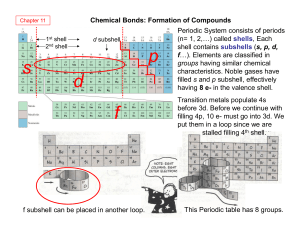
Exam 3a - Design Thinking in Education
... What I’ve drawn above are not structural formulas (showing all atoms and all bonds) so would be wrong on a test. chemical formula (shows only atoms), C3H8 or C3H8O . condensed structural formula (shows connectivity, but is symbolically encoded) as in CH3CH2CH3 or CH3CH2CH2OH . structural formula: sh ...
... What I’ve drawn above are not structural formulas (showing all atoms and all bonds) so would be wrong on a test. chemical formula (shows only atoms), C3H8 or C3H8O . condensed structural formula (shows connectivity, but is symbolically encoded) as in CH3CH2CH3 or CH3CH2CH2OH . structural formula: sh ...
Chem fundamentals 1a
... Comments on chemical notation: Single lines = single bonds = 2 electrons Double lines = double bonds = 4 electrons Nonbonding electrons (depends on the element) are not shown but are counted to balance electrons. O has 4 nonbonding electrons; N has 2. Organic chemical structures often are ...
... Comments on chemical notation: Single lines = single bonds = 2 electrons Double lines = double bonds = 4 electrons Nonbonding electrons (depends on the element) are not shown but are counted to balance electrons. O has 4 nonbonding electrons; N has 2. Organic chemical structures often are ...
MiniQuiz 3
... One of the major factors in determining the energy of an electron is its electrostatic attraction to the positive nucleus. Shielding refers to the: a) the number of electrons in the outer shell. b) the electron’s angular momentum quantum number. c•) the presence of other electrons between the electr ...
... One of the major factors in determining the energy of an electron is its electrostatic attraction to the positive nucleus. Shielding refers to the: a) the number of electrons in the outer shell. b) the electron’s angular momentum quantum number. c•) the presence of other electrons between the electr ...
Unit 1, Lecture 1
... In order to arrive at the ground state, the lowest energy state, it is necessary to follow some simple rules: Electrons occupy the lowest energy level first (also called the Aufbau Principle) No more than one alpha (or spin up) and one beta (or spin down) electron can occupy a particular orbital at ...
... In order to arrive at the ground state, the lowest energy state, it is necessary to follow some simple rules: Electrons occupy the lowest energy level first (also called the Aufbau Principle) No more than one alpha (or spin up) and one beta (or spin down) electron can occupy a particular orbital at ...
AP Chap 2
... In biological elements, remember electrons are filled in shells in the following order: ...
... In biological elements, remember electrons are filled in shells in the following order: ...
Study Guide for Exam 2_old
... Study Guide for Exam 2 You should be able to answer the following questions, solve problems involving the following concepts, or understand the following concepts so that you can describe them and answer questions about them. Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence ...
... Study Guide for Exam 2 You should be able to answer the following questions, solve problems involving the following concepts, or understand the following concepts so that you can describe them and answer questions about them. Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence ...
Document
... never involved in the bond as they are too close to their own nucleus. 2 He atoms will never form a bond because Energy of He2 > 2 He. ...
... never involved in the bond as they are too close to their own nucleus. 2 He atoms will never form a bond because Energy of He2 > 2 He. ...
Final Exam Practice Problems Set 2
... matter and energy are really the same thing. it is impossible to know anything with certainty. it is impossible to know both the exact position and momentum of an electron. there can only be one uncertain digit in a reported number. it is impossible to know how many electrons there are in an atom. ...
... matter and energy are really the same thing. it is impossible to know anything with certainty. it is impossible to know both the exact position and momentum of an electron. there can only be one uncertain digit in a reported number. it is impossible to know how many electrons there are in an atom. ...
Study Guide for Exam 2_Sp12
... Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence electrons? What is ionization energy? What is the octet rule? What are ions? How do they relate to the octet rule? How is charge balance related to writing formulas of ionic compounds? Write dot formulas for atoms, and show h ...
... Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence electrons? What is ionization energy? What is the octet rule? What are ions? How do they relate to the octet rule? How is charge balance related to writing formulas of ionic compounds? Write dot formulas for atoms, and show h ...
Chapter 2 - My Teacher Site
... – This bonding capacity is called an atom’s valence – It usually equals the number of unpaired electrons required to complete the atom’s outermost (valence) shell • Ex) Oxygen, with 6 electrons in its outermost shell, has a valence of 2 ...
... – This bonding capacity is called an atom’s valence – It usually equals the number of unpaired electrons required to complete the atom’s outermost (valence) shell • Ex) Oxygen, with 6 electrons in its outermost shell, has a valence of 2 ...
Class Syllabus Ch120a: Nature of the Chemical Bond Units: 3-0
... Courses in QM often focus more on applied mathematics rather than physical concepts. We start by understanding some of the essential differences between quantum and classical mechanics, one of which is the description of kinetic energy. These ideas are used to understand why atoms are stable and wh ...
... Courses in QM often focus more on applied mathematics rather than physical concepts. We start by understanding some of the essential differences between quantum and classical mechanics, one of which is the description of kinetic energy. These ideas are used to understand why atoms are stable and wh ...
(null): 110.ReactionsIntro
... b) KE transformed into chem PE 3) Do reduced version of Zn & HCl: one zinc pellet in test tube plus a few ml of HCl. While bubbling discuss where energy is stored and where it goes 4) Return to reaction, have Ss feel test tube (warm!) & decide if reaction followed Option 1 or 2 d. “Re-arrange” colli ...
... b) KE transformed into chem PE 3) Do reduced version of Zn & HCl: one zinc pellet in test tube plus a few ml of HCl. While bubbling discuss where energy is stored and where it goes 4) Return to reaction, have Ss feel test tube (warm!) & decide if reaction followed Option 1 or 2 d. “Re-arrange” colli ...
Chemistry 101 Chapter 4 Elements, Atoms, and Ions = =
... Natural states of the elements: some elements consist of single atoms and they are found in an isolated state (for example, Ar and He). They are called monatomic elements. Some elements are diatomic and they consist of two atoms. The atoms of these elements have special affinities for each other and ...
... Natural states of the elements: some elements consist of single atoms and they are found in an isolated state (for example, Ar and He). They are called monatomic elements. Some elements are diatomic and they consist of two atoms. The atoms of these elements have special affinities for each other and ...
Structure of Molecules and Compounds | Principles of Biology from
... Covalent bonds come in several varieties. A single bond forms between two atoms that share one pair of electrons. Consider the element carbon. It has four valence electrons. Carbon requires four additional electrons to reach a stable configuration. It can gain these electrons, for example, by combin ...
... Covalent bonds come in several varieties. A single bond forms between two atoms that share one pair of electrons. Consider the element carbon. It has four valence electrons. Carbon requires four additional electrons to reach a stable configuration. It can gain these electrons, for example, by combin ...
Document
... A solid has a mass of 20g. When it is mixed with a solution a chemical reaction occurs in which a gas is produced. If the final total mass of the products is 55g, what was the mass of the solution? 20 g + solution = 55g 55g - 20g = mass of solution 35g = mass of solution ...
... A solid has a mass of 20g. When it is mixed with a solution a chemical reaction occurs in which a gas is produced. If the final total mass of the products is 55g, what was the mass of the solution? 20 g + solution = 55g 55g - 20g = mass of solution 35g = mass of solution ...
MYP Chemistry: Final Review
... Draw a Lewis dot structure for each of the following molecules: O 2, H2O, CH2Cl2, NI3 ...
... Draw a Lewis dot structure for each of the following molecules: O 2, H2O, CH2Cl2, NI3 ...
The Basics - I`m a faculty member, and I need web space. What
... • If there is only one bond in the molecule, the bond type and polarity will be the same. • If the molecule consists of more than 2 atoms, you must consider the shape. To determine its polarity, consider the following: – Lone pairs on central atom • If so… it is polar ...
... • If there is only one bond in the molecule, the bond type and polarity will be the same. • If the molecule consists of more than 2 atoms, you must consider the shape. To determine its polarity, consider the following: – Lone pairs on central atom • If so… it is polar ...
The study of biology can help you better understand
... How many energy sublevels are contained in each of the hydrogen atom’s first three energy levels? (5.2) ...
... How many energy sublevels are contained in each of the hydrogen atom’s first three energy levels? (5.2) ...
Packet #6- Ionic and Covalent Bonding
... Note that molecules can have a double covalent bond - meaning they have two shared pairs of electrons - or a triple covalent bond - three shared pairs of electrons. A double covalent bond is shown by a double line, and a triple bond by a triple line. A molecule of oxygen (O2) consists of two oxygen ...
... Note that molecules can have a double covalent bond - meaning they have two shared pairs of electrons - or a triple covalent bond - three shared pairs of electrons. A double covalent bond is shown by a double line, and a triple bond by a triple line. A molecule of oxygen (O2) consists of two oxygen ...
Lecture notes chapter 4
... Natural states of the elements: some elements consist of single atoms and they are found in an isolated state (for example, Ar and He). They are called monatomic elements. Some elements are diatomic and they consist of two atoms. The atoms of these elements have special affinities for each other and ...
... Natural states of the elements: some elements consist of single atoms and they are found in an isolated state (for example, Ar and He). They are called monatomic elements. Some elements are diatomic and they consist of two atoms. The atoms of these elements have special affinities for each other and ...
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electrostatic force of attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are ""strong bonds"" such as covalent or ionic bonds and ""weak bonds"" such as Dipole-dipole interaction, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.Since opposite charges attract via a simple electromagnetic force, the negatively charged electrons that are orbiting the nucleus and the positively charged protons in the nucleus attract each other. An electron positioned between two nuclei will be attracted to both of them, and the nuclei will be attracted toward electrons in this position. This attraction constitutes the chemical bond. Due to the matter wave nature of electrons and their smaller mass, they must occupy a much larger amount of volume compared with the nuclei, and this volume occupied by the electrons keeps the atomic nuclei relatively far apart, as compared with the size of the nuclei themselves. This phenomenon limits the distance between nuclei and atoms in a bond.In general, strong chemical bonding is associated with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules, crystals, metals and diatomic gases—indeed most of the physical environment around us—are held together by chemical bonds, which dictate the structure and the bulk properties of matter.All bonds can be explained by quantum theory, but, in practice, simplification rules allow chemists to predict the strength, directionality, and polarity of bonds. The octet rule and VSEPR theory are two examples. More sophisticated theories are valence bond theory which includes orbital hybridization and resonance, and the linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method which includes ligand field theory. Electrostatics are used to describe bond polarities and the effects they have on chemical substances.