Dissociation of H in the energy region at the n state
... one-photon absorption from the BŽ ÕX s 19, J X s 0. level. These spectra show that at the HŽ n s 1. q HŽ n s 3. dissociation threshold, the autoionization channel closes, to be replaced by dissociation into n s 1 and n s 3 fragments. This observation is in agreement with the results from one-colour ...
... one-photon absorption from the BŽ ÕX s 19, J X s 0. level. These spectra show that at the HŽ n s 1. q HŽ n s 3. dissociation threshold, the autoionization channel closes, to be replaced by dissociation into n s 1 and n s 3 fragments. This observation is in agreement with the results from one-colour ...
Measurement of the force exerted on the surface of an object
... constant” D as the deflection-to-force conversion factor that has to be determined by the calibration. The equilibrium requires ...
... constant” D as the deflection-to-force conversion factor that has to be determined by the calibration. The equilibrium requires ...
GCE Getting Started - Edexcel
... atoms, given the atomic number, Z, up to Z = 36 ii. ions, given the atomic number, Z, and the ionic charge, for s and p block ions only, up to Z = 36. Know that elements can be classified as s-, p- and d-block elements. Understand that electronic configuration determines the chemical properties of a ...
... atoms, given the atomic number, Z, up to Z = 36 ii. ions, given the atomic number, Z, and the ionic charge, for s and p block ions only, up to Z = 36. Know that elements can be classified as s-, p- and d-block elements. Understand that electronic configuration determines the chemical properties of a ...
Chemistry - Resonance
... About 3 million organic compounds are known today. The main reasons for this huge number of organic compounds are (i) Catenation : The property of self linking of carbon atoms through covalent bonds to form long straight or branched chains and rings of different sizes is called catenation.Carbon sho ...
... About 3 million organic compounds are known today. The main reasons for this huge number of organic compounds are (i) Catenation : The property of self linking of carbon atoms through covalent bonds to form long straight or branched chains and rings of different sizes is called catenation.Carbon sho ...
Extreme Physics Explorer - High Energy Astrophysics
... Extreme Physics Explorer Time is ripe for X-ray emitting Compact Objects research to move to 3rd phase: Extreme Physics Physics-Astrophysics collaboration on Extreme Physics? Need theoretical predictions of spectral features email [email protected] if you want to join in Black Hole or `neutr ...
... Extreme Physics Explorer Time is ripe for X-ray emitting Compact Objects research to move to 3rd phase: Extreme Physics Physics-Astrophysics collaboration on Extreme Physics? Need theoretical predictions of spectral features email [email protected] if you want to join in Black Hole or `neutr ...
"Characterization of 3D-integrated Active Pixel Sensor for X-ray Detection."
... single-pixel testing but extended it to include multiple pixels. Four pixels in the same row were held in reset, and then each of them was read out one after another. The cycle of reading out four sequential pixels was repeated 130 times without resetting any of them. The device was illuminated by a ...
... single-pixel testing but extended it to include multiple pixels. Four pixels in the same row were held in reset, and then each of them was read out one after another. The cycle of reading out four sequential pixels was repeated 130 times without resetting any of them. The device was illuminated by a ...
On the combination of a linear field free trap with a time-of
... injection, i.e., the ions are typically decelerated into the trap to energies below 50 meV in order to prevent collision induced excitation or dissociation. Interaction with a buffer gas couples finally the ion temperature to that of the surrounding walls. Two phases of a rf voltage applied to the t ...
... injection, i.e., the ions are typically decelerated into the trap to energies below 50 meV in order to prevent collision induced excitation or dissociation. Interaction with a buffer gas couples finally the ion temperature to that of the surrounding walls. Two phases of a rf voltage applied to the t ...
7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds
... can see in Figure 7.8, the ions in solid sodium chloride are arranged in an orderly pattern. There are no single discrete units, only a continuous array of ions. Chemists represent the composition of substances by writing chemical formulas. A chemical formula shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in ...
... can see in Figure 7.8, the ions in solid sodium chloride are arranged in an orderly pattern. There are no single discrete units, only a continuous array of ions. Chemists represent the composition of substances by writing chemical formulas. A chemical formula shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in ...
regents chemistry midterm - irondequoit 2014_entire exam w key
... 3) The forming of the H–Cl bond absorbs energy. 4) The forming of the H–Cl bond releases energy. 26. Which is an empirical formula? 1) C2H2 3) H2O2 2) H2O 4) C6Hl2O6 27. Which symbol represents an atom in the ground state with the most stable valence electron configuration? 1) B 3) Li 2) O 4) Ne 28. ...
... 3) The forming of the H–Cl bond absorbs energy. 4) The forming of the H–Cl bond releases energy. 26. Which is an empirical formula? 1) C2H2 3) H2O2 2) H2O 4) C6Hl2O6 27. Which symbol represents an atom in the ground state with the most stable valence electron configuration? 1) B 3) Li 2) O 4) Ne 28. ...
Chemistry 400
... A) At a given temperature, lighter gas particles travel more slowly than heavier gas particles. B) The smaller a gas particle, the slower it will effuse C) The higher the temperature, the lower the average kinetic energy of the sample. D) At low temperatures, intermolecular forces become important a ...
... A) At a given temperature, lighter gas particles travel more slowly than heavier gas particles. B) The smaller a gas particle, the slower it will effuse C) The higher the temperature, the lower the average kinetic energy of the sample. D) At low temperatures, intermolecular forces become important a ...
Dynamics of H2 and C2H4 Elimination in the Y+ C2H6 Reaction
... asymptote and driven predominantly by the formation of a strongly bound YC2H4 adduct.5 However, a second product channel, resulting in YH2 + C2H4 products, is expected to be only slightly less thermodynamically favorable, owing to the formation of two relatively strong M-H bonds in YH2.26,27 This et ...
... asymptote and driven predominantly by the formation of a strongly bound YC2H4 adduct.5 However, a second product channel, resulting in YH2 + C2H4 products, is expected to be only slightly less thermodynamically favorable, owing to the formation of two relatively strong M-H bonds in YH2.26,27 This et ...
plasma/tokamak (alex/steve)new - General Atomics Fusion Education
... neon atom at low pressure in a glass tube. The light is given off when the ionized atom recombines with a free electron. The electron gives up its energy, moving to a lower orbit, when recombining with the ion. The release of this energy is through a photon at a specific visible light frequency (red ...
... neon atom at low pressure in a glass tube. The light is given off when the ionized atom recombines with a free electron. The electron gives up its energy, moving to a lower orbit, when recombining with the ion. The release of this energy is through a photon at a specific visible light frequency (red ...
File
... more dense than water. Specific gravity has no units. It is simply a number. This is because the units cancel out when the densities of the two substances are compared. ...
... more dense than water. Specific gravity has no units. It is simply a number. This is because the units cancel out when the densities of the two substances are compared. ...
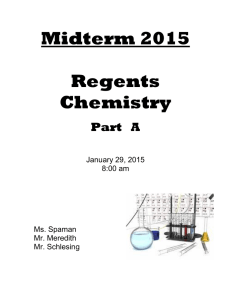
85 Q.1 A substance X melts at 1600oC. Its does
... M is an element in the third period of the Periodic Table. M forms a sulphate which has the formula M2(SO4)3. The formula of the nitrate of M is A. C. ...
... M is an element in the third period of the Periodic Table. M forms a sulphate which has the formula M2(SO4)3. The formula of the nitrate of M is A. C. ...
Adsorption of large ions from an electrolyte solution: a modified
... charged ions to highly charged surfaces [19–26], and (iii) the attractive interactions that can be observed between equally charged surfaces in the presence of multivalent counterions [27,28]. Consequently, there have been numerous attempts to improve upon the standard Poisson–Boltzmann approach [29 ...
... charged ions to highly charged surfaces [19–26], and (iii) the attractive interactions that can be observed between equally charged surfaces in the presence of multivalent counterions [27,28]. Consequently, there have been numerous attempts to improve upon the standard Poisson–Boltzmann approach [29 ...
Chains of [RE6] Octahedra Coupled by (NCN) Links in the Network
... bridging (CN2)2- to form a three-dimensional network with Cl- ions in linear channels. Compounds 1 and 2 are surprisingly stable toward air and water. They have been characterized by thermal analysis, infrared spectroscopy, and magnetic susceptibility studies. ...
... bridging (CN2)2- to form a three-dimensional network with Cl- ions in linear channels. Compounds 1 and 2 are surprisingly stable toward air and water. They have been characterized by thermal analysis, infrared spectroscopy, and magnetic susceptibility studies. ...
Fundamentals
... original wire and has a diameter of 1 m, but individual atoms are still not visible.A magnification of a 1,000,000 times barely reveals atoms. At this magnification, the original wire has become 1 km in diameter. An additional power of 10 is required to see the individual atoms that have become 2.4 ...
... original wire and has a diameter of 1 m, but individual atoms are still not visible.A magnification of a 1,000,000 times barely reveals atoms. At this magnification, the original wire has become 1 km in diameter. An additional power of 10 is required to see the individual atoms that have become 2.4 ...
Amino Acid Composition and Wavelength Effects in Matrix
... by using the height of the enthalpy of formation barrier, the distance between the minima, and the energy of the proton in the transition complex. Our proton tunneling rate calculations have been presented elsewhere.33 It is known that the transition state energy barriers are severely overestimated ...
... by using the height of the enthalpy of formation barrier, the distance between the minima, and the energy of the proton in the transition complex. Our proton tunneling rate calculations have been presented elsewhere.33 It is known that the transition state energy barriers are severely overestimated ...
Chapter 7 Plasma Basics
... •At atmospheric pressure (760 Torr), MFP of an electron is very short. Electrons are hard to get enough energy to ionize gases molecules. •Extremely strong electric field can create plasma in the form of arcing (lightening) instead of steady state glow discharge. ...
... •At atmospheric pressure (760 Torr), MFP of an electron is very short. Electrons are hard to get enough energy to ionize gases molecules. •Extremely strong electric field can create plasma in the form of arcing (lightening) instead of steady state glow discharge. ...
Metastable inner-shell molecular state

Metastable Innershell Molecular State (MIMS) is a class of ultra-high-energy short-lived molecules have the binding energy up to 1,000 times larger and bond length up to 100 times smaller than typical molecules. MIMS is formed by inner-shell electrons that are normally resistant to molecular formation. However, in stellar conditions, the inner-shell electrons become reactive to form molecular structures (MIMS) from combinations of all elements in the periodic table. MIMS upon dissociation can emit x-ray photons with energies up to 100 keV at extremely high conversion efficiencies from compression energy to photon energy. MIMS is predicted to exist and dominate radiation processes in extreme astrophysical environments, such as large planet cores, star interiors, and black hole and neutron star surroundings. There, MIMS is predicted to enable highly energy-efficient transformation of the stellar compression energy into the radiation energy.The right schematic illustration shows the proposed four stages of the K-shell MIMS (K-MIMS) formation and x-ray generation process. Stage I: Individual atoms are subjected to the stellar compression and ready for absorbing the compression energy. Stage II: The outer electron shells fuse together under increasing ""stellar"" pressure. Stage III: At the peak pressure, via pressure ionization K-shell orbits form the K-MIMS, which is vibrationally hot and encapsulated by a Rydberg-like pseudo-L-Shell structure. Stage IV: The K-MIMS cools down by ionizing (""boiling-off"") a number of pseudo-L-shell electrons and subsequent optical decay by emitting an x-ray photon. The dissociated atoms return their original atoms states and are ready for absorbing the compression energy.MIMS also can be readily produced in laboratory and industrial environments, such as hypervelocity particle impact, laser fusion and z-machine. MIMS can be exploited for highly energy-efficient production of high intensity x-ray beams for a wide range of innovative applications, such as photolithography, x-ray lasers, and inertial fusion.

















![Chains of [RE6] Octahedra Coupled by (NCN) Links in the Network](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015582545_1-0c739ec23481c3b23043e6bd2ed87368-300x300.png)