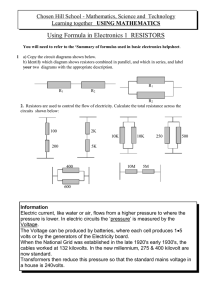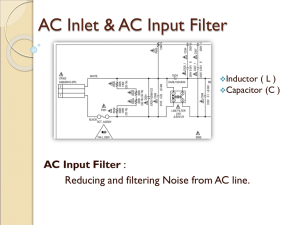
Tutorial 1
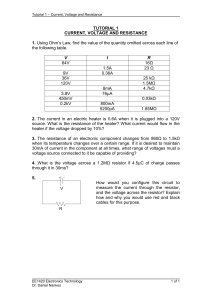
... heater if the voltage dropped by 10%? 3. The resistance of an electronic component changes from 860Ω to 1.5kΩ when its temperature changes over a certain range. If it is desired to maintain 30mA of current in the component at all times, what range of voltages must a voltage source connected to it be ...
... heater if the voltage dropped by 10%? 3. The resistance of an electronic component changes from 860Ω to 1.5kΩ when its temperature changes over a certain range. If it is desired to maintain 30mA of current in the component at all times, what range of voltages must a voltage source connected to it be ...
PHYS1120ExamIIReview.. - University of Colorado Boulder
... Review Concept Tests, CAPA problems, and Tutorial HW. (Read question and try to remember reasoning that gets to the answer) ...
... Review Concept Tests, CAPA problems, and Tutorial HW. (Read question and try to remember reasoning that gets to the answer) ...
Electrical principles: math for electronics, electronic principles
... to calculate electrical power in a DC circuit is power (P) equals voltage (E) multiplied by current (I) (T5C08) P= E × I 138 watts is the power being used in a circuit when the applied voltage is 13.8 volts DC and the current is 10 amperes. (T5C09) P = E × I or 13.8 V × 10 A = 138 W When the applied ...
... to calculate electrical power in a DC circuit is power (P) equals voltage (E) multiplied by current (I) (T5C08) P= E × I 138 watts is the power being used in a circuit when the applied voltage is 13.8 volts DC and the current is 10 amperes. (T5C09) P = E × I or 13.8 V × 10 A = 138 W When the applied ...
Electric Field
... The Formula that is used is V = I x R Using the formula allows you to work out the Voltage of a circuit if you know its Current and Resistance. From this formula we can also swap around the values to find Current (I) and Resistance (R) ...
... The Formula that is used is V = I x R Using the formula allows you to work out the Voltage of a circuit if you know its Current and Resistance. From this formula we can also swap around the values to find Current (I) and Resistance (R) ...
0002_hsm11a1_te_0501tr.indd
... Electricity Ohm’s Law V= I R relates the voltage, current, and resistance of a circuit. V is the voltage measured in volts. I is the current measured in amperes. R is the resistance measured in ohms. a. Find the voltage of a circuit with a current of 24 amperes and a resistance of 2 ohms. b. Find ...
... Electricity Ohm’s Law V= I R relates the voltage, current, and resistance of a circuit. V is the voltage measured in volts. I is the current measured in amperes. R is the resistance measured in ohms. a. Find the voltage of a circuit with a current of 24 amperes and a resistance of 2 ohms. b. Find ...
Voltage Dividers
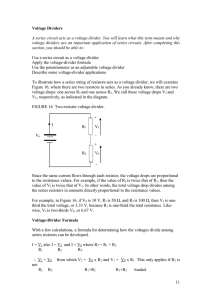
... the series resistors in amounts directly proportional to the resistance values. For example, in Figure 16, if VS is 10 V, R1 is 50 , and R2 is 100 , then V1 is onethird the total voltage, or 3.33 V, because R1 is one-third the total resistance. Likewise, V2 is two-thirds VS, or 6.67 V. Voltage-Div ...
... the series resistors in amounts directly proportional to the resistance values. For example, in Figure 16, if VS is 10 V, R1 is 50 , and R2 is 100 , then V1 is onethird the total voltage, or 3.33 V, because R1 is one-third the total resistance. Likewise, V2 is two-thirds VS, or 6.67 V. Voltage-Div ...
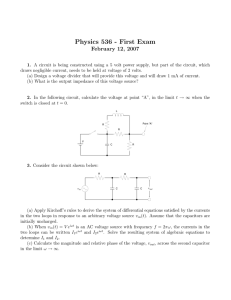
Physics 536 - First Exam February 12, 2007
... (a) Apply Kirchoff’s rules to derive the system of differential equations satisfied by the currents in the two loops in response to an arbitrary voltage source vin (t). Assume that the capacitors are initially uncharged. (b) When vin (t) = V eiωt is an AC voltage source with frequency f = 2πω, the c ...
... (a) Apply Kirchoff’s rules to derive the system of differential equations satisfied by the currents in the two loops in response to an arbitrary voltage source vin (t). Assume that the capacitors are initially uncharged. (b) When vin (t) = V eiωt is an AC voltage source with frequency f = 2πω, the c ...
Ohm`s Law - Blackboard
... Ohm’s Law V= Voltage (V) I = Current in amps (A) R = Resistance in ohm’s (Ω) For voltage use V= I x R ...
... Ohm’s Law V= Voltage (V) I = Current in amps (A) R = Resistance in ohm’s (Ω) For voltage use V= I x R ...
Josephson voltage standard

A Josephson voltage standard is a complex system that uses a superconductive integrated circuit chip operating at 4 K to generate stable voltages that depend only on an applied frequency and fundamental constants. It is an intrinsic standard in the sense that it does not depend on any physical artifact. It is the most accurate method to generate or measure voltage and, by international agreement, is the basis for voltage standards around the World.