2 Phase Diagram of 2DES on Liquid Helium
... liquid to crystal, the so-called Wigner transition. This difference is due to coupling between 2DES modes and those of liquid helium surface. The experiments are performed for a range of helium film thicknesses 1mm -100Å. For thin films the influence of the underlying substrate is of great importanc ...
... liquid to crystal, the so-called Wigner transition. This difference is due to coupling between 2DES modes and those of liquid helium surface. The experiments are performed for a range of helium film thicknesses 1mm -100Å. For thin films the influence of the underlying substrate is of great importanc ...
Chapter 4 Alchemical Free Energy Calculations: Ready for Prime
... as singularities in the r−1 (Coulombic) or r−12 (Lennard-Jones) parts of the potential energy leads to results that converge very slowly [59,61,62]. In some cases, shrinking bonds while removing a molecule can eliminate the effect of these singularities, but this can lead to dynamical instabilities, ...
... as singularities in the r−1 (Coulombic) or r−12 (Lennard-Jones) parts of the potential energy leads to results that converge very slowly [59,61,62]. In some cases, shrinking bonds while removing a molecule can eliminate the effect of these singularities, but this can lead to dynamical instabilities, ...
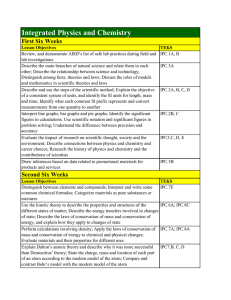
Integrated Physics and Chemistry
... atoms transfer their valence electrons to form ionic bonds, while other atoms share valence electrons to form covalent bonds; Differentiate between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds; Compare the properties of substances with different types of bonds Name simple ionic and covalent compounds; Predic ...
... atoms transfer their valence electrons to form ionic bonds, while other atoms share valence electrons to form covalent bonds; Differentiate between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds; Compare the properties of substances with different types of bonds Name simple ionic and covalent compounds; Predic ...
Slide 1
... Now there are two N atoms and four O atoms on the right. Placing the coefficient 2 in front of NO balances both the number of N atoms and O atoms: O2 + 2 NO → 2 NO2 (balanced) (c) The left box (reactants) contains four O2 molecules and eight NO molecules. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each ...
... Now there are two N atoms and four O atoms on the right. Placing the coefficient 2 in front of NO balances both the number of N atoms and O atoms: O2 + 2 NO → 2 NO2 (balanced) (c) The left box (reactants) contains four O2 molecules and eight NO molecules. Thus, the molecular ratio is one O2 for each ...
Novel Results for Condensed Matter Systems with Time Reversal Symmetry
... regime of Coulomb Blockade [10]. The fact that superconductivity is associated with breaking of particle number conservation hints at the idea that in mesoscopic systems superconductivity can quite different from that of bulk systems. In this work we focus on extreme case of the so-called zerodimens ...
... regime of Coulomb Blockade [10]. The fact that superconductivity is associated with breaking of particle number conservation hints at the idea that in mesoscopic systems superconductivity can quite different from that of bulk systems. In this work we focus on extreme case of the so-called zerodimens ...
Q - PIMS
... chamber. These ions are mostly positive. (iv) X-rays when thrown upon gaseous substances, ionize the molecules of gases. Position of negative charges in ions: The positions of negative charges in these ions can be located from the structure of these ions. The negative charge is present on the electr ...
... chamber. These ions are mostly positive. (iv) X-rays when thrown upon gaseous substances, ionize the molecules of gases. Position of negative charges in ions: The positions of negative charges in these ions can be located from the structure of these ions. The negative charge is present on the electr ...
Interactions of Ammonia with a NiO( 100) Surface
... lone pair on the nitrogen atom which acts as a donor ligand that bonds to metal atoms both in organometallic compounds] and on surface^,^,^ Accordingly, the bonding configuration and adsorption geometry of NH3 to single-crystal metal surfaces have been a focus of intensive research2-I7 for the past ...
... lone pair on the nitrogen atom which acts as a donor ligand that bonds to metal atoms both in organometallic compounds] and on surface^,^,^ Accordingly, the bonding configuration and adsorption geometry of NH3 to single-crystal metal surfaces have been a focus of intensive research2-I7 for the past ...
Imaging electrostatically confined Dirac fermions in graphene
... but reflects them at larger angles of incidence1,4,5 . In a potential well with circular symmetry, electrons with high angular momenta are obliquely incident on the barrier and are internally reflected, thus leading to particle confinement and the formation of quasibound quantum dot states7–12 . As ...
... but reflects them at larger angles of incidence1,4,5 . In a potential well with circular symmetry, electrons with high angular momenta are obliquely incident on the barrier and are internally reflected, thus leading to particle confinement and the formation of quasibound quantum dot states7–12 . As ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... How much is left of the excess reagent ?. ...
... How much is left of the excess reagent ?. ...
Nonlinear Susceptibilities of Donor
... calculate the static as well as the dynamic polarizabilities. The sum-over-states (SOS) procedure has been widely used as well, in particular for identifying the excited states which dominate the resonant r e s p o n ~ e . ~ *Electron ~ ~ ~ , ' ~correlation effects may be incorporated into the state ...
... calculate the static as well as the dynamic polarizabilities. The sum-over-states (SOS) procedure has been widely used as well, in particular for identifying the excited states which dominate the resonant r e s p o n ~ e . ~ *Electron ~ ~ ~ , ' ~correlation effects may be incorporated into the state ...
Photoemission studies of quantum well states in thin films
... high, and spectroscopic studies can yield results very similar to the truly con®ned case. These partially con®ned states are often referred to as quantum well resonances. A gap is effective for electron con®nement if the overlayer and substrate are lattice matched or have a commensurate epitaxial re ...
... high, and spectroscopic studies can yield results very similar to the truly con®ned case. These partially con®ned states are often referred to as quantum well resonances. A gap is effective for electron con®nement if the overlayer and substrate are lattice matched or have a commensurate epitaxial re ...
Chemistry Review 2 answer key
... Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and expensive to isolate aluminum from bauxite ore. In 1886, a brother and sister team, Charles and Julia Hall, found that molten (melted) c ...
... Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and expensive to isolate aluminum from bauxite ore. In 1886, a brother and sister team, Charles and Julia Hall, found that molten (melted) c ...
The Emergence of a Coupled Quantum Dot Array in a Doped Silicon
... mainly focused on obtaining ultrathin NWs from lithography followed by etching procedures to reduce the NW width.32-37 Single-electron effects have been observed in these devices, but the results disagree with the designed device geometry; the etching processes introduce defects and roughness that, ...
... mainly focused on obtaining ultrathin NWs from lithography followed by etching procedures to reduce the NW width.32-37 Single-electron effects have been observed in these devices, but the results disagree with the designed device geometry; the etching processes introduce defects and roughness that, ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.