Lab 2
... Figure 2.5 Photointerrupter 10. Build the part of the circuit in Figure 2.6 labeled ‘A’. Connect the 1k resistor to any of pins P0 through P15 on the Basic Stamp 2SX (denoted xx below). Don’t forget that you need to supply power and ground to the Basic Stamp 2SX. ...
... Figure 2.5 Photointerrupter 10. Build the part of the circuit in Figure 2.6 labeled ‘A’. Connect the 1k resistor to any of pins P0 through P15 on the Basic Stamp 2SX (denoted xx below). Don’t forget that you need to supply power and ground to the Basic Stamp 2SX. ...
Four Wire System Farm Wiring Review
... Use a car battery to test for AC power system resistances or interconnections. ...
... Use a car battery to test for AC power system resistances or interconnections. ...
Chapter 18: Basic Electric Circuits
... Answer: The current through R5 must be the same as through R1, because both resistors carry whatever current came directly from the battery. The current through R3 and R4 can be determined from Kirchhoff’s junction rule: subtract the current in R2 from the current in R1 and that’s what’s left over f ...
... Answer: The current through R5 must be the same as through R1, because both resistors carry whatever current came directly from the battery. The current through R3 and R4 can be determined from Kirchhoff’s junction rule: subtract the current in R2 from the current in R1 and that’s what’s left over f ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... charged or discharged linearly between two voltages whose difference is VCC/2. Then in one half cycle of the input frequency or a time equal to 1/2fIN, the change in charge on the timing capacitor is equal to VCC/2 × C1. V0= VCC×fIN×C1×R1×K, where K is the gain constant and typically of the value of ...
... charged or discharged linearly between two voltages whose difference is VCC/2. Then in one half cycle of the input frequency or a time equal to 1/2fIN, the change in charge on the timing capacitor is equal to VCC/2 × C1. V0= VCC×fIN×C1×R1×K, where K is the gain constant and typically of the value of ...
Chapter 19 Concept Tests - University of Colorado Boulder
... Answer: Depends on the circuit. If the resistors (the light bulbs) are in series, the larger R will be brighter. But if the resistors are in parallel, the smaller R will be brighter. CRKT-9. Two light bulbs are in series attached to a battery as shown. The bulbs are marked 40W and 60W. Which bulb is ...
... Answer: Depends on the circuit. If the resistors (the light bulbs) are in series, the larger R will be brighter. But if the resistors are in parallel, the smaller R will be brighter. CRKT-9. Two light bulbs are in series attached to a battery as shown. The bulbs are marked 40W and 60W. Which bulb is ...
MS Word - Marist Library
... The teacher will demonstrate the measurement of one voltage-current point for the 1000 ohm resistor. Ask the students the following: 1. What will happen to the current if you increase the voltage? 2. What will happen to the current if you decrease the voltage? 3. What happens if you change the sign ...
... The teacher will demonstrate the measurement of one voltage-current point for the 1000 ohm resistor. Ask the students the following: 1. What will happen to the current if you increase the voltage? 2. What will happen to the current if you decrease the voltage? 3. What happens if you change the sign ...
Experiment: Series and Parallel Circuits
... Click on the Statistics button, , and record the average current in the data table. Determine the average current in the second graph following the same procedure. 8. Connect the parallel circuit as shown in Figure 5 using the 50-Ω resistor and the 68-Ω resistor. The two Current Probes will measure ...
... Click on the Statistics button, , and record the average current in the data table. Determine the average current in the second graph following the same procedure. 8. Connect the parallel circuit as shown in Figure 5 using the 50-Ω resistor and the 68-Ω resistor. The two Current Probes will measure ...
Combined Series and Parallel Circuits
... You have now found all the voltages across all the resistors, and are ready to go on to the current measurements. Caution when using the current measurement terminals on the multimeter (“A” or ” µAmA”). DO NOT apply the meter leads across any voltage source without a series resistance! Applying live ...
... You have now found all the voltages across all the resistors, and are ready to go on to the current measurements. Caution when using the current measurement terminals on the multimeter (“A” or ” µAmA”). DO NOT apply the meter leads across any voltage source without a series resistance! Applying live ...
1 (t). - s3.amazonaws.com
... Practical sources vs. ideal sources •Up to now we have been working exclusively with ideal voltage source and current sources •Ideal voltage source: No matter what is the current through the voltage source, the output voltage does not change. •Ideal current source: No matter what is the voltage acr ...
... Practical sources vs. ideal sources •Up to now we have been working exclusively with ideal voltage source and current sources •Ideal voltage source: No matter what is the current through the voltage source, the output voltage does not change. •Ideal current source: No matter what is the voltage acr ...
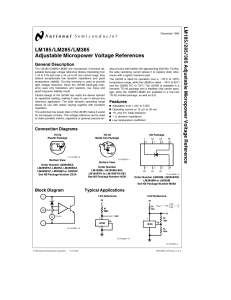
LM185 LM285 LM385 Adjustable Micropower Voltage References
... The LM185/LM285/LM385 are micropower 3-terminal adjustable band-gap voltage reference diodes. Operating from 1.24 to 5.3V and over a 10 mA to 20 mA current range, they feature exceptionally low dynamic impedance and good temperature stability. On-chip trimming is used to provide tight voltage tolera ...
... The LM185/LM285/LM385 are micropower 3-terminal adjustable band-gap voltage reference diodes. Operating from 1.24 to 5.3V and over a 10 mA to 20 mA current range, they feature exceptionally low dynamic impedance and good temperature stability. On-chip trimming is used to provide tight voltage tolera ...
1 - BrainMass
... How many 90-W, 120-V light bulbs can be connected to a 20-A, 120-V circuit without tripping the circuit breaker? (Note: This description of a light bulb gives the power it dissipates when connected to the stated potential difference; that is, a 25-W, 120-V light bulb dissipates 25 W when connected t ...
... How many 90-W, 120-V light bulbs can be connected to a 20-A, 120-V circuit without tripping the circuit breaker? (Note: This description of a light bulb gives the power it dissipates when connected to the stated potential difference; that is, a 25-W, 120-V light bulb dissipates 25 W when connected t ...
Calibration of the Keithley 6485 Picoammeter to 400 Femto
... precisely, the resistance, R, we can then measure the current, I6485, by the picoammeter and compare Ical with I6485 in order to calibrate the picoammeter. However, the precision of the resistor given by the manufacturer is not precise enough. Note that in order to generate an ultra low current, the ...
... precisely, the resistance, R, we can then measure the current, I6485, by the picoammeter and compare Ical with I6485 in order to calibrate the picoammeter. However, the precision of the resistor given by the manufacturer is not precise enough. Note that in order to generate an ultra low current, the ...
DS90C031 LVDS Quad CMOS Differential Line Driver L VDS
... the loop as shown in Figure 6. AC or unterminated configurations are not allowed. The 3.4 mA loop current will develop a differential voltage of 340 mV across the 100Ω termination resistor which the receiver detects with a 240 mV minimum differential noise margin neglecting resistive line losses (dr ...
... the loop as shown in Figure 6. AC or unterminated configurations are not allowed. The 3.4 mA loop current will develop a differential voltage of 340 mV across the 100Ω termination resistor which the receiver detects with a 240 mV minimum differential noise margin neglecting resistive line losses (dr ...
PHY 102 Lab Manual: LCR circuit
... resonance, that difference will be zero, and only R will limit the current flow in the circuit. The above graph shows normalized values of current through a series RLC circuit at frequencies ranging from 0.01 times the resonant frequency, to 100 times that frequency. Beyond that range, as you can s ...
... resonance, that difference will be zero, and only R will limit the current flow in the circuit. The above graph shows normalized values of current through a series RLC circuit at frequencies ranging from 0.01 times the resonant frequency, to 100 times that frequency. Beyond that range, as you can s ...
Chapter 2 - Basic Op-Amp Circuits
... The output swing of a zero-crossing detector may be too large in some applications. In some applications, necessary to limit the output voltage levels of comparator to a value less than provided by the saturated op-amp. We can bound the output by using a zener diode – limit the output voltage to the ...
... The output swing of a zero-crossing detector may be too large in some applications. In some applications, necessary to limit the output voltage levels of comparator to a value less than provided by the saturated op-amp. We can bound the output by using a zener diode – limit the output voltage to the ...
TYPES OF POWER SUPPLY
... is filtered by the capacitor, C1 which filters the undesired ripples before it is connected to terminal 1. • The regulated output voltage of +5V is produced at terminal 2 filter by the capacitor C2. • C2 will also filter all the high frequency distortion in the system. • Terminal 3 is grounded. ...
... is filtered by the capacitor, C1 which filters the undesired ripples before it is connected to terminal 1. • The regulated output voltage of +5V is produced at terminal 2 filter by the capacitor C2. • C2 will also filter all the high frequency distortion in the system. • Terminal 3 is grounded. ...
Josephson voltage standard

A Josephson voltage standard is a complex system that uses a superconductive integrated circuit chip operating at 4 K to generate stable voltages that depend only on an applied frequency and fundamental constants. It is an intrinsic standard in the sense that it does not depend on any physical artifact. It is the most accurate method to generate or measure voltage and, by international agreement, is the basis for voltage standards around the World.