Electronic structure of correlated electron systems
... • Obtain the correct ground state crystal structure and quite accurate lattice parameters for a large diversity of systems • Obtain the correct magnetic structure for a large diversity of materials • First principles method to calculate electron phonon coupling by introducing lattice distortions and ...
... • Obtain the correct ground state crystal structure and quite accurate lattice parameters for a large diversity of systems • Obtain the correct magnetic structure for a large diversity of materials • First principles method to calculate electron phonon coupling by introducing lattice distortions and ...
Xe and Kr gas filled proportional counters and characteristic X
... was produced when a beam of electrons struck the material. In time he discovered that the X-ray penetrating power and their absorption in targets such as aluminum. Characteristic X-rays are those X-rays produced when electrons are transited between atomic shells and rearrange themselves following ex ...
... was produced when a beam of electrons struck the material. In time he discovered that the X-ray penetrating power and their absorption in targets such as aluminum. Characteristic X-rays are those X-rays produced when electrons are transited between atomic shells and rearrange themselves following ex ...
ESR Theory - Personal WWW Pages
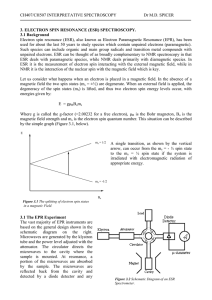
... Figure 3.5 Tetragonal Distortion in Octahedral Complexes and the Resulting Spectral Form ...
... Figure 3.5 Tetragonal Distortion in Octahedral Complexes and the Resulting Spectral Form ...
K,7th Grade Test Review: Atoms and Chemical Reactions PART
... PART FOUR: Chemical Equations. For each equation, label the products and reactants. Then, count the number of atoms of each element on each side. Then fill in the blanks. ...
... PART FOUR: Chemical Equations. For each equation, label the products and reactants. Then, count the number of atoms of each element on each side. Then fill in the blanks. ...
wave-particle duality
... light increases, force increases, so KE of ejected electrons should increase. Electrons should be emitted whatever the frequency ν of the light, so long as E is sufficiently large For very low intensities, expect a time lag between light exposure and emission, while electrons absorb enough energy to ...
... light increases, force increases, so KE of ejected electrons should increase. Electrons should be emitted whatever the frequency ν of the light, so long as E is sufficiently large For very low intensities, expect a time lag between light exposure and emission, while electrons absorb enough energy to ...
Ionic Bonding - cloudfront.net
... The 7 diatomic elements are all gases: _________________________________ ...
... The 7 diatomic elements are all gases: _________________________________ ...
Name Date: __ ______ Chemistry Semester I Final Exam Review
... 49. The half-life of polonium-210 is 138.4 days. How many milligrams of polonium-210 remain after 415.2 days if you start with 2.0 mg of the isotope? ...
... 49. The half-life of polonium-210 is 138.4 days. How many milligrams of polonium-210 remain after 415.2 days if you start with 2.0 mg of the isotope? ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Reactions
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.