4.1Atoms and Isotopes
... charge is written in the top right if there is a charge 32S2e.g. 16 How many protons, electrons, and neutrons? 16 protons, 16 neutrons, 18 electrons ...
... charge is written in the top right if there is a charge 32S2e.g. 16 How many protons, electrons, and neutrons? 16 protons, 16 neutrons, 18 electrons ...
CHEMISTRY
... Some atoms achieve a ______________ electron structure by sharing electrons with another element. The mutual attraction that each atom has for the shared electrons is called a ___________________. One covalent bond consists of 2 shared electrons. Generally, covalent bonds exist between _____________ ...
... Some atoms achieve a ______________ electron structure by sharing electrons with another element. The mutual attraction that each atom has for the shared electrons is called a ___________________. One covalent bond consists of 2 shared electrons. Generally, covalent bonds exist between _____________ ...
H3AsO4 + 3 I- + 2 H3O+ H3AsO3 + I3- + H2O
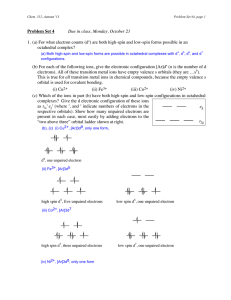
... the orbital in space. For a given value of l, ml can have integral values ranging from –l to +l. The spin quantum number ms defines the orientation of the electron's magnetic field and has two possible values +½ and –½. The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have ...
... the orbital in space. For a given value of l, ml can have integral values ranging from –l to +l. The spin quantum number ms defines the orientation of the electron's magnetic field and has two possible values +½ and –½. The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have ...
chemistry in the 8th grade
... If a liquid is heated, the temperature will rise. The particles of the liquid will move faster as the temperature rises. At the boiling point, the particles gain enough energy so they can move independently of each other, and the liquid is converted to a gas. Since the particles in a gas can move i ...
... If a liquid is heated, the temperature will rise. The particles of the liquid will move faster as the temperature rises. At the boiling point, the particles gain enough energy so they can move independently of each other, and the liquid is converted to a gas. Since the particles in a gas can move i ...
Unit A Review Questions
... The zinc electrode is gaining mass because the copper ions are coming out of the solution and are being reduced by the zinc metal being oxidized. This would also account for the colour change in the copper nitrate solution. As the copper ions come out of the solution, the solution becomes a fainter ...
... The zinc electrode is gaining mass because the copper ions are coming out of the solution and are being reduced by the zinc metal being oxidized. This would also account for the colour change in the copper nitrate solution. As the copper ions come out of the solution, the solution becomes a fainter ...
Your views are welcomed upon the theme of
... arrangements and are not commonly found. This same type of pattern extends (with exceptions) to molecules. So in NH3, for example, all of the atoms are said to have noble gas electronic structures. Of course, the analogy with the noble gas atoms has to be somewhat stretched. O2- has an analogous ele ...
... arrangements and are not commonly found. This same type of pattern extends (with exceptions) to molecules. So in NH3, for example, all of the atoms are said to have noble gas electronic structures. Of course, the analogy with the noble gas atoms has to be somewhat stretched. O2- has an analogous ele ...
Chapter 07 and 08 Chemical Bonding and Molecular
... • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell which is LOWER IN E ...
... • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell which is LOWER IN E ...
Basic Introduction of Computational Chemistry
... Not including: Quantum chromodynamics Calculations on Jellium Continuum models Computational fluid dynamics Data mining Rule based derivations ...
... Not including: Quantum chromodynamics Calculations on Jellium Continuum models Computational fluid dynamics Data mining Rule based derivations ...
1st mid unit test formative (pre-test)
... The horizontal rows of the periodic table are called periods. The horizontal columns are called families or groups. Metals are on the left and in the center of the table. Non-metals are located on the right-hand side of the table. Metals are separated from non-metals by a staircase of elements calle ...
... The horizontal rows of the periodic table are called periods. The horizontal columns are called families or groups. Metals are on the left and in the center of the table. Non-metals are located on the right-hand side of the table. Metals are separated from non-metals by a staircase of elements calle ...
1st mid unit test formative (pre-test)
... The horizontal rows of the periodic table are called periods. The horizontal columns are called families or groups. Metals are on the left and in the center of the table. Non-metals are located on the right-hand side of the table. Metals are separated from non-metals by a staircase of elements calle ...
... The horizontal rows of the periodic table are called periods. The horizontal columns are called families or groups. Metals are on the left and in the center of the table. Non-metals are located on the right-hand side of the table. Metals are separated from non-metals by a staircase of elements calle ...
Hints for Names and Formulas (Ch. 4 in Zumdahl Chemistry)
... ● only 10 elements exist as molecules when free in nature: H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2, At2, P4, S8 ● these 10 elements may have different subscripts when in combination with other elements ◘ examples: H2O, CO, CCl4, CaBr2 (ionic), Na2O (ionic) ◘ reaction: 4 Na(s) + O2 (g) → 2 Na2O(s) (3) molecules ...
... ● only 10 elements exist as molecules when free in nature: H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2, At2, P4, S8 ● these 10 elements may have different subscripts when in combination with other elements ◘ examples: H2O, CO, CCl4, CaBr2 (ionic), Na2O (ionic) ◘ reaction: 4 Na(s) + O2 (g) → 2 Na2O(s) (3) molecules ...
Molecular Modeling Activity for Carbohydrates
... the hydroxyl group (-OH) on carbon-4 are reversed. Galactose is not usually found free in nature in large quantities but, rather, combines with glucose to form a disaccharide called lactose which is present in milk and other dairy products. ...
... the hydroxyl group (-OH) on carbon-4 are reversed. Galactose is not usually found free in nature in large quantities but, rather, combines with glucose to form a disaccharide called lactose which is present in milk and other dairy products. ...
Unit 1 Notes
... 2) Compounds – substances that contain atoms of more than one element combined in a definite, fixed proportion. Compounds are represented by chemical formulas that contain two or more different symbols. e.g. Water’s chemical formula is H2O – (2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom make 1 water molecul ...
... 2) Compounds – substances that contain atoms of more than one element combined in a definite, fixed proportion. Compounds are represented by chemical formulas that contain two or more different symbols. e.g. Water’s chemical formula is H2O – (2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom make 1 water molecul ...
Atoms and Materials for Engineering
... entry. We only know that they are second-level p orbitals (2p). The number 4 after the p indicates that there are 4 electrons in 2p orbitals. It is expected that we already know there are a maximum of three p orbitals at level 2, two contain Figure 5 oxygen one electron each and the other has 2 elec ...
... entry. We only know that they are second-level p orbitals (2p). The number 4 after the p indicates that there are 4 electrons in 2p orbitals. It is expected that we already know there are a maximum of three p orbitals at level 2, two contain Figure 5 oxygen one electron each and the other has 2 elec ...
Chapter 10 - Chemical Reactions
... empirical formula : simplest whole number ratio of elements in a compound -general description of how to assemble the compound ionic-exists as separate ions -empirical formula is the right description -simple mixture of ions Na+ and Cl- ions molecular (covalent)-exists as a particular bonded entity ...
... empirical formula : simplest whole number ratio of elements in a compound -general description of how to assemble the compound ionic-exists as separate ions -empirical formula is the right description -simple mixture of ions Na+ and Cl- ions molecular (covalent)-exists as a particular bonded entity ...
atomic number
... Elements are any single thing found in the periodic table (often called the periodic table of elements) Examples of elements: Au, Gold; S, Sulfur; Pb, Lead; Na, Sodium… In 1803, Dalton proposed an atomic theory that is still the basis for many of our theories about the atom. ...
... Elements are any single thing found in the periodic table (often called the periodic table of elements) Examples of elements: Au, Gold; S, Sulfur; Pb, Lead; Na, Sodium… In 1803, Dalton proposed an atomic theory that is still the basis for many of our theories about the atom. ...
Chem312 Au03 Problem Set 4
... because a photon can be absorbed by promotion of one electron from the t2g set of orbitals to the t2g eg set. In a diagram like the one at right, add ground state excited state electrons to represent the ground state and the lowest energy excited state. When you put the electrons in, you should foll ...
... because a photon can be absorbed by promotion of one electron from the t2g set of orbitals to the t2g eg set. In a diagram like the one at right, add ground state excited state electrons to represent the ground state and the lowest energy excited state. When you put the electrons in, you should foll ...
Chemistry Final Exam Practice Test
... 43. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom can be calculated by ____. a) adding together the number of electrons and protons b) subtracting the number of electrons from the number of protons c) subtracting the atomic number from the mass number d) adding the mass number to the number of e ...
... 43. The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom can be calculated by ____. a) adding together the number of electrons and protons b) subtracting the number of electrons from the number of protons c) subtracting the atomic number from the mass number d) adding the mass number to the number of e ...
CHEMISTRY FALL FINAL PRACTICE 2016
... a. Get the atomic number _________ b. Identify the element __________________ c. Find the mass number of the most common isotope of an element _________ d. Get how many neutrons the most common isotope has _________ e. How many valence electrons an element has _________ f. What is its charge/oxidati ...
... a. Get the atomic number _________ b. Identify the element __________________ c. Find the mass number of the most common isotope of an element _________ d. Get how many neutrons the most common isotope has _________ e. How many valence electrons an element has _________ f. What is its charge/oxidati ...
Chemistry exam review
... 2.1.5 Explain the relationships among pressure, temperature, volume, and quantity of gas, both quantitative and qualitative. 1. What happens to the pressure of a constant mass of gas at constant temperature when the volume is doubled? a. The pressure is doubled. b. The pressure remains the same. c. ...
... 2.1.5 Explain the relationships among pressure, temperature, volume, and quantity of gas, both quantitative and qualitative. 1. What happens to the pressure of a constant mass of gas at constant temperature when the volume is doubled? a. The pressure is doubled. b. The pressure remains the same. c. ...
104 Homework Packet - Rogue Community College
... According to Le Chatelier’s Principle, adding reactants (or removing products) drives the equilibrium to the __________, adding products (or removing reactants) drives the equilibrium to the __________, increasing temperature favors the ___________________ reaction, decreasing temperature favors the ...
... According to Le Chatelier’s Principle, adding reactants (or removing products) drives the equilibrium to the __________, adding products (or removing reactants) drives the equilibrium to the __________, increasing temperature favors the ___________________ reaction, decreasing temperature favors the ...
Chemistry at Karlsruhe 1860
... • Butyl Alcohol and ether both same formula but different properties • Butyric acid and hydroxyethylene both C2H2O according to Liebig – One an acidic liquid and one a volatile alcohol ...
... • Butyl Alcohol and ether both same formula but different properties • Butyric acid and hydroxyethylene both C2H2O according to Liebig – One an acidic liquid and one a volatile alcohol ...
Investigating Chemistry - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... molecular and has covalent bonds. • When two elements from the upper right corner of the periodic table combine, we use a different system for naming these covalent compounds. • This results in discrete molecules with directional bonds. For example, H2O. • It can also result in an infinite network o ...
... molecular and has covalent bonds. • When two elements from the upper right corner of the periodic table combine, we use a different system for naming these covalent compounds. • This results in discrete molecules with directional bonds. For example, H2O. • It can also result in an infinite network o ...
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance or mesomerism is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis formula. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several contributing structures (also called resonance structures or canonical forms).Each contributing structure can be represented by a Lewis structure, with only an integer number of covalent bonds between each pair of atoms within the structure. Several Lewis structures are used collectively to describe the actual molecular structure, which is an approximate intermediate between the canonical forms called a resonance hybrid. Contributing structures differ only in the position of electrons, not in the position of nuclei.Electron delocalization lowers the potential energy of the substance and thus makes it more stable than any of the contributing structures. The difference between the potential energy of the actual structure and that of the contributing structure with the lowest potential energy is called the resonance energy or delocalization energy.Resonance is distinguished from tautomerism and conformational isomerism, which involve the formation of isomers, thus the rearrangement of the nuclear positions.