The Emergence of a Coupled Quantum Dot Array in a Doped Silicon
... mainly focused on obtaining ultrathin NWs from lithography followed by etching procedures to reduce the NW width.32-37 Single-electron effects have been observed in these devices, but the results disagree with the designed device geometry; the etching processes introduce defects and roughness that, ...
... mainly focused on obtaining ultrathin NWs from lithography followed by etching procedures to reduce the NW width.32-37 Single-electron effects have been observed in these devices, but the results disagree with the designed device geometry; the etching processes introduce defects and roughness that, ...
FREE Sample Here
... 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? A) carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen B) carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxyg ...
... 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? A) carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen B) carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxyg ...
FREE Sample Here
... 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? A) carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen B) carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxyg ...
... 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? A) carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen B) carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxyg ...
Effects of culture conditions on ligninolytic enzymes and protease
... of Mn7+ was 4.68%. These results indicated that the potassium permanganate decomposed during the modification, and a portion was reduced by the surface organic functional groups or carbons. (Dash et al., 2009) also found that potassium permanganate could be reduced into MnO2 and formed complexes wit ...
... of Mn7+ was 4.68%. These results indicated that the potassium permanganate decomposed during the modification, and a portion was reduced by the surface organic functional groups or carbons. (Dash et al., 2009) also found that potassium permanganate could be reduced into MnO2 and formed complexes wit ...
Biology, 8e (Campbell) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life
... 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? A) carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen B) carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxyg ...
... 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? A) carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen B) carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxyg ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms of Atoms
... • Under the right conditions, a photon can strike the metal surface and be absorbed. Then it transfers it’s energy to an electron in the metal. Once enough energy is absorbed, the electron is emitted from the metal • The minimum energy to release the electron is different for different metals Elect ...
... • Under the right conditions, a photon can strike the metal surface and be absorbed. Then it transfers it’s energy to an electron in the metal. Once enough energy is absorbed, the electron is emitted from the metal • The minimum energy to release the electron is different for different metals Elect ...
Biology, 8e (Campbell) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of Life
... 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? A) carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen B) carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxyg ...
... 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? A) carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen B) carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxyg ...
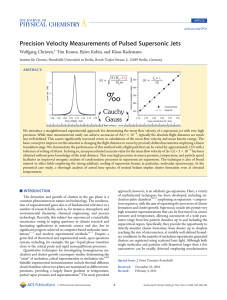
Precision Velocity Measurements of Pulsed Supersonic Jets
... superfluidity.28 As a matter of fact, helium clusters have established new research areas in low-temperature physics and spectroscopy.29-34 There are also several other applications of supersonic beams where the mean flow velocity of particles needs to be obtained with high accuracy, e.g. reactivity s ...
... superfluidity.28 As a matter of fact, helium clusters have established new research areas in low-temperature physics and spectroscopy.29-34 There are also several other applications of supersonic beams where the mean flow velocity of particles needs to be obtained with high accuracy, e.g. reactivity s ...
Kondo-model for quantum-dots with spin
... combine to produce the Kondo effect, which leads to the appearance of an extra resonance at the Fermi energy. Since transport properties, such as conductance, are determined by electrons with energies close to the Fermi level, the extra resonance can dramatically change the conductance. (e) The enhan ...
... combine to produce the Kondo effect, which leads to the appearance of an extra resonance at the Fermi energy. Since transport properties, such as conductance, are determined by electrons with energies close to the Fermi level, the extra resonance can dramatically change the conductance. (e) The enhan ...
Chapter 18 - WordPress.com
... Each half-reaction includes electrons electrons go on the product side of the oxidation halfreaction – loss of electrons electrons go on the reactant side of the reduction halfreaction – gain of electrons ...
... Each half-reaction includes electrons electrons go on the product side of the oxidation halfreaction – loss of electrons electrons go on the reactant side of the reduction halfreaction – gain of electrons ...
Biology, 8e (Campbell)
... 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? A) carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen B) carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxyg ...
... 1) About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? A) carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen B) carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen C) oxygen, hydrogen, calcium, sodium D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxyg ...
Topological insulator with time
... † Seems that the spin-orbit coupling can give us TIs without breaking the time-reversal symmetry, but there are two things one needs to notice (which are the key discoveries Kane and Mele made): 1. The edge states are only protected in the presence of the time-reversal symmetry. If we break the time ...
... † Seems that the spin-orbit coupling can give us TIs without breaking the time-reversal symmetry, but there are two things one needs to notice (which are the key discoveries Kane and Mele made): 1. The edge states are only protected in the presence of the time-reversal symmetry. If we break the time ...
Chemical Reactivity as Described by Quantum Chemical Methods
... the latter branch of DFT, conceptual DFT is highlighted following Parr's dictum "to calculate a molecule is not to understand it". An overview is given of the most important reactivity descriptors and the principles they are couched in. Examples are given on the evolution of the structure-property-w ...
... the latter branch of DFT, conceptual DFT is highlighted following Parr's dictum "to calculate a molecule is not to understand it". An overview is given of the most important reactivity descriptors and the principles they are couched in. Examples are given on the evolution of the structure-property-w ...
Monday, Oct. 3, 2016
... • For a greater stability, the energy levels fill up from the bottom up to the Fermi level – Fermi level: Highest, fully occupied energy level (EF) ...
... • For a greater stability, the energy levels fill up from the bottom up to the Fermi level – Fermi level: Highest, fully occupied energy level (EF) ...
Charge and spin quantum fluids generated by many
... functions and the pseudoparticle energy dispersions are presented in Appendix C. Often the low-energy excitations generated by the occupancy configurations of the c and s1 pseudoparticle branches are identified with holons and spinons, respectively [3,13,15]. In this paper we find that the missing l ...
... functions and the pseudoparticle energy dispersions are presented in Appendix C. Often the low-energy excitations generated by the occupancy configurations of the c and s1 pseudoparticle branches are identified with holons and spinons, respectively [3,13,15]. In this paper we find that the missing l ...
Th tical lifetime eore Positronium: A
... based on our knowledge of the nonrelativistic counterpart. We should note that Dirac's equation is difficult to solve for positronium. This is because of the identical mass of the two particles positronium is composed of. Since the two particles have the same mass, the simplifying approximation wher ...
... based on our knowledge of the nonrelativistic counterpart. We should note that Dirac's equation is difficult to solve for positronium. This is because of the identical mass of the two particles positronium is composed of. Since the two particles have the same mass, the simplifying approximation wher ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.