
Answers to NHSCE 2002 Part A Page 1
... eyes.) Even though battery acid generates heat when mixed with water, it will not be as great as the heat generated by reaction with alkali, and an excess of water will ensure that the skin is cooled without further damage. In the case of acids spilled on benches or the floor, it is appropriate to u ...
... eyes.) Even though battery acid generates heat when mixed with water, it will not be as great as the heat generated by reaction with alkali, and an excess of water will ensure that the skin is cooled without further damage. In the case of acids spilled on benches or the floor, it is appropriate to u ...
Ions in Crystals - American Chemical Society
... calculations at the experimental geometry.14 The aiPI method is a localized Hartree-Fock (HF) scheme60,63,64 that has been extensively used to describe accurately the electronic structure, geometry, and thermodynamical properties of ionic and partly ionic pure and defective solids.60,65-71 The multi ...
... calculations at the experimental geometry.14 The aiPI method is a localized Hartree-Fock (HF) scheme60,63,64 that has been extensively used to describe accurately the electronic structure, geometry, and thermodynamical properties of ionic and partly ionic pure and defective solids.60,65-71 The multi ...
Chapter 3 Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
... - hold atoms together to form compounds - are forces of attraction between atoms. - the bonding attraction comes from attractions between protons and electrons. i.) Ionic bonds - result when electrons have been transferred between atoms, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other - ...
... - hold atoms together to form compounds - are forces of attraction between atoms. - the bonding attraction comes from attractions between protons and electrons. i.) Ionic bonds - result when electrons have been transferred between atoms, resulting in oppositely charged ions that attract each other - ...
Comparison between Free and Immobilized Ion
... neglected (see the Supporting Information). When investigating free ion effects, 1 M concentration (approximately 80 ions) of various alkali halides is added to the solution. Such concentration has been used in previous simulation work to study the free ion effect, and in past simulations the Hofmeist ...
... neglected (see the Supporting Information). When investigating free ion effects, 1 M concentration (approximately 80 ions) of various alkali halides is added to the solution. Such concentration has been used in previous simulation work to study the free ion effect, and in past simulations the Hofmeist ...
SwissFEL ATHOS Science Case
... beamline at SwissFEL, one may study the transient effect of an applied electric field on the magnetic order, with potential applications in novel switching devices. Lower: With sufficiently intense pulses of soft X-rays, it should be possible to observe phenomena beyond the linear regime, in an exte ...
... beamline at SwissFEL, one may study the transient effect of an applied electric field on the magnetic order, with potential applications in novel switching devices. Lower: With sufficiently intense pulses of soft X-rays, it should be possible to observe phenomena beyond the linear regime, in an exte ...
- EPJ Web of Conferences
... energies. The nature of the reagent is another matter of concern. Historically the experimental techniques that have been developed in the field of very low temperature chemistry have first dealt with charged species [18, 19]. The main reason is that ions can be easily manipulated, stored by electro ...
... energies. The nature of the reagent is another matter of concern. Historically the experimental techniques that have been developed in the field of very low temperature chemistry have first dealt with charged species [18, 19]. The main reason is that ions can be easily manipulated, stored by electro ...
X-ray telescopes
... be reflected from a polished surface. In recognition of the fact that the angle of incidence was so small with respect to the plane of the surface (51") the term 'glancing' or 'grazing incidence reflection' was born. Obviously, total external reflection occurred which meant that the interaction of x ...
... be reflected from a polished surface. In recognition of the fact that the angle of incidence was so small with respect to the plane of the surface (51") the term 'glancing' or 'grazing incidence reflection' was born. Obviously, total external reflection occurred which meant that the interaction of x ...
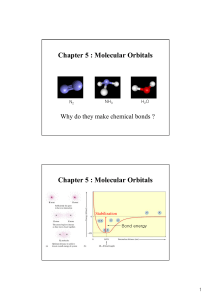
Chemical bonding
... 22) How many lone pairs of electrons are present in a molecule of SF4? 23) What is hybridization? 24) Write the shape and bond angle of sp hybrid orbitals? 25) Give an example of a molecule having sp hybridization? 26) What is the percentage of s character in sp hybridization? 27) What is the shape ...
... 22) How many lone pairs of electrons are present in a molecule of SF4? 23) What is hybridization? 24) Write the shape and bond angle of sp hybrid orbitals? 25) Give an example of a molecule having sp hybridization? 26) What is the percentage of s character in sp hybridization? 27) What is the shape ...
Asymmetry of Electron Transmission through Monolayers of Helical
... the surface normal, and θ1,2 represent the angles between the transition moment and the helix axis. The values of θ1 and θ2 were taken to be 39 and 75°, respectively.23 The value of the tilt angle of the helix from the surface normal was found to be 47 ( 2°. In this calculation we assumed the unifor ...
... the surface normal, and θ1,2 represent the angles between the transition moment and the helix axis. The values of θ1 and θ2 were taken to be 39 and 75°, respectively.23 The value of the tilt angle of the helix from the surface normal was found to be 47 ( 2°. In this calculation we assumed the unifor ...
First Semester Final Review
... percent. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this difference? a. Strong initial heating caused some of the hydrate sample to spatter out of the crucible. b. The dehydrated sample absorbed moisture after heating. c. The amount of the hydrate sample used was too small. d. The cru ...
... percent. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this difference? a. Strong initial heating caused some of the hydrate sample to spatter out of the crucible. b. The dehydrated sample absorbed moisture after heating. c. The amount of the hydrate sample used was too small. d. The cru ...
Final Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... 9. Deviations from the ideal gas law are greater at: A) low temperatures and low pressures B) high temperatures and high pressures C) low temperatures and high pressures D) high temperatures and low pressures E) STP Gases are most ideal when the pressure is low (large volume, thus large distances b ...
... 9. Deviations from the ideal gas law are greater at: A) low temperatures and low pressures B) high temperatures and high pressures C) low temperatures and high pressures D) high temperatures and low pressures E) STP Gases are most ideal when the pressure is low (large volume, thus large distances b ...
On the electron-ion temperature ratio established by - Hal-CEA
... electrons (dashed black line, Eq. (22)), and for magnetised plasmas with β = 0.01, 0.1, 1 (blue dashed line, Eq 31). In addition the expected ratio is shown if on top of various thermodynamic effects there is energy exchange between the electrons and ions at the level of 5% (magenta dashed line, Eq. ...
... electrons (dashed black line, Eq. (22)), and for magnetised plasmas with β = 0.01, 0.1, 1 (blue dashed line, Eq 31). In addition the expected ratio is shown if on top of various thermodynamic effects there is energy exchange between the electrons and ions at the level of 5% (magenta dashed line, Eq. ...
RESEARCH ACTIVITIES
... isomerization along the reaction coordinates, electronically excited states, unstable electronic structures of radical systems, and multiple covalent bindings in molecular metal complexes, etc. Our resultant works to be reported here are (1) to develop a type of the multireference correlation model ...
... isomerization along the reaction coordinates, electronically excited states, unstable electronic structures of radical systems, and multiple covalent bindings in molecular metal complexes, etc. Our resultant works to be reported here are (1) to develop a type of the multireference correlation model ...
Class XI Physical Chemistry Short note
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. 5. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That is, atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply ...
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. 5. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That is, atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply ...
L-Cysteine as a Chiral Linker in Lanthanide–Cucurbit[6]uril
... respectively, in agreement with the values in previous complexes. The L-cys ligand is in its zwitterionic, neutral form, and is monodentate through one carboxylate oxygen atom, with Ln–O bond lengths in the range 2.31–2.38 Å (in 2 and 3, the bond length for Ln2 is slightly larger than that for Ln1 d ...
... respectively, in agreement with the values in previous complexes. The L-cys ligand is in its zwitterionic, neutral form, and is monodentate through one carboxylate oxygen atom, with Ln–O bond lengths in the range 2.31–2.38 Å (in 2 and 3, the bond length for Ln2 is slightly larger than that for Ln1 d ...
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry
... As you have learned, ions are atoms or molecules bearing an electrical charge. A cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative ion) forms when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons in its valence shell. Compounds c ...
... As you have learned, ions are atoms or molecules bearing an electrical charge. A cation (a positive ion) forms when a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative ion) forms when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons in its valence shell. Compounds c ...
Full text
... ìSuppose that there are n electrons in our atom. Then let us first guess plausible wave functions for each of these electrons. ÖNow choose one of the electrons and find the average field provided by all the others. Ö This process allows us to write down, and then to solve, the wave equation for our ...
... ìSuppose that there are n electrons in our atom. Then let us first guess plausible wave functions for each of these electrons. ÖNow choose one of the electrons and find the average field provided by all the others. Ö This process allows us to write down, and then to solve, the wave equation for our ...
Metastable inner-shell molecular state

Metastable Innershell Molecular State (MIMS) is a class of ultra-high-energy short-lived molecules have the binding energy up to 1,000 times larger and bond length up to 100 times smaller than typical molecules. MIMS is formed by inner-shell electrons that are normally resistant to molecular formation. However, in stellar conditions, the inner-shell electrons become reactive to form molecular structures (MIMS) from combinations of all elements in the periodic table. MIMS upon dissociation can emit x-ray photons with energies up to 100 keV at extremely high conversion efficiencies from compression energy to photon energy. MIMS is predicted to exist and dominate radiation processes in extreme astrophysical environments, such as large planet cores, star interiors, and black hole and neutron star surroundings. There, MIMS is predicted to enable highly energy-efficient transformation of the stellar compression energy into the radiation energy.The right schematic illustration shows the proposed four stages of the K-shell MIMS (K-MIMS) formation and x-ray generation process. Stage I: Individual atoms are subjected to the stellar compression and ready for absorbing the compression energy. Stage II: The outer electron shells fuse together under increasing ""stellar"" pressure. Stage III: At the peak pressure, via pressure ionization K-shell orbits form the K-MIMS, which is vibrationally hot and encapsulated by a Rydberg-like pseudo-L-Shell structure. Stage IV: The K-MIMS cools down by ionizing (""boiling-off"") a number of pseudo-L-shell electrons and subsequent optical decay by emitting an x-ray photon. The dissociated atoms return their original atoms states and are ready for absorbing the compression energy.MIMS also can be readily produced in laboratory and industrial environments, such as hypervelocity particle impact, laser fusion and z-machine. MIMS can be exploited for highly energy-efficient production of high intensity x-ray beams for a wide range of innovative applications, such as photolithography, x-ray lasers, and inertial fusion.



















![L-Cysteine as a Chiral Linker in Lanthanide–Cucurbit[6]uril](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002388013_1-9387091f243aaed6c7cd4b5e1425ce91-300x300.png)

