Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 10 Periodic Trends Why? The
... Owing to their relatively low ionization energies, metals tend to form cations, and when they combine with nonmetals they form ionic substances. For example, when metals combine with oxygen they form ionic oxides. 4 Fe(s) + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3(s) Metal oxides tend to dissolve in water to form hydroxide i ...
... Owing to their relatively low ionization energies, metals tend to form cations, and when they combine with nonmetals they form ionic substances. For example, when metals combine with oxygen they form ionic oxides. 4 Fe(s) + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3(s) Metal oxides tend to dissolve in water to form hydroxide i ...
Sample
... Ethene Benzene 1- Position of (π) bond electrons: 2- Shape: 28- Write indicator dissociation constant expression KIn for an acidic indicator HIn? H+(aq) + In-(aq) ...
... Ethene Benzene 1- Position of (π) bond electrons: 2- Shape: 28- Write indicator dissociation constant expression KIn for an acidic indicator HIn? H+(aq) + In-(aq) ...
PART 2 – CHEMISTRY
... Let's look at why and how elements combine to form the molecules of every substance around us. If there are 2 electrons in a single shell surrounding the nucleus or 8 electrons in the outermost shell in the case where the atom has more than one shell, then the atom is said to be stable. This means t ...
... Let's look at why and how elements combine to form the molecules of every substance around us. If there are 2 electrons in a single shell surrounding the nucleus or 8 electrons in the outermost shell in the case where the atom has more than one shell, then the atom is said to be stable. This means t ...
COUNTING ATOMS
... represents the number of each atom present. • Example: • H2 + O2 H20 • N2 + H2 NH3 ...
... represents the number of each atom present. • Example: • H2 + O2 H20 • N2 + H2 NH3 ...
Term 1 and 2 Powerpoints
... deteriorated, and what percent of our atmosphere is made up harmful pollutants? Well when fossil fuels are burned, or maybe even things like wood or who knows, scientists most likely calculate the molecules given off so they can come up with these statistics. Well maybe they deal with moles or liter ...
... deteriorated, and what percent of our atmosphere is made up harmful pollutants? Well when fossil fuels are burned, or maybe even things like wood or who knows, scientists most likely calculate the molecules given off so they can come up with these statistics. Well maybe they deal with moles or liter ...
CHM100PracticeExam2
... Do not begin the exam until you have been instructed to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. There are 50 multiple choice questions. You must use a number 2 pencil. You may use a scientific calculator. Make sure that you have written your name legibly on the scantron form. Circle bubbl ...
... Do not begin the exam until you have been instructed to do so. You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. There are 50 multiple choice questions. You must use a number 2 pencil. You may use a scientific calculator. Make sure that you have written your name legibly on the scantron form. Circle bubbl ...
Flexbook - Ions and Ion Formation
... An atom’s attraction for adding electrons is related to how close the new electron can approach the nucleus of the atom. In the case of fluorine (electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p5 ), the first energy level is full but the second one is not full. This allows an approaching electron to penetrate the ...
... An atom’s attraction for adding electrons is related to how close the new electron can approach the nucleus of the atom. In the case of fluorine (electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p5 ), the first energy level is full but the second one is not full. This allows an approaching electron to penetrate the ...
chapter 2
... a. Alkali Metals – most reactive metals, react violently with water b. Alkaline Earth Metals – reactive metals but less so than alkali c. Halogens – most reactive non-metals, most are poisonous gases d. Noble Gases – do not react 3. If a noble gas could form a +1 ion, which of the noble gases would ...
... a. Alkali Metals – most reactive metals, react violently with water b. Alkaline Earth Metals – reactive metals but less so than alkali c. Halogens – most reactive non-metals, most are poisonous gases d. Noble Gases – do not react 3. If a noble gas could form a +1 ion, which of the noble gases would ...
1001_3rd Exam_1001214
... C) Within a given sublevel, each orbital is usually occupied by a single electron before any orbital has two electrons. D) When a metallic element unites with a nonmetallic element, electrons are lost by atoms of the metal and gained by atoms of the nonmetals. E) Ba2+ is smaller than Ba+ . Answer: B ...
... C) Within a given sublevel, each orbital is usually occupied by a single electron before any orbital has two electrons. D) When a metallic element unites with a nonmetallic element, electrons are lost by atoms of the metal and gained by atoms of the nonmetals. E) Ba2+ is smaller than Ba+ . Answer: B ...
Atoms in Molecules
... of matter, while at the same time specifically warning against the use of the wave function in this regard, because of its unphysical nature.1 Chemistry is presently in transition between the methods used to glean chemical insight from a calculated wave function. Orbital models relate atomic and bon ...
... of matter, while at the same time specifically warning against the use of the wave function in this regard, because of its unphysical nature.1 Chemistry is presently in transition between the methods used to glean chemical insight from a calculated wave function. Orbital models relate atomic and bon ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... d. oxygen molecule, how many unshared electron pairs 2. Ionic compounds generally form: surround the carbon? a. Liquids a. 2 b. Gases b. 0 c. Crystals c. 8 d. molecules d. 4 3. In metallic bonding, the valence electrons of all 12. In nonpolar covalent bonds, valence electrons are atoms are shared in ...
... d. oxygen molecule, how many unshared electron pairs 2. Ionic compounds generally form: surround the carbon? a. Liquids a. 2 b. Gases b. 0 c. Crystals c. 8 d. molecules d. 4 3. In metallic bonding, the valence electrons of all 12. In nonpolar covalent bonds, valence electrons are atoms are shared in ...
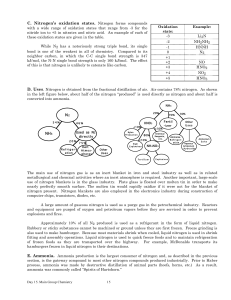
Nitrogen`s oxidation states
... which each P atom is bonded to three other P atoms. The sp3 lone pair is directed outwards from each atom. White phosphorus is extremely reactive. It catches fire immediately in air and is usually stored under water in which it is insoluble. White phosphorus must never be directly handled because it ...
... which each P atom is bonded to three other P atoms. The sp3 lone pair is directed outwards from each atom. White phosphorus is extremely reactive. It catches fire immediately in air and is usually stored under water in which it is insoluble. White phosphorus must never be directly handled because it ...
atomic number - geraldinescience
... elements on the periodic table are arranged in columns, which are called groups. • An atom’s chemical properties are largely determined by the number of the outermost electrons in an atom’s electron cloud. These electrons are called valence electrons. ...
... elements on the periodic table are arranged in columns, which are called groups. • An atom’s chemical properties are largely determined by the number of the outermost electrons in an atom’s electron cloud. These electrons are called valence electrons. ...
Chemical bonding and structure
... Remember that in forming the ionic compound there is no net loss or gain of electrons, and so the ionic compound, like the atoms that formed it, must be electrically neutral. Writing the formula for the ionic compound therefore involves balancing the total number of positive and negative charges, ta ...
... Remember that in forming the ionic compound there is no net loss or gain of electrons, and so the ionic compound, like the atoms that formed it, must be electrically neutral. Writing the formula for the ionic compound therefore involves balancing the total number of positive and negative charges, ta ...
General and Organic Chemistry Review Primer
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
name chemistry final review
... Bent, 117º (Trigonal Planar) Trigonal Pyramid, Bent 104.5 º (Tetrahedron) See-saw, T-Shaped, Linear (Trigonal Bipyramid) ...
... Bent, 117º (Trigonal Planar) Trigonal Pyramid, Bent 104.5 º (Tetrahedron) See-saw, T-Shaped, Linear (Trigonal Bipyramid) ...
View
... Disciplinary Core Ideas PS1.A: Structure and Properties of Matter A stable molecule has less energy than the same set of atoms separated; one must provide at least this energy in order to take the molecule apart. PS1.B: Chemical Reactions Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energ ...
... Disciplinary Core Ideas PS1.A: Structure and Properties of Matter A stable molecule has less energy than the same set of atoms separated; one must provide at least this energy in order to take the molecule apart. PS1.B: Chemical Reactions Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energ ...
atom - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... Dalton’s law of multiple proportions The law of multiple proportions states that when two elements combine to give more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with the fixed mass of the other are in a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... Dalton’s law of multiple proportions The law of multiple proportions states that when two elements combine to give more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with the fixed mass of the other are in a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
Slide 1
... never found as free elements in nature. They are always bonded with another element. ...
... never found as free elements in nature. They are always bonded with another element. ...
Chapter 2
... Energy is… • The ability to change or move matter. • Energy can not be created or destroyed (The law of conservation of energy) • Energy is either used to do work on the molecules, moving, them out of the crystal lattice at the melting point, or moving them farther from each other into gas state a ...
... Energy is… • The ability to change or move matter. • Energy can not be created or destroyed (The law of conservation of energy) • Energy is either used to do work on the molecules, moving, them out of the crystal lattice at the melting point, or moving them farther from each other into gas state a ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons, Neutrons, Electrons Proton
... 7. Aluminum: valence = _____ for a full/empty orbital __________________charge= _______ 8. Beryllium: valence = _____ for a full/empty orbital __________________charge= _______ ...
... 7. Aluminum: valence = _____ for a full/empty orbital __________________charge= _______ 8. Beryllium: valence = _____ for a full/empty orbital __________________charge= _______ ...
Molecular geometry
... Valence bond theory (VB): An advanced model of chemical bonding in which electrons reside in quantum-mechanical orbitals localized on individual atoms that are a hybridized blend of standard atomic orbitals; chemical bonds result from an overlap of these orbitals. Molecular orbital theory (MO): ...
... Valence bond theory (VB): An advanced model of chemical bonding in which electrons reside in quantum-mechanical orbitals localized on individual atoms that are a hybridized blend of standard atomic orbitals; chemical bonds result from an overlap of these orbitals. Molecular orbital theory (MO): ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons,
... now has a charge. For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a ...
... now has a charge. For example, if a hydrogen atom has one proton (+) and one electron (-‐) the two charges cancel each other out. When the electron is lost the hydrogen atom is only a ...
Thermochemistry only Sp 12 unit I
... reaction in which one mole of the compound in its standard state is formed from its elements in their standard states. For example, C(s) + H2 (g) CH4 (g) ΔHf°= - 74.9 kj/mole The above elements are in their standard states. ΔHf° are important since they can be used to calculate heats of reaction t ...
... reaction in which one mole of the compound in its standard state is formed from its elements in their standard states. For example, C(s) + H2 (g) CH4 (g) ΔHf°= - 74.9 kj/mole The above elements are in their standard states. ΔHf° are important since they can be used to calculate heats of reaction t ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.