CHAPTER 9
... (1) Electron loss is always associated with an increase in oxidation number. (2) An exothermic reaction occurs when the energy required to break bonds in reactants is less than the energy released by bond formation in the products. (3) The concentrations of pure liquids and pure solids are never inc ...
... (1) Electron loss is always associated with an increase in oxidation number. (2) An exothermic reaction occurs when the energy required to break bonds in reactants is less than the energy released by bond formation in the products. (3) The concentrations of pure liquids and pure solids are never inc ...
Standard Enthalpy of Formation
... Hence ∆U per mole of glucose burned is: (-31.34k/J)(0.001119mol)= -2801 kJ/mol ...
... Hence ∆U per mole of glucose burned is: (-31.34k/J)(0.001119mol)= -2801 kJ/mol ...
New substances are formed by chemical reactions. When elements
... Covalent bonds Compounds formed from non-metals consist of molecules. The atoms in a molecule are joined together by covalent bonds. These bonds form when atoms share pairs of electrons. Chemical formulas The chemical formula of a compound shows how many of each type of atom join together to make th ...
... Covalent bonds Compounds formed from non-metals consist of molecules. The atoms in a molecule are joined together by covalent bonds. These bonds form when atoms share pairs of electrons. Chemical formulas The chemical formula of a compound shows how many of each type of atom join together to make th ...
K,7th Grade Test Review: Atoms and Chemical Reactions PART
... PART FOUR: Chemical Equations. For each equation, label the products and reactants. Then, count the number of atoms of each element on each side. Then fill in the blanks. ...
... PART FOUR: Chemical Equations. For each equation, label the products and reactants. Then, count the number of atoms of each element on each side. Then fill in the blanks. ...
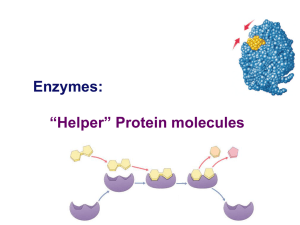
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Enzymes aren’t used up Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily – like a taxi re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
... Enzymes aren’t used up Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily – like a taxi re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
Chemistry Module 1- Basic Revision Notes 1.1a Atomic Structure 1.1
... These metals are the most chemically reactive group of metals and increase in reactivity down the group, they also, are known as soft metals(i.e. can be cut easily by a knife) are low in density(i.e. they even float on water) are stored under paraffin (oil) due to their high reactivity with wa ...
... These metals are the most chemically reactive group of metals and increase in reactivity down the group, they also, are known as soft metals(i.e. can be cut easily by a knife) are low in density(i.e. they even float on water) are stored under paraffin (oil) due to their high reactivity with wa ...
No Slide Title
... 3. Cancel the spectator ions on both sides of the ionic equation 4. Check that charges and number of atoms are balanced in the net ionic equation ...
... 3. Cancel the spectator ions on both sides of the ionic equation 4. Check that charges and number of atoms are balanced in the net ionic equation ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... 2. What is standard temperature and standard pressure? 3. Know how to solve problems using Boyle’s law, Charles law, Gay-Lussac, Combined, Ideal, Density and Molar mass using the Ideal gas law and Dalton’s law of partial pressure. a) A gas occupies a volume of 200. ml at 100. mmHg. What volume will ...
... 2. What is standard temperature and standard pressure? 3. Know how to solve problems using Boyle’s law, Charles law, Gay-Lussac, Combined, Ideal, Density and Molar mass using the Ideal gas law and Dalton’s law of partial pressure. a) A gas occupies a volume of 200. ml at 100. mmHg. What volume will ...
advanced placement chemistry alamo heights high school scope
... Students examine a demonstration size model of DNA or an alpha helix, and use their fingers to identify which atoms / base pairs are particularly involved in hydrogen bonding within the molecule, causin ...
... Students examine a demonstration size model of DNA or an alpha helix, and use their fingers to identify which atoms / base pairs are particularly involved in hydrogen bonding within the molecule, causin ...
Free response review
... the sample exists entirely as diatomic molecules? Explain your answer. d. Calculate the mass of the chlorine molecule having the largest molecular mass. e. What is the mass of the most abundant molecule? Calculate its % abundance. 2. Like chlorine, iodine is a halogen and forms similar compounds. Wr ...
... the sample exists entirely as diatomic molecules? Explain your answer. d. Calculate the mass of the chlorine molecule having the largest molecular mass. e. What is the mass of the most abundant molecule? Calculate its % abundance. 2. Like chlorine, iodine is a halogen and forms similar compounds. Wr ...
Writing Chemical Reactions
... this has more to do with potential questions about reactions than with balancing techniques for nontrivial redox reactions. For example, some reactions students have been asked to write in the past are things they would never have seen. Whether this will remain the case is not known, but if it does, ...
... this has more to do with potential questions about reactions than with balancing techniques for nontrivial redox reactions. For example, some reactions students have been asked to write in the past are things they would never have seen. Whether this will remain the case is not known, but if it does, ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.