study packet for chapter 5
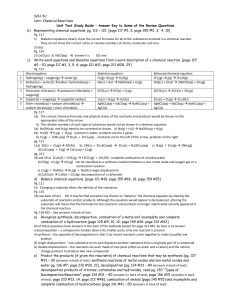
... 17) A chemical reaction that absorbs heat from the surroundings is said to be ________ and has a ________ ΔH at constant pressure. A) endothermic, positive B) endothermic, negative C) exothermic, negative D) exothermic, positive E) exothermic, neutral 18) A chemical reaction that releases heat to th ...
... 17) A chemical reaction that absorbs heat from the surroundings is said to be ________ and has a ________ ΔH at constant pressure. A) endothermic, positive B) endothermic, negative C) exothermic, negative D) exothermic, positive E) exothermic, neutral 18) A chemical reaction that releases heat to th ...
Review Worksheet
... c) These particles are considered to be dimensionless points which occupy zero volume. The volume of real gas molecules is assumed to be __________ for most purposes. This above statement is NOT TRUE. Real gas molecules do occupy volume and it does have an impact on the behavior of the gas. This imp ...
... c) These particles are considered to be dimensionless points which occupy zero volume. The volume of real gas molecules is assumed to be __________ for most purposes. This above statement is NOT TRUE. Real gas molecules do occupy volume and it does have an impact on the behavior of the gas. This imp ...
Preview Sample 1
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
... Chemicals used as reagents, such as bromthymol blue or sodium iodide, may permanently stain clothing. Use with caution. ...
SCH 3U - mquagliaoths
... 20) non-metal oxides form acids in water and metal oxides form bases a) base (BaOH) b) acid (H3PO4) c) acid (H2CO3) d) base (LiOH) 21) a non-metal oxide 24) The flame showing complete combustion is on the right. It is a stronger, blue-white flame indicating lots of oxygen is present and the fuel is ...
... 20) non-metal oxides form acids in water and metal oxides form bases a) base (BaOH) b) acid (H3PO4) c) acid (H2CO3) d) base (LiOH) 21) a non-metal oxide 24) The flame showing complete combustion is on the right. It is a stronger, blue-white flame indicating lots of oxygen is present and the fuel is ...
Electrochemistry - Menihek Home Page
... Application of Oxidation Numbers to Redox Reactions To determine the redox half-reactions for a chemical reaction, you must first determine whether the reaction is redox or not. To do this, assign oxidation numbers to each atom or ion and then compare.....if the oxidation numbers do not change it is ...
... Application of Oxidation Numbers to Redox Reactions To determine the redox half-reactions for a chemical reaction, you must first determine whether the reaction is redox or not. To do this, assign oxidation numbers to each atom or ion and then compare.....if the oxidation numbers do not change it is ...
C6_rev - boswellsrcd
... • These show the increasing amount of product or the decreasing amount of reactant. ...
... • These show the increasing amount of product or the decreasing amount of reactant. ...
chapter 4 lecture slides
... non electrolytes are written as molecules 3. Cancel the spectator ions on both sides of the ionic equation 4. Check that charges and number of atoms are balanced in the net ionic equation Write the net ionic equation for the reaction of silver nitrate with sodium chloride. ...
... non electrolytes are written as molecules 3. Cancel the spectator ions on both sides of the ionic equation 4. Check that charges and number of atoms are balanced in the net ionic equation Write the net ionic equation for the reaction of silver nitrate with sodium chloride. ...
Lecture 4
... 4. Cancel the spectator ions on both sides of the ionic equation Write the net ionic equation for the reaction of silver nitrate with sodium chloride. ...
... 4. Cancel the spectator ions on both sides of the ionic equation Write the net ionic equation for the reaction of silver nitrate with sodium chloride. ...
Topic 4
... Topic 4 Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions are the heart of chemistry. Chemical reactions involve a change from reactant substances to product substances. The products have physical and chemical properties different from those of the reactants. ...
... Topic 4 Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions are the heart of chemistry. Chemical reactions involve a change from reactant substances to product substances. The products have physical and chemical properties different from those of the reactants. ...
Biology\Ch 2 Chemistry
... pulls harder on the electrons than the hydrogens do. So, the oxygen “edge” is more negative than the hydrogen portions. This makes water almost magnetic, so it likes to cling to surfaces. This is called adhesion. Because water is polar, ionic substances, like NaCl, dissolve easily in it. Nonpolar su ...
... pulls harder on the electrons than the hydrogens do. So, the oxygen “edge” is more negative than the hydrogen portions. This makes water almost magnetic, so it likes to cling to surfaces. This is called adhesion. Because water is polar, ionic substances, like NaCl, dissolve easily in it. Nonpolar su ...
Sample % Sulfate Absolute Deviation A 44.02 B 44.11 C 43.98 D
... unreacted red powder. If the mass of the resulting mixture is 82.5 g, how much oxygen was produced during the heating? Which law are you making use of for this answer? ...
... unreacted red powder. If the mass of the resulting mixture is 82.5 g, how much oxygen was produced during the heating? Which law are you making use of for this answer? ...
Review Outline for Atomic Structure Test
... A) Identifying elements by atomic number a. Atomic # is the number of? protons B) Identifying elements with the same number of valence electrons (which column?)-see first periodic table below a. Which elements have one valence electron? Group/Family 1 b. Which elements have two valence electrons? Gr ...
... A) Identifying elements by atomic number a. Atomic # is the number of? protons B) Identifying elements with the same number of valence electrons (which column?)-see first periodic table below a. Which elements have one valence electron? Group/Family 1 b. Which elements have two valence electrons? Gr ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.