Within a family (vertical group in the periodic table) of representative elements atomic radii increase from top to bottom. c. Electrons in inner shells screen, or shield, electron ...
... a. The effective nuclear charge experienced by an electron in an outer shell is less than the actual nuclear charge. b. Within a family (vertical group in the periodic table) of representative elements atomic radii increase from top to bottom. c. Electrons in inner shells screen, or shield, electron ...
Study Guide Answers
... classify as either metal, nonmetal, or metalloid: Ca, Cl, I, Ir, Si, and Ti. Metals Ca-calcium Ir-iridium Ti-titanium ...
... classify as either metal, nonmetal, or metalloid: Ca, Cl, I, Ir, Si, and Ti. Metals Ca-calcium Ir-iridium Ti-titanium ...
So where did all the matter on Earth come from - Bennatti
... letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letters only the first letter is capitalized. For example the chemical symbol for the element magnesium is Mg. Note the letter g is lower case. This is important as Co is the element cobalt but CO is the compound carbon monoxide ...
... letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letters only the first letter is capitalized. For example the chemical symbol for the element magnesium is Mg. Note the letter g is lower case. This is important as Co is the element cobalt but CO is the compound carbon monoxide ...
Elements, Isotopes and Ions
... 1. Any atom of Calcium can have 20, 22, or 24 neutrons. These different versions of Calcium are called ...
... 1. Any atom of Calcium can have 20, 22, or 24 neutrons. These different versions of Calcium are called ...
Section 2.1
... • All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but atoms of an element are unique to that element only. • Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither created nor destroyed. • Compounds are fo ...
... • All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, but atoms of an element are unique to that element only. • Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; they are neither created nor destroyed. • Compounds are fo ...
atomic structure (see second part of ppt)
... 1913Bohr said electrons located outside the nucleus could only be located in specific paths called orbitals. This was supported by the line spectra of atoms His model is called the planetary model ...
... 1913Bohr said electrons located outside the nucleus could only be located in specific paths called orbitals. This was supported by the line spectra of atoms His model is called the planetary model ...
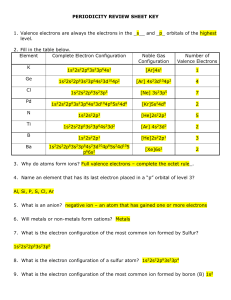
periodicity review sheet key
... increases(I), decreases (D), or remains the same (R). __R___ 14. As the number of neutrons in an atom of a given element increases, its atomic number generally ________________ . __I___ 15. Going down a group of elements, the atomic radius (size)? __D___ 16. Going down a group of elements, the ioniz ...
... increases(I), decreases (D), or remains the same (R). __R___ 14. As the number of neutrons in an atom of a given element increases, its atomic number generally ________________ . __I___ 15. Going down a group of elements, the atomic radius (size)? __D___ 16. Going down a group of elements, the ioniz ...
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
... All groups except for the ones in the transition metals and metalloids all have similar characteristics ...
... All groups except for the ones in the transition metals and metalloids all have similar characteristics ...
C2 Topic 1 Atomic structure and the periodic table PP
... Using the periodic table • Atomic number (proton number): is the number of protons in an atom - The elements are arranged in the Periodic Table in ascending order of atomic number • Mass number: is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom • Relative atomic mass (Ar): is the average mass ...
... Using the periodic table • Atomic number (proton number): is the number of protons in an atom - The elements are arranged in the Periodic Table in ascending order of atomic number • Mass number: is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom • Relative atomic mass (Ar): is the average mass ...
Early Models of the Atom
... “Raison bun model” (plum pudding model) of the atom – positive charges all around (the bun) and negative pieces inside (the raisons) – everything was floating around in one big ball Analyzed uranium to see Becquerel rays Uranium was the source of the emission – later Marie gave these emissions the n ...
... “Raison bun model” (plum pudding model) of the atom – positive charges all around (the bun) and negative pieces inside (the raisons) – everything was floating around in one big ball Analyzed uranium to see Becquerel rays Uranium was the source of the emission – later Marie gave these emissions the n ...
CHAPTER 4 ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... When an atom does not have the same ________of neutrons Same atomic number but different mass #’s Ex. Oxygen-16, 17, and 18 All oxygen atoms have 8 protons, but some have 9 or 10 neutrons • Ques. 1-7 pg. 112 ...
... When an atom does not have the same ________of neutrons Same atomic number but different mass #’s Ex. Oxygen-16, 17, and 18 All oxygen atoms have 8 protons, but some have 9 or 10 neutrons • Ques. 1-7 pg. 112 ...
Key Concepts - Chemistry Classes of Professor Alba
... proportions led John Dalton to reformulate the atomic theory with the following postulates: (1) each element is composed of indestructible particles called atoms; (2) all atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties; (3) atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compou ...
... proportions led John Dalton to reformulate the atomic theory with the following postulates: (1) each element is composed of indestructible particles called atoms; (2) all atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties; (3) atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compou ...
The Periodic Table
... (the solar system model). 1. Draw a nucleus 2. Determine the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus and write this number in the nucleus 3. Determine how many electrons there are and place each one in its appropriate energy level ...
... (the solar system model). 1. Draw a nucleus 2. Determine the number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus and write this number in the nucleus 3. Determine how many electrons there are and place each one in its appropriate energy level ...
Midterm Review File
... 25. If an atom has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p2, how many valence electrons does it have? ...
... 25. If an atom has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p2, how many valence electrons does it have? ...
Document
... a) an element which has 5 electrons in each atom b) an element which has 5 electrons in its outer energy level c) an element for which the second energy level is completely filled d) an element which forms ions by gaining only one electron e) how many elements are there in the sixth period? f) the e ...
... a) an element which has 5 electrons in each atom b) an element which has 5 electrons in its outer energy level c) an element for which the second energy level is completely filled d) an element which forms ions by gaining only one electron e) how many elements are there in the sixth period? f) the e ...
Unit 4: Periodic Table - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... because of similarities in the chemical properties of various “families” of elements 6. What does the name periodic table refer to? the fact that as we increase the atomic number, every so often an element occurs that has properties similar to those of an earlier element 7. How is a family (also cal ...
... because of similarities in the chemical properties of various “families” of elements 6. What does the name periodic table refer to? the fact that as we increase the atomic number, every so often an element occurs that has properties similar to those of an earlier element 7. How is a family (also cal ...