Chapter 9 - HCC Learning Web
... 60. Nitrous oxide, N2O, is sometimes called "laughing gas". What is the formal charge on the central nitrogen atom in the best Lewis structure for nitrous oxide? (The atom connectivity is N-N-O.) A. -2 B. -1 C. 0 D. +1 E. +2 62. In the Lewis structure of the iodate ion, IO3-, that satisfies the octe ...
... 60. Nitrous oxide, N2O, is sometimes called "laughing gas". What is the formal charge on the central nitrogen atom in the best Lewis structure for nitrous oxide? (The atom connectivity is N-N-O.) A. -2 B. -1 C. 0 D. +1 E. +2 62. In the Lewis structure of the iodate ion, IO3-, that satisfies the octe ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... • Elements become more stable as they gain more valence electrons. • As a result, atoms will gain, lose or share electrons to form compounds so that they have 8 valence electrons or a full shell. • This is called the Octet Rule. However there are many exceptions, but this is an easy way to predict c ...
... • Elements become more stable as they gain more valence electrons. • As a result, atoms will gain, lose or share electrons to form compounds so that they have 8 valence electrons or a full shell. • This is called the Octet Rule. However there are many exceptions, but this is an easy way to predict c ...
111 Exam II Outline
... The Born- Haber cycle uses the law of Hess to determine the Lattice Energy. The lattice energy is the enthalphy change, ∆H, associated when gaseous cations and anions from a crystal: Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s) ∆H = - 788KJ Since heat is always evolved in these processes, all lattice energies have a n ...
... The Born- Haber cycle uses the law of Hess to determine the Lattice Energy. The lattice energy is the enthalphy change, ∆H, associated when gaseous cations and anions from a crystal: Na+(g) + Cl-(g) NaCl(s) ∆H = - 788KJ Since heat is always evolved in these processes, all lattice energies have a n ...
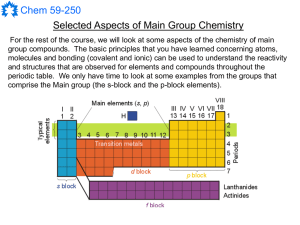
Main Group Notes 1
... compounds is that they tend to form clusters under conditions where no other sources of electrons are available. The pyrolysis of B2H6 produces a variety of clusters and evolves H2 gas. Once formed, many of these polyboranes are stable compounds and many other elements can be placed into the skeleto ...
... compounds is that they tend to form clusters under conditions where no other sources of electrons are available. The pyrolysis of B2H6 produces a variety of clusters and evolves H2 gas. Once formed, many of these polyboranes are stable compounds and many other elements can be placed into the skeleto ...
Part 2. The Quantum Particle in a Box
... electrons alone, they would ultimately occupy their equilibrium distribution. As you might imagine, at equilibrium, the lowest energy states are filled first, and then the next lowest, and so on. At T = 0K, state filling proceeds this way until there are no electrons left. Thus, at T = 0K, the distr ...
... electrons alone, they would ultimately occupy their equilibrium distribution. As you might imagine, at equilibrium, the lowest energy states are filled first, and then the next lowest, and so on. At T = 0K, state filling proceeds this way until there are no electrons left. Thus, at T = 0K, the distr ...
Chemical Calculations, Chemical Equations
... Atoms forming negative ions always generate one, predictable kind (gaining all electrons to bring the s&p orbital sum to 8). However, some atoms can form more than one positively charged ion, having the ability to lose different amount of electrons each time. This behavior is difficult to predict, a ...
... Atoms forming negative ions always generate one, predictable kind (gaining all electrons to bring the s&p orbital sum to 8). However, some atoms can form more than one positively charged ion, having the ability to lose different amount of electrons each time. This behavior is difficult to predict, a ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... 2.3 × 1014 hertz. Using your graph, estimate the energy associated with this spectral line. [1] 68 Explain, in terms of subatomic particles and energy states, why light is emitted by the hydrogen gas. [1] 69 Identify one condition not mentioned in the passage, under which hydrogen gas behaves most l ...
... 2.3 × 1014 hertz. Using your graph, estimate the energy associated with this spectral line. [1] 68 Explain, in terms of subatomic particles and energy states, why light is emitted by the hydrogen gas. [1] 69 Identify one condition not mentioned in the passage, under which hydrogen gas behaves most l ...
File
... into reactants in order for their bonds to break, that minium enegy is called activation energy. The Relationship Between Kinetic (K.E.) and Potential Energy (P.E) Potential energy is defined as energy of position. Energy is conserved in chemical and physical changes. That means kinetic energy (ener ...
... into reactants in order for their bonds to break, that minium enegy is called activation energy. The Relationship Between Kinetic (K.E.) and Potential Energy (P.E) Potential energy is defined as energy of position. Energy is conserved in chemical and physical changes. That means kinetic energy (ener ...
File
... 20. Element whose atoms lose electrons in chemical reactions to become positive ions. 21. Groups 3-12 on the periodic table. 22. Scientist who performed the gold foil experiment, and concluded that an atom must be composed of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively-charged nucleus. 23. An ...
... 20. Element whose atoms lose electrons in chemical reactions to become positive ions. 21. Groups 3-12 on the periodic table. 22. Scientist who performed the gold foil experiment, and concluded that an atom must be composed of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively-charged nucleus. 23. An ...
organic chemistry - Peoria Public Schools
... It is important to note that alkenes also easily combust and undergo both complete and incomplete combustion. Alkanes undergo addition reaction that means that atoms are added to the molecule at either side of the double bond so any addition reaction increases the number of atoms in the molecule. Du ...
... It is important to note that alkenes also easily combust and undergo both complete and incomplete combustion. Alkanes undergo addition reaction that means that atoms are added to the molecule at either side of the double bond so any addition reaction increases the number of atoms in the molecule. Du ...
FYBSc Revised Syllabus
... 1.1 Allotrophy of carbon: Structure and properties of diamond, graphite, fullerenes, carbon nanotubes. 1.2 Hybridization: sp3, sp2, sp hybridization of carbon and nitrogen; sp3 and sp2 hybridizations of oxygen in Organic compounds. 1.3 Overlap of atomic orbitals; Overlaps of atomic orbitals to form ...
... 1.1 Allotrophy of carbon: Structure and properties of diamond, graphite, fullerenes, carbon nanotubes. 1.2 Hybridization: sp3, sp2, sp hybridization of carbon and nitrogen; sp3 and sp2 hybridizations of oxygen in Organic compounds. 1.3 Overlap of atomic orbitals; Overlaps of atomic orbitals to form ...
Chemistry I Exams and Answer Keys 2015 Season
... A pure metal is made up of atoms that are held together by all valence electrons that are not held exclusively by any particular atoms, but move freely around them. This statement is best described as A. a correct definition of a chemical term or expression, either in terms of experimental behavior ...
... A pure metal is made up of atoms that are held together by all valence electrons that are not held exclusively by any particular atoms, but move freely around them. This statement is best described as A. a correct definition of a chemical term or expression, either in terms of experimental behavior ...
Topic 2
... Atomic Theory of Matter – An element is a substance whose atoms all have the same atomic number (Z). The #protons defines the identity of an atom and can be found on the periodic table (large number in top of element box). – The neutron is a nuclear particle having a mass almost identical to that o ...
... Atomic Theory of Matter – An element is a substance whose atoms all have the same atomic number (Z). The #protons defines the identity of an atom and can be found on the periodic table (large number in top of element box). – The neutron is a nuclear particle having a mass almost identical to that o ...
The Mole - Rothschild Science
... carbon dioxide. One mole of calcium carbonate reacts to form one mole of calcium oxide and one mole of carbon dioxide. ...
... carbon dioxide. One mole of calcium carbonate reacts to form one mole of calcium oxide and one mole of carbon dioxide. ...
Chemical Composition
... • If I want to know how many O2 molecules I will need or how many CO2 molecules I can make, I will need to know how many C atoms are in the sample of carbon I am starting with • Dalton used the percentages of elements in compounds and the chemical formulas to deduce the relative masses of atoms • Un ...
... • If I want to know how many O2 molecules I will need or how many CO2 molecules I can make, I will need to know how many C atoms are in the sample of carbon I am starting with • Dalton used the percentages of elements in compounds and the chemical formulas to deduce the relative masses of atoms • Un ...
Summer - Honors Chemistry
... Compounds are composed of two or more different elements chemically bonded in a very definite ratio (both by number of atoms and by mass of atoms). Each compound has at two or more element symbols with subscripts indicating the number of each type of atom (e.g. C6H12O6). Compounds can be decomposed ...
... Compounds are composed of two or more different elements chemically bonded in a very definite ratio (both by number of atoms and by mass of atoms). Each compound has at two or more element symbols with subscripts indicating the number of each type of atom (e.g. C6H12O6). Compounds can be decomposed ...
1A - The changing atom History of the atom • The model of the atom
... As the atom has the same number of protons and electrons it will have the same chemical properties. They are all hydrogen atoms because they all have the same number of protons Hydrogen can be used as an example:- ...
... As the atom has the same number of protons and electrons it will have the same chemical properties. They are all hydrogen atoms because they all have the same number of protons Hydrogen can be used as an example:- ...
Review # 3
... A gas at STP which contains 6.02 x 1023 atoms and forms diatomic molecules will occupy a. 11.2 L b. 22.4 L c. 33.6 L d. 67.2 L ...
... A gas at STP which contains 6.02 x 1023 atoms and forms diatomic molecules will occupy a. 11.2 L b. 22.4 L c. 33.6 L d. 67.2 L ...
Diodes and Transistors HOW Theq Work
... "Valence" means the number of bonds the atom forms. For instance, the valence of silicon atoms in a crystal is four, because every atom forms four bonds. As mentioned previously, the electrons in the valence shell are called the atom's valence electrons. The rest of the atom, consisting of filled sh ...
... "Valence" means the number of bonds the atom forms. For instance, the valence of silicon atoms in a crystal is four, because every atom forms four bonds. As mentioned previously, the electrons in the valence shell are called the atom's valence electrons. The rest of the atom, consisting of filled sh ...
Gas-Phase Basicity of (CH3)3N
... +1) and the midpoint of the two carboxylate oxygen atoms (q2 ) -1). These values, subtracted from the GB of benzoate (solid line), along with the calculated and measured GB values for the three TMAB isomers and betaine are shown in Figure 2. This extremely simplistic model provides a rough estimate ...
... +1) and the midpoint of the two carboxylate oxygen atoms (q2 ) -1). These values, subtracted from the GB of benzoate (solid line), along with the calculated and measured GB values for the three TMAB isomers and betaine are shown in Figure 2. This extremely simplistic model provides a rough estimate ...
States of Matter
... You can think of a simple liquid such as argon or methane as a collection of loosely-packed marbles that can assume various shapes. Although the overall arrangement of the individual molecular units is entirely random, there is a certain amount of short-range order: the presence of one molecule at a ...
... You can think of a simple liquid such as argon or methane as a collection of loosely-packed marbles that can assume various shapes. Although the overall arrangement of the individual molecular units is entirely random, there is a certain amount of short-range order: the presence of one molecule at a ...
Scientific Measurement
... the time. _____40. I can state the conditions under which real gases behave most like ideal ...
... the time. _____40. I can state the conditions under which real gases behave most like ideal ...
Chapter 3
... Nitrous oxide (N2O) is also called “laughing gas.” It can be prepared by the thermal decomposition of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3). The other product is H2O. The balanced equation for this reaction is: NH4NO3 N2O + 2H2O How many grams of N2O are formed if 0.46 mole of NH4NO3 is used in the reaction? A) ...
... Nitrous oxide (N2O) is also called “laughing gas.” It can be prepared by the thermal decomposition of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3). The other product is H2O. The balanced equation for this reaction is: NH4NO3 N2O + 2H2O How many grams of N2O are formed if 0.46 mole of NH4NO3 is used in the reaction? A) ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.