C C C H1 H H
... The atomic mass unit (amu) is a special unit for measuring the mass of very small particles such as atoms. The relationship between amu and grams is the following: 1.00 amu = 1.66 x 10-24g Note the following diagrams comparing atoms and ions. ...
... The atomic mass unit (amu) is a special unit for measuring the mass of very small particles such as atoms. The relationship between amu and grams is the following: 1.00 amu = 1.66 x 10-24g Note the following diagrams comparing atoms and ions. ...
Ch 3 notes ppt
... * the electrons come from changes in the nucleus * in the process that produces beta radiation, a neutron changes into a proton and an electron * the proton remains in the nucleus and the electron (now the beta particle) is propelled out of the nucleus at high speed * the mass number for a beta part ...
... * the electrons come from changes in the nucleus * in the process that produces beta radiation, a neutron changes into a proton and an electron * the proton remains in the nucleus and the electron (now the beta particle) is propelled out of the nucleus at high speed * the mass number for a beta part ...
Thomson (the electron)
... Half-Life Problem The half life of polonium-210 is 138.4 days. How many milligrams of polonium-210 remain after 415.2 days if you start with 2.0 mg of the isotope? Answer: 0.25 mg ...
... Half-Life Problem The half life of polonium-210 is 138.4 days. How many milligrams of polonium-210 remain after 415.2 days if you start with 2.0 mg of the isotope? Answer: 0.25 mg ...
C C C H1 H H
... The atomic mass unit (amu) is a special unit for measuring the mass of very small particles such as atoms. The relationship between amu and grams is the following: 1.00 amu = 1.66 x 10-24g Note the following diagrams comparing atoms and ions. ...
... The atomic mass unit (amu) is a special unit for measuring the mass of very small particles such as atoms. The relationship between amu and grams is the following: 1.00 amu = 1.66 x 10-24g Note the following diagrams comparing atoms and ions. ...
Elements
... The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table In early part of 19th century many chemical facts were being obtained for the elements known (at that time) As the number of known elements increased, scientists began to attempt useful classifications Scientists had discovered that certain groups of elem ...
... The Periodic Law and the Periodic Table In early part of 19th century many chemical facts were being obtained for the elements known (at that time) As the number of known elements increased, scientists began to attempt useful classifications Scientists had discovered that certain groups of elem ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements
... 1. In Exploration 1, select the element from period 2, group 1, on the periodic table. When selected, the group and period number will be highlighted by red circles. 2. Select the element’s period (row) number, represented by a red circle. 3. Record the element’s properties from the list provided in ...
... 1. In Exploration 1, select the element from period 2, group 1, on the periodic table. When selected, the group and period number will be highlighted by red circles. 2. Select the element’s period (row) number, represented by a red circle. 3. Record the element’s properties from the list provided in ...
ic Structure - Phillips Scientific Methods
... conservation of mass, which states that in any chemical reaction, the mass of the substances that react equals the mass of the products that are formed. ...
... conservation of mass, which states that in any chemical reaction, the mass of the substances that react equals the mass of the products that are formed. ...
Chapter 8: Periodic Properties of the Elements
... lower in energy than d orbitals of the previous principal level (4s is lower than 3d) • The energy separations between one set of orbitals and the next become smaller beyond the 4s so the ordering can vary among elements causing variations (exceptions) in the electron configurations of the transitio ...
... lower in energy than d orbitals of the previous principal level (4s is lower than 3d) • The energy separations between one set of orbitals and the next become smaller beyond the 4s so the ordering can vary among elements causing variations (exceptions) in the electron configurations of the transitio ...
CHAPTER 6
... Important exceptions at Be & Mg, N & P, etc. due to filled and half-filled subshells. IE1 generally decreases moving down a family. IE1 for Li > IE1 for Na, etc. ...
... Important exceptions at Be & Mg, N & P, etc. due to filled and half-filled subshells. IE1 generally decreases moving down a family. IE1 for Li > IE1 for Na, etc. ...
PRACTICE PROBLEMS EXAM 1,2 and 3 1311
... 14) The average atomic weight of copper, which has two naturally occurring isotopes, is 63.5. One of the isotopes has an atomic weight of 62.9 amu and constitutes 69.1% of the copper isotopes. The other isotope has an abundance of 30.9%. The atomic weight (amu) of the second isotope is __________ am ...
... 14) The average atomic weight of copper, which has two naturally occurring isotopes, is 63.5. One of the isotopes has an atomic weight of 62.9 amu and constitutes 69.1% of the copper isotopes. The other isotope has an abundance of 30.9%. The atomic weight (amu) of the second isotope is __________ am ...
Introduction to the Atom
... • This is the most recent model of the atom. • This model supports Bohr for the most part, but suggests that electrons do not exist in fixed orbits or a fixed definite path. Instead, they electrons exist anywhere within an electron cloud. • Determining where an electron will be at any given moment i ...
... • This is the most recent model of the atom. • This model supports Bohr for the most part, but suggests that electrons do not exist in fixed orbits or a fixed definite path. Instead, they electrons exist anywhere within an electron cloud. • Determining where an electron will be at any given moment i ...
Chapter 5 - cloudfront.net
... corresponds to one exact frequency of light emitted by the atom Ground State – lowest possible energy of the electron in the Bohr model The light emitted by an electron moving from higher to a lower energy level has a frequency directly proportional to the energy change of the electron ...
... corresponds to one exact frequency of light emitted by the atom Ground State – lowest possible energy of the electron in the Bohr model The light emitted by an electron moving from higher to a lower energy level has a frequency directly proportional to the energy change of the electron ...
Chapter 5 - cloudfront.net
... model (Bohr was a student of Rutherford) He noticed that light given out when atoms were heated always had specific amounts of energy, so Niels Bohr proposed a model that electrons in an atom must be orbiting the nucleus and can reside only in fixed energy levels ...
... model (Bohr was a student of Rutherford) He noticed that light given out when atoms were heated always had specific amounts of energy, so Niels Bohr proposed a model that electrons in an atom must be orbiting the nucleus and can reside only in fixed energy levels ...
CHAPTER 6
... Important exceptions at Be & Mg, N & P, etc. due to filled and half-filled subshells. IE1 generally decreases moving down a family. IE1 for Li > IE1 for Na, etc. ...
... Important exceptions at Be & Mg, N & P, etc. due to filled and half-filled subshells. IE1 generally decreases moving down a family. IE1 for Li > IE1 for Na, etc. ...
The Chemical Context of Life PPT
... What’s the big deal? • Molecules that were not originally attracted to one another, now find each other quite attractive, thus more energy is required to separate them! • In other words, molecules become “sticky” or adhere to one another. • Collectively, such interactions can be strong, as between ...
... What’s the big deal? • Molecules that were not originally attracted to one another, now find each other quite attractive, thus more energy is required to separate them! • In other words, molecules become “sticky” or adhere to one another. • Collectively, such interactions can be strong, as between ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun. ...
... electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun. ...
The Chemical Context of Life
... What’s the big deal? • Molecules that were not originally attracted to one another, now find each other quite attractive, thus more energy is required to separate them! • In other words, molecules become “sticky” or adhere to one another. • Collectively, such interactions can be strong, as between ...
... What’s the big deal? • Molecules that were not originally attracted to one another, now find each other quite attractive, thus more energy is required to separate them! • In other words, molecules become “sticky” or adhere to one another. • Collectively, such interactions can be strong, as between ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun. ...
... electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun. ...
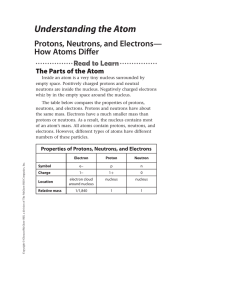
Understanding the Atom
... Look at the periodic table on the inside back cover of this book. Notice that more than 115 different elements have been identified. Recall that an element is a substance made from atoms that all have the same number of protons. For example, the element carbon is made from atoms that all have six pr ...
... Look at the periodic table on the inside back cover of this book. Notice that more than 115 different elements have been identified. Recall that an element is a substance made from atoms that all have the same number of protons. For example, the element carbon is made from atoms that all have six pr ...
periodic table trends assignment 2013 billo
... The electronegativity of an atom is a measure of the ability of the atom to attract an electron from another atom. If an atom is really good at ‘stealing’ electrons from another atom, then it has a high electronegativity value. The Noble Gas elements do not have electronegativity values since they a ...
... The electronegativity of an atom is a measure of the ability of the atom to attract an electron from another atom. If an atom is really good at ‘stealing’ electrons from another atom, then it has a high electronegativity value. The Noble Gas elements do not have electronegativity values since they a ...
Democritus
... But … The idea of atoms were rejected by other Greek Philosophers like Aristotle “If everything was made up of particles with empty space between the particles with wouldn’t things like rocks or even people not fall apart?” The idea of the “ATOM” wasn’t re-investigated for almost 2 thousand years! D ...
... But … The idea of atoms were rejected by other Greek Philosophers like Aristotle “If everything was made up of particles with empty space between the particles with wouldn’t things like rocks or even people not fall apart?” The idea of the “ATOM” wasn’t re-investigated for almost 2 thousand years! D ...
Atoms Molecules and Ions Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Modern Atomic Theory Several changes have been made to Dalton’s theory. Dalton said: Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, size mass mass, and other properties Modern theory states states: Atoms of an element have a c ...
... Modern Atomic Theory Several changes have been made to Dalton’s theory. Dalton said: Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, size mass mass, and other properties Modern theory states states: Atoms of an element have a c ...