AI Systems
... rational agents • Not restricted to human actions and human environments • Not restricted to human thought ...
... rational agents • Not restricted to human actions and human environments • Not restricted to human thought ...
CIS 690 - Kansas State University
... • Omniscience: knowing actual outcome of all actions • Rationality: knowing plausible outcome of all actions • Example: is crossing the street to greet a friend too risky? – Key question in AI • What is a plausible outcome? • Especially important in knowledge-based expert systems • Of practical impo ...
... • Omniscience: knowing actual outcome of all actions • Rationality: knowing plausible outcome of all actions • Example: is crossing the street to greet a friend too risky? – Key question in AI • What is a plausible outcome? • Especially important in knowledge-based expert systems • Of practical impo ...
Flyer
... BIH’16 addresses the computational, cognitive, physiological, biological, physical, ecological and social perspectives of brain informatics, as well as topics relating to mental health and well-being. It also welcomes emerging information technologies, including but not limited to Internet/Web of Th ...
... BIH’16 addresses the computational, cognitive, physiological, biological, physical, ecological and social perspectives of brain informatics, as well as topics relating to mental health and well-being. It also welcomes emerging information technologies, including but not limited to Internet/Web of Th ...
AI & Expert Systems
... What is Artificial Intelligence? • AI is the effort to develop systems that can behave/act like humans. • Turing Test • The problem = unrestricted domains ...
... What is Artificial Intelligence? • AI is the effort to develop systems that can behave/act like humans. • Turing Test • The problem = unrestricted domains ...
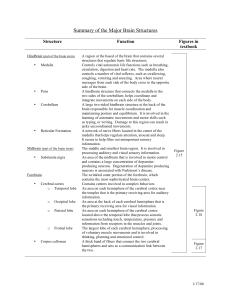
Summary of the Major Brain Structures
... also regulates the autonomic nervous system. A large structure embedded in the temporal lobe that plays a role in the ability to form new memories. An almond shaped structure that is involved in controlling a variety of emotional response patterns, including fear, anger, and disgust. It is also invo ...
... also regulates the autonomic nervous system. A large structure embedded in the temporal lobe that plays a role in the ability to form new memories. An almond shaped structure that is involved in controlling a variety of emotional response patterns, including fear, anger, and disgust. It is also invo ...
Introduction
... self-driving cars) / physical robot or software robot (e.g. an electronic trading system)) This course is about designing rational agents • For any given class of environments and tasks, we seek the agent (or class of agents) with the best performance ...
... self-driving cars) / physical robot or software robot (e.g. an electronic trading system)) This course is about designing rational agents • For any given class of environments and tasks, we seek the agent (or class of agents) with the best performance ...
an assignment - UBC Computer Science
... • You may not work with or copy work from anyone else – May talk about solution approaches on high level with others – May not look at another student’s solution, or previous sample ...
... • You may not work with or copy work from anyone else – May talk about solution approaches on high level with others – May not look at another student’s solution, or previous sample ...
an assignment - UBC Computer Science
... • You may not work with or copy work from anyone else – May talk about solution approaches on high level with others – May not look at another student’s solution, or previous sample ...
... • You may not work with or copy work from anyone else – May talk about solution approaches on high level with others – May not look at another student’s solution, or previous sample ...
(pdf)
... the world (i.e. an “autonomous system” (e.g. self-driving cars) / physical robot or software robot (e.g. an electronic trading system)) This course is about designing rational agents • For any given class of environments and tasks, we seek the agent (or class of agents) with the best performance • ...
... the world (i.e. an “autonomous system” (e.g. self-driving cars) / physical robot or software robot (e.g. an electronic trading system)) This course is about designing rational agents • For any given class of environments and tasks, we seek the agent (or class of agents) with the best performance • ...
a. autotrophic/heterotrophic organisms
... j. converting glucose into usable energy in the mitochondria of the cell Respiration k. exothermic animals like snakes and lizards must bask in the sun to maintain their body temperature Regulation l. Worms get rid of nitrogenous waste (like our urine) through structures called nephridia Excretion ...
... j. converting glucose into usable energy in the mitochondria of the cell Respiration k. exothermic animals like snakes and lizards must bask in the sun to maintain their body temperature Regulation l. Worms get rid of nitrogenous waste (like our urine) through structures called nephridia Excretion ...
Modules 16-21: Sensation and Perception
... ○ Athletes can play through pain. Socio-Cultural Influences: ○ When others are feeling pain, we tend to feel more pain. Anosmia- people who are unable to smell. Kinesthesia- the system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts. Vestibular Sense- the sense of body movement and po ...
... ○ Athletes can play through pain. Socio-Cultural Influences: ○ When others are feeling pain, we tend to feel more pain. Anosmia- people who are unable to smell. Kinesthesia- the system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts. Vestibular Sense- the sense of body movement and po ...
Bio-inspired
... acting in the face of uncertain and unpredictable environments. It was reasoned that if a single robot required complex systems and techniques in order to perform in a reliable manner, then perhaps intelligent systems could be designed with many “simpler” robots using a minimalist approach to sensin ...
... acting in the face of uncertain and unpredictable environments. It was reasoned that if a single robot required complex systems and techniques in order to perform in a reliable manner, then perhaps intelligent systems could be designed with many “simpler” robots using a minimalist approach to sensin ...
An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology - Home
... Multidimensional Models One-Dimensional Models ...
... Multidimensional Models One-Dimensional Models ...
Progress and Challenges in Interactive Cognitive Systems
... most work on cognitive systems: • The ability to encode, manipulate, and interpret symbol structures is necessary and sufficient for general intelligent action. • Problem solving involves heuristic search through a space of states (symbol structures) generated by mental operators. We offer a third ...
... most work on cognitive systems: • The ability to encode, manipulate, and interpret symbol structures is necessary and sufficient for general intelligent action. • Problem solving involves heuristic search through a space of states (symbol structures) generated by mental operators. We offer a third ...
Reflex and autonomic nervous system
... Has sensory receptors that collect information form internal and external environments. The information is passed on to the central nervous system. Pair share: name 2 things that the sensory receptors might collect from the internal and external environment. ...
... Has sensory receptors that collect information form internal and external environments. The information is passed on to the central nervous system. Pair share: name 2 things that the sensory receptors might collect from the internal and external environment. ...
Study of human brain yields intelligent robots
... Artificial intelligence had its origins in 1950, when the mathematician Alan Turing proposed a test to determine whether a machine could think. The test involved having a person face two computer terminals, only one of which had a human behind it. If a human judge could not tell which terminal was c ...
... Artificial intelligence had its origins in 1950, when the mathematician Alan Turing proposed a test to determine whether a machine could think. The test involved having a person face two computer terminals, only one of which had a human behind it. If a human judge could not tell which terminal was c ...
Study of human brain yields intelligent robots
... Artificial intelligence had its origins in 1950, when the mathematician Alan Turing proposed a test to determine whether a machine could think. The test involved having a person face two computer terminals, only one of which had a human behind it. If a human judge could not tell which terminal was c ...
... Artificial intelligence had its origins in 1950, when the mathematician Alan Turing proposed a test to determine whether a machine could think. The test involved having a person face two computer terminals, only one of which had a human behind it. If a human judge could not tell which terminal was c ...
Chapter 03 - Jen Wright
... 14. Please explain the difference between the ontogeny and phylogeny of the brain. 15. How does studying people with brain damage help scientists to better understand the brain? As a classic example, what did the case of Phineas Gage teach us? 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, an ...
... 14. Please explain the difference between the ontogeny and phylogeny of the brain. 15. How does studying people with brain damage help scientists to better understand the brain? As a classic example, what did the case of Phineas Gage teach us? 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, an ...
Psychology 101 Exam 1
... a. Using single cases to disprove a well established cause b. Stereotypic thinking c. Assigning salience to low probability events d. Reliance on base rates 13) A situation in which a science major does well in a physics course but not in a poetry course and an English major shows the reverse patter ...
... a. Using single cases to disprove a well established cause b. Stereotypic thinking c. Assigning salience to low probability events d. Reliance on base rates 13) A situation in which a science major does well in a physics course but not in a poetry course and an English major shows the reverse patter ...
PPT - Ubiquitous Computing Lab
... A deadlock problem was the key feature of the short story in which Asimov first introduced the laws. He constructed the type of stand- off commonly referred to as the "Buridan's ass" problem. It involved a balance between a strong third- law self- protection tendency, causing the robot to try to av ...
... A deadlock problem was the key feature of the short story in which Asimov first introduced the laws. He constructed the type of stand- off commonly referred to as the "Buridan's ass" problem. It involved a balance between a strong third- law self- protection tendency, causing the robot to try to av ...
The Brain - cloudfront.net
... – Hippocampus: responsible for processing of long term memory and emotional responses • Short term to long term memory and learning ...
... – Hippocampus: responsible for processing of long term memory and emotional responses • Short term to long term memory and learning ...