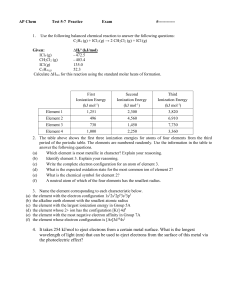
The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this
... Group. The trends and patterns are captured in this version of the Periodic Table obtained from the Internet: ...
... Group. The trends and patterns are captured in this version of the Periodic Table obtained from the Internet: ...
The Periodic table
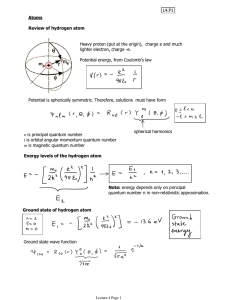
... A quantized property is a property that can have only certain values. The energy of an electron is quantized, only certain behavior patterns are allowed. ...
... A quantized property is a property that can have only certain values. The energy of an electron is quantized, only certain behavior patterns are allowed. ...
chapter 7: atomic structure and periodicity
... 1) Electrons can occupy only certain _________________ around the nucleus. 2) Each orbit has an energy associated with it. 3) Energy is absorbed by an electron when it moves from a _____________ to _____________ orbit. Energy is released (in the form of photons) when a e- moves from a ______________ ...
... 1) Electrons can occupy only certain _________________ around the nucleus. 2) Each orbit has an energy associated with it. 3) Energy is absorbed by an electron when it moves from a _____________ to _____________ orbit. Energy is released (in the form of photons) when a e- moves from a ______________ ...
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
... the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 the element with the most negative electron affinity in Group 7A the element whose electron configuration is [Ar]3d104s2 ...
... the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 the element with the most negative electron affinity in Group 7A the element whose electron configuration is [Ar]3d104s2 ...
Electron Configurations
... electrons that are involved. The amount of valence electrons makes a big difference in how the element will bond, so to make it easy to predict, we draw electron dot diagrams. ...
... electrons that are involved. The amount of valence electrons makes a big difference in how the element will bond, so to make it easy to predict, we draw electron dot diagrams. ...
Corso di Fisica Moderna
... possible for an electron to move in an orbit for which its orbital angular momentum L is and integral mulAple of h, Planck’s constant. 3) Despite the fact that it is constantly acceleraAng, an ...
... possible for an electron to move in an orbit for which its orbital angular momentum L is and integral mulAple of h, Planck’s constant. 3) Despite the fact that it is constantly acceleraAng, an ...
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
... that completely and perfectly absorbs any light energy that falls on it and then perfectly reradiates the energy as light energy. The energy it reradiates can be depicted as a blackbody curve, which depends on temperature only. In the figure to the right, note that the 6000 K curve, corresponding to ...
... that completely and perfectly absorbs any light energy that falls on it and then perfectly reradiates the energy as light energy. The energy it reradiates can be depicted as a blackbody curve, which depends on temperature only. In the figure to the right, note that the 6000 K curve, corresponding to ...
CH 6 electrons in atoms
... probability of finding that citizen if we look in the boundaries of the city. The same is true for an electron. We believe there is a good chance or a high probability of finding the electron within the boundaries of the orbital. Explain the differences between Bohr and Schrödinger’s models of the a ...
... probability of finding that citizen if we look in the boundaries of the city. The same is true for an electron. We believe there is a good chance or a high probability of finding the electron within the boundaries of the orbital. Explain the differences between Bohr and Schrödinger’s models of the a ...
4 - College of Arts and Sciences
... A sample of acetominophen (C8H9O2N) has 6.02 x 1023 atoms of Hydrogen. What is the mass in grams of the sample? How many atoms of H in one mole of C8H9O2N ? 9 x (6.02 x 1023) atoms of H Therefore have 1/9 of a mole of acetominophen What is the molecular weight of acetominophen ? ...
... A sample of acetominophen (C8H9O2N) has 6.02 x 1023 atoms of Hydrogen. What is the mass in grams of the sample? How many atoms of H in one mole of C8H9O2N ? 9 x (6.02 x 1023) atoms of H Therefore have 1/9 of a mole of acetominophen What is the molecular weight of acetominophen ? ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.