Optically polarized atoms_Atomic_Transitions
... D. DeMille, D. Budker, N. Derr, and E. Deveney, How we know that photons are bosons: experimental tests of spin-statistics for photons, in: Proceedings of the International Conference on SpinStatistics Connection and Commutation Relations: Experimental Tests and Theoretical Implications, Anacapri, I ...
... D. DeMille, D. Budker, N. Derr, and E. Deveney, How we know that photons are bosons: experimental tests of spin-statistics for photons, in: Proceedings of the International Conference on SpinStatistics Connection and Commutation Relations: Experimental Tests and Theoretical Implications, Anacapri, I ...
Optical Properties of Low Dimensional Semiconductor Materials
... range of potential applications including long-wavelength semiconductor lasers and ...
... range of potential applications including long-wavelength semiconductor lasers and ...
Deans Community High School Intermediate 2 Revision Notes www
... sufficient energy to break any bonds within the reactants. For example nitrogen and oxygen particles collide in the air very frequently, but do not normally undergo a chemical reaction as there is insufficient energy in the collisions. Factors affecting reaction rate - Surface area If a large piece ...
... sufficient energy to break any bonds within the reactants. For example nitrogen and oxygen particles collide in the air very frequently, but do not normally undergo a chemical reaction as there is insufficient energy in the collisions. Factors affecting reaction rate - Surface area If a large piece ...
Experimental - AIP FTP Server
... where Eint(HCCO) is the internal energy in the HCCO primary fragments and we neglect any (small) internal energy in the jet-cooled parent ketene molecules. H atom count rates with the photolysis laser blocked are negligible, thus eliminating unintentional photolysis by the Lyman- probe laser radiat ...
... where Eint(HCCO) is the internal energy in the HCCO primary fragments and we neglect any (small) internal energy in the jet-cooled parent ketene molecules. H atom count rates with the photolysis laser blocked are negligible, thus eliminating unintentional photolysis by the Lyman- probe laser radiat ...
Spring 2013 Semester Exam Study Guide (Bonding, Nomenclature
... b. same number of each kind of atom appears in the reactants and in the products. c. products and reactants are the same chemicals. d. subscripts of the reactants equal the subscripts of the products. ____ 96. In the word equation, sodium oxide + water sodium hydroxide, the formula for sodium hydr ...
... b. same number of each kind of atom appears in the reactants and in the products. c. products and reactants are the same chemicals. d. subscripts of the reactants equal the subscripts of the products. ____ 96. In the word equation, sodium oxide + water sodium hydroxide, the formula for sodium hydr ...
CHAPTER 23 The Interaction of Light with Matter: I
... Figure 22: Illustration of the scattering cross section of an atom or ion with at least one bound electron. At high (low) frequency, scattering is in the Thomson (Rayleigh) regime; at specific, intermediate frequencies, set by the transition energies of the atom/ion, resonant scattering dominates; ...
... Figure 22: Illustration of the scattering cross section of an atom or ion with at least one bound electron. At high (low) frequency, scattering is in the Thomson (Rayleigh) regime; at specific, intermediate frequencies, set by the transition energies of the atom/ion, resonant scattering dominates; ...
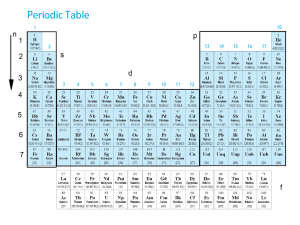
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... In 1800s Hertz started kicking electrons with EM radiation Structure Prentice - Intelliome A. S. LLC 2005 ...
... In 1800s Hertz started kicking electrons with EM radiation Structure Prentice - Intelliome A. S. LLC 2005 ...
Lecture Notes: Condensed Matter Theory I (TKM1)
... up to the Fermi energy. Thus, even at T = 0 are states with rather high energy involved. The ground state of a Bose gas is clearly di¤erent. At T = 0 all bosons occupy the state with lowest energy, which is in our case p = 0. An interesting question is then whether this macroscopic occupation of one ...
... up to the Fermi energy. Thus, even at T = 0 are states with rather high energy involved. The ground state of a Bose gas is clearly di¤erent. At T = 0 all bosons occupy the state with lowest energy, which is in our case p = 0. An interesting question is then whether this macroscopic occupation of one ...
Document
... Micro-Evolution in the Primary Atmosphere and Hydrosphere (3,5,6) Utilizing the Harvard classification of stars, Oparin pointed out that in the hottest stars of the ultraviolet type, with surface temperatures of approximately 50,000º C., the elements carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen are present largely ...
... Micro-Evolution in the Primary Atmosphere and Hydrosphere (3,5,6) Utilizing the Harvard classification of stars, Oparin pointed out that in the hottest stars of the ultraviolet type, with surface temperatures of approximately 50,000º C., the elements carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen are present largely ...
How does a solar cell work? by Finley R. Shapiro First, let`s be clear
... the valence band. We call an electron in the conduction band a “free electron,” to distinguish it from the electrons that are still in the valence band or in other quantum states. A free electron moves around more easily than other electrons, but it still is not free to leave the crystal. When the e ...
... the valence band. We call an electron in the conduction band a “free electron,” to distinguish it from the electrons that are still in the valence band or in other quantum states. A free electron moves around more easily than other electrons, but it still is not free to leave the crystal. When the e ...
Quantum effects in energy and charge transfer in an
... where ωμν = E μ − E ν , and the heat-bath operator Aμν is defined in Eq. (7). Here, we use the fact that the Hamiltonian H in Eq. (6) is also expressed in terms of the operators ρμν taken at the same moment of time t. For two of these operators, ρμν (t) and ραβ (t), we have simple multiplication rul ...
... where ωμν = E μ − E ν , and the heat-bath operator Aμν is defined in Eq. (7). Here, we use the fact that the Hamiltonian H in Eq. (6) is also expressed in terms of the operators ρμν taken at the same moment of time t. For two of these operators, ρμν (t) and ραβ (t), we have simple multiplication rul ...
Effect of an industrial chemical waste on the uptake
... At the beginning, it was found sensible to estimate the relationship between characteristic molecular-energy values and the quantity kT , where k is the Boltzmann constant and T the temperature. In the present study, instead of energy, the wave number, = E/hc, expressed in cm–1 (1 J is equivalent ...
... At the beginning, it was found sensible to estimate the relationship between characteristic molecular-energy values and the quantity kT , where k is the Boltzmann constant and T the temperature. In the present study, instead of energy, the wave number, = E/hc, expressed in cm–1 (1 J is equivalent ...
The Formation of Solvated Electrons in the Photochemistry of the
... chemical data" where the value 0.2 to 0.3 was obtained. The ratio (ks,o + e , , - ) , j ( k H s o + + as calculated from radiation chemicalI2 and photochemical1@data is approximately il.9. One therefore gets k~~ + e a e - j k ~+z ~ e4Q- = 0.4 to 0.6, in fair agreement with the value obtained in our ...
... chemical data" where the value 0.2 to 0.3 was obtained. The ratio (ks,o + e , , - ) , j ( k H s o + + as calculated from radiation chemicalI2 and photochemical1@data is approximately il.9. One therefore gets k~~ + e a e - j k ~+z ~ e4Q- = 0.4 to 0.6, in fair agreement with the value obtained in our ...
CHEM1901/3 Tutorials The problem sheets on the following pages
... energy. Mass did not enter into the discussion of energy. Chemists must have been tempted to conclude that E = mc 2 had no relevance for their discipline. Today’s general chemistry students have good reason to be confused about mass and energy conservation. Early in the course they are told that mas ...
... energy. Mass did not enter into the discussion of energy. Chemists must have been tempted to conclude that E = mc 2 had no relevance for their discipline. Today’s general chemistry students have good reason to be confused about mass and energy conservation. Early in the course they are told that mas ...
Thermal properties of materials
... that the above values are for bulk materials while those for thin films can be significantly different largely because of the relative importance of the boundary (the same is true of electrical conductivity, heat capacity etc) ENG2000: R.I. Hornsey ...
... that the above values are for bulk materials while those for thin films can be significantly different largely because of the relative importance of the boundary (the same is true of electrical conductivity, heat capacity etc) ENG2000: R.I. Hornsey ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.