CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
Question to answer… - Rochester Century High School
... - shorthand way to describe chemical reactions using symbols and formulas Instead of writing: “When you add solid silver to hydrogen sulfide gas, you get solid silver (I) sulfide and diatomic hydrogen gas.” You can just write: Ag(s) + H2S(g) --> Ag2S(s) + H2 (g) ...
... - shorthand way to describe chemical reactions using symbols and formulas Instead of writing: “When you add solid silver to hydrogen sulfide gas, you get solid silver (I) sulfide and diatomic hydrogen gas.” You can just write: Ag(s) + H2S(g) --> Ag2S(s) + H2 (g) ...
Viju B - IS MU
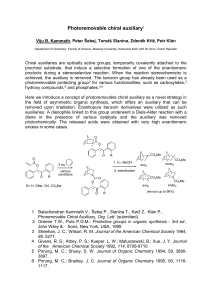
... products during a stereoselective reaction. When the reaction stereochemistry is achieved, the auxiliary is removed. The benzoin group has already been used as a photoremovable protecting group2 for various functionalities, such as carboxylates,3 hydroxy compounds,6 and phosphates.4,5 Here we introd ...
... products during a stereoselective reaction. When the reaction stereochemistry is achieved, the auxiliary is removed. The benzoin group has already been used as a photoremovable protecting group2 for various functionalities, such as carboxylates,3 hydroxy compounds,6 and phosphates.4,5 Here we introd ...
Fall Exam 4
... is a high-energy transition state that molecules must go through to convert from reactants to products. represents the fraction of molecules that have enough energy to make it over the activation barrier on a given approach. is the energy barrier that must be surmounted for reactants to be transform ...
... is a high-energy transition state that molecules must go through to convert from reactants to products. represents the fraction of molecules that have enough energy to make it over the activation barrier on a given approach. is the energy barrier that must be surmounted for reactants to be transform ...
Second Semester Extra Review
... 1. What is a reversible reaction? 2. Define equilibrium. 3. What two substances do you NOT write in an equilibrium expression? 4. Find the equilibrium constant for 2 CO + O2 2 CO2 if the concentration of CO is 0.500M, O2 is 1.50M and CO2 is 0.250M. 5. Calculate the Ka of HF if [HF] = 0.500 M and the ...
... 1. What is a reversible reaction? 2. Define equilibrium. 3. What two substances do you NOT write in an equilibrium expression? 4. Find the equilibrium constant for 2 CO + O2 2 CO2 if the concentration of CO is 0.500M, O2 is 1.50M and CO2 is 0.250M. 5. Calculate the Ka of HF if [HF] = 0.500 M and the ...
Document
... In a chemical equation, like the one below, you will notice that there are regular sized numbers in front of some of the molecules and small numbers after certain atoms within a molecule. The little number is called the subscript and tells how many of a certain type of atom are in a molecule. The bi ...
... In a chemical equation, like the one below, you will notice that there are regular sized numbers in front of some of the molecules and small numbers after certain atoms within a molecule. The little number is called the subscript and tells how many of a certain type of atom are in a molecule. The bi ...
2. NH3 - Huffman Chemistry Website!
... Explain what determines if one single metal may or may not replace another metal from a compound in a single replacement reaction. ...
... Explain what determines if one single metal may or may not replace another metal from a compound in a single replacement reaction. ...
Project Advance Chemistry 106 Sample Questions
... 18. Uric acid, a weak monoprotic acid (HA), is a metabolic end product and is excreted from the body in urine. The acid dissociation constant of uric acid is Ka = 4.0 10-6 M. The pH of a urine sample is 6.00. What is the ratio of urate ion to uric acid in the urine? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 18. Uric acid, a weak monoprotic acid (HA), is a metabolic end product and is excreted from the body in urine. The acid dissociation constant of uric acid is Ka = 4.0 10-6 M. The pH of a urine sample is 6.00. What is the ratio of urate ion to uric acid in the urine? A. B. C. D. E. ...
final exam review chapter 1-4
... salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
... salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
Reactions and Balancing
... changes in the chemical composition of matter (the making of new materials with new properties) energy changes ...
... changes in the chemical composition of matter (the making of new materials with new properties) energy changes ...
Chapter 4
... Balancing Chemical Equations 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water C2H6 + O2 ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations 1. Write the correct formula(s) for the reactants on the left side and the correct formula(s) for the product(s) on the right side of the equation. Ethane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water C2H6 + O2 ...
Science Notes on Physical and Chemical Properties
... in bubbling. When an acid reacts with another substance, usually hydrogen gas (which is highly explosive) is released 3. Other Reactions – include heat being released, bubbling, strong odor, smoke, flame, change of color, etc. 4. Non-Reactivity – when something fails to react…example…platinum droppe ...
... in bubbling. When an acid reacts with another substance, usually hydrogen gas (which is highly explosive) is released 3. Other Reactions – include heat being released, bubbling, strong odor, smoke, flame, change of color, etc. 4. Non-Reactivity – when something fails to react…example…platinum droppe ...
PERIODIC TABLE
... to the following equation: a C8H16 + b O2 → c CO2 + d H2O In a balanced equation, the factors a, b, c, and d have the values: a- (a = 1, b = 1, c = 1, d = 1) b- (a = 1, b = 12, c = 8, d = 16) c- (a = 1, b = 12, c = 8, d = 8) d- (a = 1, b = 6, c = 8, d = 16) 41- If the equilibrium constant (K1) for t ...
... to the following equation: a C8H16 + b O2 → c CO2 + d H2O In a balanced equation, the factors a, b, c, and d have the values: a- (a = 1, b = 1, c = 1, d = 1) b- (a = 1, b = 12, c = 8, d = 16) c- (a = 1, b = 12, c = 8, d = 8) d- (a = 1, b = 6, c = 8, d = 16) 41- If the equilibrium constant (K1) for t ...
Ch 19 test_take-home
... A) the reverse process is spontaneous but the forward process is not B) the forward and the reverse processes are both spontaneous C) the forward process is spontaneous but the reverse process is not D) the process is not spontaneous in either direction E) both forward and reverse processes have sto ...
... A) the reverse process is spontaneous but the forward process is not B) the forward and the reverse processes are both spontaneous C) the forward process is spontaneous but the reverse process is not D) the process is not spontaneous in either direction E) both forward and reverse processes have sto ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.