Fundamentals of Chemistry
... More on the Atom • An atom is uniquely defined by #p+ = Z = atomic number (see Periodic Table) • In a neutral atom, #p+ = #e-; note that #n is not equal to #p+ nor #e-. • In an atomic ion, #p+ ≠ #e- resulting in a net nonzero charge on the species – Neutral atoms can lose electrons producing a posi ...
... More on the Atom • An atom is uniquely defined by #p+ = Z = atomic number (see Periodic Table) • In a neutral atom, #p+ = #e-; note that #n is not equal to #p+ nor #e-. • In an atomic ion, #p+ ≠ #e- resulting in a net nonzero charge on the species – Neutral atoms can lose electrons producing a posi ...
Aps midREVIEW
... D. larger and contains little of the atom’s mass 23. The atomic number of any atom is equal to the number of A. neutrons in the atom, only B. protons in the atom, only C. neutrons plus protons in the atoms D. protons plus electrons in the atom 24. What is the correct formula for iron (II) b ...
... D. larger and contains little of the atom’s mass 23. The atomic number of any atom is equal to the number of A. neutrons in the atom, only B. protons in the atom, only C. neutrons plus protons in the atoms D. protons plus electrons in the atom 24. What is the correct formula for iron (II) b ...
Neutron
... The mass found in each element block on the periodic table must account for all isotopes of that element that are in existence and how abundant they are in nature ...
... The mass found in each element block on the periodic table must account for all isotopes of that element that are in existence and how abundant they are in nature ...
The Egyptian American International School
... Louis De Broglie’s wave-particle theory Heisenberg uncertainty principle The 4 Quantum numbers describe the properties of orbitals and predict the number of electrons in orbitals. 11.3 Atomic Orbitals The Bohr model assumed electrons travel around the nucleus in circular orbits which is inco ...
... Louis De Broglie’s wave-particle theory Heisenberg uncertainty principle The 4 Quantum numbers describe the properties of orbitals and predict the number of electrons in orbitals. 11.3 Atomic Orbitals The Bohr model assumed electrons travel around the nucleus in circular orbits which is inco ...
The Periodic Table
... elements according to their properties Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, there was a repeating pattern to their properties This is known as Periodicity Mendeleev left some spaces on his table blank, but was able to predict the properties ...
... elements according to their properties Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, there was a repeating pattern to their properties This is known as Periodicity Mendeleev left some spaces on his table blank, but was able to predict the properties ...
mystery elements
... After looking at a summary of John Dalton’s 1808 Atomic Theory, which 2 statements are not true? (Continue reading ‘Modern Atomic Theory’ if you’re not sure) ...
... After looking at a summary of John Dalton’s 1808 Atomic Theory, which 2 statements are not true? (Continue reading ‘Modern Atomic Theory’ if you’re not sure) ...
September 20th, 2012
... Magnesium has three isotopes, with mass numbers 24, 25, and 26. a) write the complete chemical symbol (subscript and superscript) of each. b) how many neutrons are in an atom of ...
... Magnesium has three isotopes, with mass numbers 24, 25, and 26. a) write the complete chemical symbol (subscript and superscript) of each. b) how many neutrons are in an atom of ...
Element A pure substance made of only one type of atom which
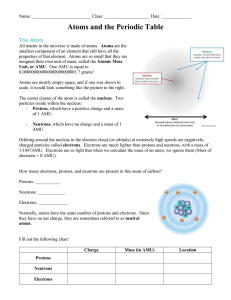
... Atoms consist of electrons that surround a nucleus. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. NEUtrons are NEUtral (have a neutral charge) PROtons are POsitively charged (have a charge of +1) Electrons are negatively charged (have a charge of -1) The mass number (aka nucleon number) is the sum of t ...
... Atoms consist of electrons that surround a nucleus. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. NEUtrons are NEUtral (have a neutral charge) PROtons are POsitively charged (have a charge of +1) Electrons are negatively charged (have a charge of -1) The mass number (aka nucleon number) is the sum of t ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... TRUE or FALSE - the atomic mass increases by ONE from element to element TRUE or FALSE - the elements become more non metallic TRUE or FALSE - the ionization energy of the elements generally decreases TRUE or FALSE - the elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number TRUE or FALSE - eac ...
... TRUE or FALSE - the atomic mass increases by ONE from element to element TRUE or FALSE - the elements become more non metallic TRUE or FALSE - the ionization energy of the elements generally decreases TRUE or FALSE - the elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number TRUE or FALSE - eac ...
FXM Rev 1 Key - Grande Cache Community High School
... the Planetary Atomic Model. hydrocarbons These are organic compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen. Methane (CH4) is an example. Avogadro’s number This is a number that groups a very large amount of atoms or molecules to facilitate measurement and calculations in chemistry. It is the number ...
... the Planetary Atomic Model. hydrocarbons These are organic compounds that contain both carbon and hydrogen. Methane (CH4) is an example. Avogadro’s number This is a number that groups a very large amount of atoms or molecules to facilitate measurement and calculations in chemistry. It is the number ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... It depends, because there are different kinds of oxygen atoms. We are more concerned with the average atomic mass. This is based on the abundance (percentage) of each variety of that element in nature. ...
... It depends, because there are different kinds of oxygen atoms. We are more concerned with the average atomic mass. This is based on the abundance (percentage) of each variety of that element in nature. ...
biology biology - Napa Valley College
... An orbital is the three-dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time ...
... An orbital is the three-dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time ...
Electron Proton Neutron
... The mass number of an element is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons present in the atom of that element. For example, the atom of boron has 5 protons and 6 neutrons. So, the mass number of boron is 5 + 6 = 11. ...
... The mass number of an element is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons present in the atom of that element. For example, the atom of boron has 5 protons and 6 neutrons. So, the mass number of boron is 5 + 6 = 11. ...
Periodic Trends
... 1) The net charge that pulls on the valence electrons in an atom. The greater the effective core charge, the greater the pull. It is determined by subtracting the number of core electrons from the number of protons in the nucleus For example: Magnesium ...
... 1) The net charge that pulls on the valence electrons in an atom. The greater the effective core charge, the greater the pull. It is determined by subtracting the number of core electrons from the number of protons in the nucleus For example: Magnesium ...
Vocabulary Review
... e. Give the element name and isotope notation of Atom A. f. Give the element name and isotope notation of Atom B. g. What word describes the relationship between these two atoms? 4. Why don’t the protons in the nucleus repel each other and break the atom apart? ...
... e. Give the element name and isotope notation of Atom A. f. Give the element name and isotope notation of Atom B. g. What word describes the relationship between these two atoms? 4. Why don’t the protons in the nucleus repel each other and break the atom apart? ...
File
... 1. Take your deck of cards with your group and try to determine an orderly arrangement for their cards. (color, number, shape?) Be creative! 2. After completing their ordering, choose one card from the arrangement and write a procedure on locating its position in the arrangement 3. After the procedu ...
... 1. Take your deck of cards with your group and try to determine an orderly arrangement for their cards. (color, number, shape?) Be creative! 2. After completing their ordering, choose one card from the arrangement and write a procedure on locating its position in the arrangement 3. After the procedu ...
Atoms of an element are identical
... d. Of different elements cannot combine _____6. Which of the following is NOT part of Dalton’s atomic theory? a. Atoms cannot be divided, created, or destroyed b. The number of protons in an atom is its atomic number c. In a chemical reaction atoms are combined. d. All matter is composed of extremel ...
... d. Of different elements cannot combine _____6. Which of the following is NOT part of Dalton’s atomic theory? a. Atoms cannot be divided, created, or destroyed b. The number of protons in an atom is its atomic number c. In a chemical reaction atoms are combined. d. All matter is composed of extremel ...
atom
... •the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. •electrons in space around the nucleus. •extremely small. One teaspoon of water has 3 times as many atoms as the Atlantic Ocean has teaspoons of water. ...
... •the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. •electrons in space around the nucleus. •extremely small. One teaspoon of water has 3 times as many atoms as the Atlantic Ocean has teaspoons of water. ...
Study Guide Chapters 4
... Explain what makes elements and isotopes different from each other and the same Construct and understand chemical (shorthand) notation for isotopes of elements ...
... Explain what makes elements and isotopes different from each other and the same Construct and understand chemical (shorthand) notation for isotopes of elements ...
File
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
... All atoms of the same element will always have the same number of protons. Protons determine the identity of the element. Different atoms of an element may have different numbers of electrons; this forms ions. Atoms may also differ in their number of neutrons, creating isotopes. Isotopes of the same ...
Essential Standard: 8.P.1 Understand the properties of matter and
... elements and their relationship to one another. By arranging the elements in a grid, he was able to identify similarities among them. Mendeleev’s hypothesized the physical characteristics of the elements repeated in a cyclical manner. The periodic table developed by Mendeleev has remained largely un ...
... elements and their relationship to one another. By arranging the elements in a grid, he was able to identify similarities among them. Mendeleev’s hypothesized the physical characteristics of the elements repeated in a cyclical manner. The periodic table developed by Mendeleev has remained largely un ...