Electronegativity - Sierra Vista Chemistry
... In a covalent bond between two different elements, the electron density is not shared equally. This is because different elements have differing abilities to attract the bonding electron pair. This ability is called an element’s electronegativity. ...
... In a covalent bond between two different elements, the electron density is not shared equally. This is because different elements have differing abilities to attract the bonding electron pair. This ability is called an element’s electronegativity. ...
Masses of Atoms
... Atomic Mass Unit ~ 1/12th of the mass of one carbon-12 atom The periodic table shows the atomic mass of Nickel as 58.693. How can there be a decimal point, if the mass is whole numbers of protons and neutrons? ...
... Atomic Mass Unit ~ 1/12th of the mass of one carbon-12 atom The periodic table shows the atomic mass of Nickel as 58.693. How can there be a decimal point, if the mass is whole numbers of protons and neutrons? ...
Electronegativity
... In a covalent bond between two different elements, the electron density is not shared equally. This is because different elements have differing abilities to attract the bonding electron pair. This ability is called an element’s electronegativity. ...
... In a covalent bond between two different elements, the electron density is not shared equally. This is because different elements have differing abilities to attract the bonding electron pair. This ability is called an element’s electronegativity. ...
Atomic Theory Powerpoint
... nucleus (think of planets orbiting around the sun). • Bohr used the term energy levels (or shells) to describe these orbits of differing energy. He said that the energy of an electron is quantized, meaning electrons can have one energy level or another but nothing in between. ...
... nucleus (think of planets orbiting around the sun). • Bohr used the term energy levels (or shells) to describe these orbits of differing energy. He said that the energy of an electron is quantized, meaning electrons can have one energy level or another but nothing in between. ...
Chapter 2 - My Teacher Site
... using radioactive tracers to monitor the synthesis of DNA and looking for “hot spots” of activity ...
... using radioactive tracers to monitor the synthesis of DNA and looking for “hot spots” of activity ...
Niels BOHR Bohr`s model was the first proposal that predicted the
... Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom are called VALENCE electrons. THESE electrons are normally involved in chemical bonding. Remember: Potassium tends to lose a single electron (forming a cation) in chemical reactions. ...
... Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom are called VALENCE electrons. THESE electrons are normally involved in chemical bonding. Remember: Potassium tends to lose a single electron (forming a cation) in chemical reactions. ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun. ...
... electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun. ...
Atomic Theory
... Modern atomic theory describes the electronic structure of the atom as the probability of finding electrons within certain regions of space (orbitals). ...
... Modern atomic theory describes the electronic structure of the atom as the probability of finding electrons within certain regions of space (orbitals). ...
Atomic Systems and Bonding
... It valance electrons are far from the nucleus and thus are not too tightly bound (making it easier to ‘move out’) outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is calle ...
... It valance electrons are far from the nucleus and thus are not too tightly bound (making it easier to ‘move out’) outside shell had only one electron When the valence electron in any atom gains sufficient energy from some outside force, it can break away from the parent atom and become what is calle ...
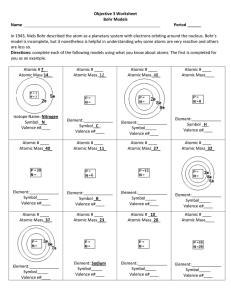
Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name Period In 1943, Niels
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
File
... 6. It will change in the future as we get new technology and new information 7. No, we have never seen it so we cannot know for sure if it is completely correct 8. Build upon previous knowledge…they don’t just throw away old info, they add to it and make changes to make it more correct (look at atom ...
... 6. It will change in the future as we get new technology and new information 7. No, we have never seen it so we cannot know for sure if it is completely correct 8. Build upon previous knowledge…they don’t just throw away old info, they add to it and make changes to make it more correct (look at atom ...
Atomic Structure
... g. isotope i. mass number b. electron e. nucleus h. average atomic j. atomic number c. proton f. nucleon mass k. ion Dalton’s Atomic Theory - John Dalton (1766-1844) a. State the main ideas of Dalton’s Atomic Theory (4) b. Which parts of Dalton’s theory are still considered to be true? c. Which part ...
... g. isotope i. mass number b. electron e. nucleus h. average atomic j. atomic number c. proton f. nucleon mass k. ion Dalton’s Atomic Theory - John Dalton (1766-1844) a. State the main ideas of Dalton’s Atomic Theory (4) b. Which parts of Dalton’s theory are still considered to be true? c. Which part ...
Periods and Blocks of the Periodic Table
... • Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. • Repeating patterns are referred to as periodic. • Mendeleev created a table in which elements with similar properties were g ...
... • Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. • Repeating patterns are referred to as periodic. • Mendeleev created a table in which elements with similar properties were g ...
Drawing Bohr Atoms An atom consists of a dense nucleus
... representing electrons opposite each other on the larger circle. A maximum of two electrons is allowed in the first shell. ...
... representing electrons opposite each other on the larger circle. A maximum of two electrons is allowed in the first shell. ...
Interactive Notebook 2 for 2011-2012
... unique properties of an element. This number of protons is called the element’s atomic number. Elements are arranged on the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number. Historically, elements were ordered by atomic mass, but now scientists know that this order would lead to misplaced element ...
... unique properties of an element. This number of protons is called the element’s atomic number. Elements are arranged on the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number. Historically, elements were ordered by atomic mass, but now scientists know that this order would lead to misplaced element ...
Ch 6.7 - Explaining the Atom
... - The maximum number of electrons in the first, second, and third orbits is 2, 8, and 8, respectively. Electrons fill lower orbits before filling higher orbits. - Bohr-Rutherford diagrams of atoms show the number and location of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atom. - All atoms within each f ...
... - The maximum number of electrons in the first, second, and third orbits is 2, 8, and 8, respectively. Electrons fill lower orbits before filling higher orbits. - Bohr-Rutherford diagrams of atoms show the number and location of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atom. - All atoms within each f ...
unit 6: periodic table - St. Dominic High School
... Lists elements according to their atomic number Still used columns called families which consist of elements with similar properties Still uses rows called periods . Elements increase by 1 moving from left to right. Periodic table lists 118 element. May need to be revised as new elements are di ...
... Lists elements according to their atomic number Still used columns called families which consist of elements with similar properties Still uses rows called periods . Elements increase by 1 moving from left to right. Periodic table lists 118 element. May need to be revised as new elements are di ...
Periodic Table - Red Deer Public
... the p-block is Group IIIA - VIIIA. The d-block is the transition metals, and the f-block are the Lanthanides and Actinide metals The way the periodic table usually shown is a compressed view. The Lanthanides and actinides (F block)are cut out and placed at the bottom of the table. ...
... the p-block is Group IIIA - VIIIA. The d-block is the transition metals, and the f-block are the Lanthanides and Actinide metals The way the periodic table usually shown is a compressed view. The Lanthanides and actinides (F block)are cut out and placed at the bottom of the table. ...
the atom
... 1) Atoms are the smallest identifiable units of elements. 2) Atoms of a given element are identical to one another, but different from atoms of any other element. 3) Atoms are rearranged in chemical reactions, but neither the number nor the types of atoms is changed in reaction 4) Compounds are form ...
... 1) Atoms are the smallest identifiable units of elements. 2) Atoms of a given element are identical to one another, but different from atoms of any other element. 3) Atoms are rearranged in chemical reactions, but neither the number nor the types of atoms is changed in reaction 4) Compounds are form ...
atom
... • 1.15 – I can define atomic/ionic radius and explain how it relates to the charge of the nucleus and the electron. Furthermore, I can explain how this trend changes as you move throughout the Periodic Table. ...
... • 1.15 – I can define atomic/ionic radius and explain how it relates to the charge of the nucleus and the electron. Furthermore, I can explain how this trend changes as you move throughout the Periodic Table. ...