isotopes
... The number of protons does not change in an ion. The number of neutrons does not change in an ion. So, both the atomic number and the atomic mass remain the same. ...
... The number of protons does not change in an ion. The number of neutrons does not change in an ion. So, both the atomic number and the atomic mass remain the same. ...
Chemistry Topic III – The Atom
... a. Considering the laws above, the ratios in the law of multiple proportions were always _________________ numbers and the law of definite proportions were always the same. b. From this, he believed that matter was made of some basic unit, since the ratios were always WHOLE and the same. 3. Dalton’s ...
... a. Considering the laws above, the ratios in the law of multiple proportions were always _________________ numbers and the law of definite proportions were always the same. b. From this, he believed that matter was made of some basic unit, since the ratios were always WHOLE and the same. 3. Dalton’s ...
Regents Chemistry Study Tips
... There are three common isotopes of hydrogen, Hydrogen - 1 is an isotope Deuterium also known as Hydrogen -2 is a second isotope Tritium also known as hydrogen-3 is a third isotope Mass no. is the sum of protons and neutrons Atomic mass is weighted avg of isotopes of that atom Bohr’s model of the ato ...
... There are three common isotopes of hydrogen, Hydrogen - 1 is an isotope Deuterium also known as Hydrogen -2 is a second isotope Tritium also known as hydrogen-3 is a third isotope Mass no. is the sum of protons and neutrons Atomic mass is weighted avg of isotopes of that atom Bohr’s model of the ato ...
chemical bonds notes
... • The compound as a whole is neutral because the sum of the charges on the ions is zero. • Ionic bonds are usually formed between metals and nonmetals. • Ionic compounds are often formed by elements across the periodic table from each other. • They are typically crystalline solids with high melting ...
... • The compound as a whole is neutral because the sum of the charges on the ions is zero. • Ionic bonds are usually formed between metals and nonmetals. • Ionic compounds are often formed by elements across the periodic table from each other. • They are typically crystalline solids with high melting ...
In an atom
... first electron shell would be about one kilometer from the golf ball, the second shell about four kilometers, the third nine kilometers and so on. If you find that hard to visualize then try this. The period at the end of this sentence, (depending on your monitor and the font you are using), is prob ...
... first electron shell would be about one kilometer from the golf ball, the second shell about four kilometers, the third nine kilometers and so on. If you find that hard to visualize then try this. The period at the end of this sentence, (depending on your monitor and the font you are using), is prob ...
CMC Chapter 04
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
Chapter 4 power point notes
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
ch 4 ppt - Madison County Schools
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
3-3 Modern Atomic Theory
... Neutrons are slightly larger than protons ** Electrons are so small that their mass is said to be negligible ...
... Neutrons are slightly larger than protons ** Electrons are so small that their mass is said to be negligible ...
Chapter 4 PPT
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
... radioactive decay. • Unstable radioactive elements undergo radioactive decay thus forming stable nonradioactive elements. ...
Chapter 4
... Strategy Because elements in the same group tend to have similar properties, you should identify elements in the same group (7A) as chlorine. Solution Fluorine, bromine, and iodine, the other nonmetals in Group 7A, should have properties most similar to those of chlorine. Think About It Astatine (At ...
... Strategy Because elements in the same group tend to have similar properties, you should identify elements in the same group (7A) as chlorine. Solution Fluorine, bromine, and iodine, the other nonmetals in Group 7A, should have properties most similar to those of chlorine. Think About It Astatine (At ...
File
... isotope. Atomic molar mass is given under the name for each element in the periodic table. b. The atomic molar mass of hydrogen is 1.01 g/mol. It is not exactly 1 because it is the average mass of the three naturally occurring isotopes of hydrogen on Earth. 22. The magnesium ion is a cation, since i ...
... isotope. Atomic molar mass is given under the name for each element in the periodic table. b. The atomic molar mass of hydrogen is 1.01 g/mol. It is not exactly 1 because it is the average mass of the three naturally occurring isotopes of hydrogen on Earth. 22. The magnesium ion is a cation, since i ...
Ionization Energy
... compare the ionization energies. Na has one valence electron and Mg has two. Solution IE1(Mg) > IE1(Na) because Mg is to the right of Na in the periodic table (i.e., Mg has the greater Zeff, so it is more difficult to remove its electron). IE2(Na) > IE2(Mg) because the second ionization of Mg remove ...
... compare the ionization energies. Na has one valence electron and Mg has two. Solution IE1(Mg) > IE1(Na) because Mg is to the right of Na in the periodic table (i.e., Mg has the greater Zeff, so it is more difficult to remove its electron). IE2(Na) > IE2(Mg) because the second ionization of Mg remove ...
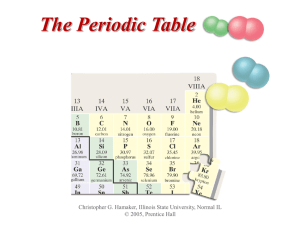
The Periodic Table
... • As one goes down a column, less energy is required to remove the first electron. – For atoms in the same group, the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus. ...
... • As one goes down a column, less energy is required to remove the first electron. – For atoms in the same group, the valence electrons are farther from the nucleus. ...
Henry Moseley, the Atomic Number, and Synthesis
... to advance the understanding of the elements and solve the problem with Mendeleev’s periodic table. Explain that organizing the elements by their weight did not always give a periodic alignment of their chemical properties. Moseley noticed that shooting electrons at elements caused them to release x ...
... to advance the understanding of the elements and solve the problem with Mendeleev’s periodic table. Explain that organizing the elements by their weight did not always give a periodic alignment of their chemical properties. Moseley noticed that shooting electrons at elements caused them to release x ...
Henry Moseley, the Atomic Number, and Synthesis
... to advance the understanding of the elements and solve the problem with Mendeleev’s periodic table. Explain that organizing the elements by their weight did not always give a periodic alignment of their chemical properties. Moseley noticed that shooting electrons at elements caused them to release x ...
... to advance the understanding of the elements and solve the problem with Mendeleev’s periodic table. Explain that organizing the elements by their weight did not always give a periodic alignment of their chemical properties. Moseley noticed that shooting electrons at elements caused them to release x ...
Ch 3 PPT - mvhs
... Atom is divisible and has three subatomic particleselectrons, protons and neutrons, which further are made up of sub sub atomic particle (such as mesons, antineutrino etc.). Protons and neutrons are present in the nucleus while the electrons move around the nucleus in an electron cloud. Electron clo ...
... Atom is divisible and has three subatomic particleselectrons, protons and neutrons, which further are made up of sub sub atomic particle (such as mesons, antineutrino etc.). Protons and neutrons are present in the nucleus while the electrons move around the nucleus in an electron cloud. Electron clo ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... Periods – Rows are called periods. The elements in these rows change conductivity and number of electrons as you move across the table. Groups – Columns are called groups or families. These elements have the same properties because of the number of electrons. ...
... Periods – Rows are called periods. The elements in these rows change conductivity and number of electrons as you move across the table. Groups – Columns are called groups or families. These elements have the same properties because of the number of electrons. ...
internal geodynamics - Ninova
... charges were of the atoms of individual elements in the periodic table of Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev (1834-1907). Mendeleev and his predecessors who attempted to find a sort of periodic relationship between successive elements, used atomic weights. The concept of atomic weight had been introduced by ...
... charges were of the atoms of individual elements in the periodic table of Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev (1834-1907). Mendeleev and his predecessors who attempted to find a sort of periodic relationship between successive elements, used atomic weights. The concept of atomic weight had been introduced by ...
Atomic Theory and Bonding
... The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Electrons exist in the space surrounding the nucleus. # of protons = # of electrons in every atom Nuclear charge = charge on the nucleus = # of protons Atomic number = # of protons = # of electrons ...
... The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Electrons exist in the space surrounding the nucleus. # of protons = # of electrons in every atom Nuclear charge = charge on the nucleus = # of protons Atomic number = # of protons = # of electrons ...
Atomic Theory and Bonding
... The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Electrons exist in the space surrounding the nucleus. # of protons = # of electrons in every atom Nuclear charge = charge on the nucleus = # of protons Atomic number = # of protons = # of electrons ...
... The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Electrons exist in the space surrounding the nucleus. # of protons = # of electrons in every atom Nuclear charge = charge on the nucleus = # of protons Atomic number = # of protons = # of electrons ...
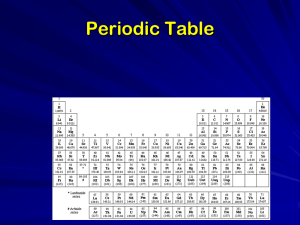
PeriodicTableA
... molecules, the electric field from these ions or molecules has a unequal effect on the energies of the various d orbitals and d electrons. The colors of the ions and complex ions of d block elements depends on a variety of factors including: – The particular element – The oxidation state – The kind ...
... molecules, the electric field from these ions or molecules has a unequal effect on the energies of the various d orbitals and d electrons. The colors of the ions and complex ions of d block elements depends on a variety of factors including: – The particular element – The oxidation state – The kind ...
Periodic Table - Red Deer Public
... molecules, the electric field from these ions or molecules has a unequal effect on the energies of the various d orbitals and d electrons. The colors of the ions and complex ions of d block elements depends on a variety of factors including: – The particular element – The oxidation state – The kind ...
... molecules, the electric field from these ions or molecules has a unequal effect on the energies of the various d orbitals and d electrons. The colors of the ions and complex ions of d block elements depends on a variety of factors including: – The particular element – The oxidation state – The kind ...
Periodic Trends - Chemwiki
... valence electrons are further away from the nucleus as ‘n’ increases. Electron shielding prevents these outer electrons from being attracted to the nucleus; thus, they are loosely held, and the resulting atomic radius is large. Atomic radius decreases from left to right within a period. This is caus ...
... valence electrons are further away from the nucleus as ‘n’ increases. Electron shielding prevents these outer electrons from being attracted to the nucleus; thus, they are loosely held, and the resulting atomic radius is large. Atomic radius decreases from left to right within a period. This is caus ...