Capacitor Self
... voltage sources with a resistance of zero and will be instructed to replace the source with a short). Calculate the current(s) and/or voltage(s) with the one remaining source in the circuit for the resistor(s) in which you have an interest. Record the amount and direction of current and/or the magni ...
... voltage sources with a resistance of zero and will be instructed to replace the source with a short). Calculate the current(s) and/or voltage(s) with the one remaining source in the circuit for the resistor(s) in which you have an interest. Record the amount and direction of current and/or the magni ...
What is a Thyristor Surge Protective Device?
... has subsided. Figure 1 illustrates performance of the TSPD as the transient drives the device first to V(BO), crowbar to on-state, then on to restoration. Minimum holding current values typically range from 50mA to 250mA @ 25oC (depending on device surge current rating) and decrease by 60% at 100oC, ...
... has subsided. Figure 1 illustrates performance of the TSPD as the transient drives the device first to V(BO), crowbar to on-state, then on to restoration. Minimum holding current values typically range from 50mA to 250mA @ 25oC (depending on device surge current rating) and decrease by 60% at 100oC, ...
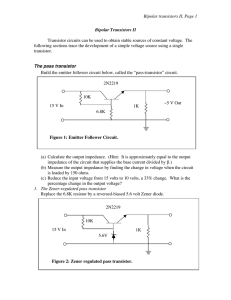
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... “NC” means no connections to the center tap on the transformer. Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with tw ...
... “NC” means no connections to the center tap on the transformer. Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with tw ...
Experiment 4: Sensor Bridge Circuits I. Introduction. From Voltage
... The main advantage of the 3-wire configuration is that it allows the resistance in all the three leads that are included with the sensor to be surrounded at the same temperature environment. Temperature affects the resistance of the lead wires, and these effects become more significant when the sens ...
... The main advantage of the 3-wire configuration is that it allows the resistance in all the three leads that are included with the sensor to be surrounded at the same temperature environment. Temperature affects the resistance of the lead wires, and these effects become more significant when the sens ...
The Comparator
... A voltage divider is a circuit that produces an output voltage (Vout) that is a fraction of its input Vout is the voltage across the R2 Worked out by the resistor ratio ...
... A voltage divider is a circuit that produces an output voltage (Vout) that is a fraction of its input Vout is the voltage across the R2 Worked out by the resistor ratio ...
Series and Parallel Circuits 2 - Instructor Outline
... Exploration stage: 55 minutes – Group Lab-Work The students measure current and voltage for a circuit that combines series and parallel light bulbs. They observe where the current flows based on what happens when they unscrew various bulbs. The also make observations regarding bulb brightness and re ...
... Exploration stage: 55 minutes – Group Lab-Work The students measure current and voltage for a circuit that combines series and parallel light bulbs. They observe where the current flows based on what happens when they unscrew various bulbs. The also make observations regarding bulb brightness and re ...
Self-Calibration and Digital Trimming of Successive Approximation
... correcting static mismatches in Capacitive Digital-to-Analog Converter (CDAC) used in Successive Approximation Register Analog to Digital Converters (SAR-ADCs) is proposed. The algorithm uses a dynamic error correction (DEC) capacitor to cancel the static errors occurring in each capacitor of the ar ...
... correcting static mismatches in Capacitive Digital-to-Analog Converter (CDAC) used in Successive Approximation Register Analog to Digital Converters (SAR-ADCs) is proposed. The algorithm uses a dynamic error correction (DEC) capacitor to cancel the static errors occurring in each capacitor of the ar ...
14.1 Series Circuits
... •I=V/R • You can calculate current (I) if you know voltage and resistance ...
... •I=V/R • You can calculate current (I) if you know voltage and resistance ...
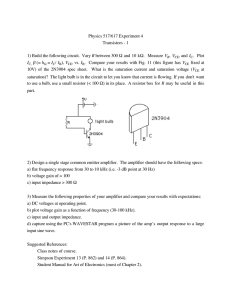
Physics 517/617 Experiment 4 Transistors - 1 R I
... 2) Design a single stage common emitter amplifier. The amplifier should have the following specs: a) flat frequency response from 30 to 10 kHz (i.e. -3 dB point at 30 Hz) b) voltage gain of ª 100 c) input impedance > 300 W 3) Measure the following properties of your amplifier and compare your result ...
... 2) Design a single stage common emitter amplifier. The amplifier should have the following specs: a) flat frequency response from 30 to 10 kHz (i.e. -3 dB point at 30 Hz) b) voltage gain of ª 100 c) input impedance > 300 W 3) Measure the following properties of your amplifier and compare your result ...
Serious ‘XM (That’s W2XM) presents
... Motional C, motional L, and loss R all in series; with a shunt C representing electrode and stray C back ...
... Motional C, motional L, and loss R all in series; with a shunt C representing electrode and stray C back ...
Serious `XM (That`s W2XM) presents
... Motional C, motional L, and loss R all in series; with a shunt C representing electrode and stray C back ...
... Motional C, motional L, and loss R all in series; with a shunt C representing electrode and stray C back ...
Self Study Unit 1.2
... Unit 1.2 Electronic Principles: Ohm’s Law Ohm’s Law is the relationship between voltage, current, and the resistance in a DC circuit. When you know any two of these values, you can calculate the third. The most basic equation for Ohm’s Law is: E = I ×R In other words, when you know the current going ...
... Unit 1.2 Electronic Principles: Ohm’s Law Ohm’s Law is the relationship between voltage, current, and the resistance in a DC circuit. When you know any two of these values, you can calculate the third. The most basic equation for Ohm’s Law is: E = I ×R In other words, when you know the current going ...
Notes18
... 1 volt, V, is a measure of electric potential (i.e. the “pressure” of electrical flow) ...
... 1 volt, V, is a measure of electric potential (i.e. the “pressure” of electrical flow) ...
experiment_V
... • Presence of the capacitor affects the size of the current in the circuit in a frequency-dependent way. • “phases” of signals across voltage source, resistor, and capacitor differ • math is most easily done by modeling the voltage source as V V0eit instead of V V0 cos(t ) and an imaginary rea ...
... • Presence of the capacitor affects the size of the current in the circuit in a frequency-dependent way. • “phases” of signals across voltage source, resistor, and capacitor differ • math is most easily done by modeling the voltage source as V V0eit instead of V V0 cos(t ) and an imaginary rea ...
ECE1250F14_HW2_2p1soln
... linearity of Ohm's law. That is, doubling the applied voltage will double the current everywhere in the resistor network. To prove the statement about currents flowing out of any bubble, observe that, for neighboring nodes, the currents flowing out of neighboring nodes toward each other are equal bu ...
... linearity of Ohm's law. That is, doubling the applied voltage will double the current everywhere in the resistor network. To prove the statement about currents flowing out of any bubble, observe that, for neighboring nodes, the currents flowing out of neighboring nodes toward each other are equal bu ...
Josephson voltage standard

A Josephson voltage standard is a complex system that uses a superconductive integrated circuit chip operating at 4 K to generate stable voltages that depend only on an applied frequency and fundamental constants. It is an intrinsic standard in the sense that it does not depend on any physical artifact. It is the most accurate method to generate or measure voltage and, by international agreement, is the basis for voltage standards around the World.