key concepts of matter
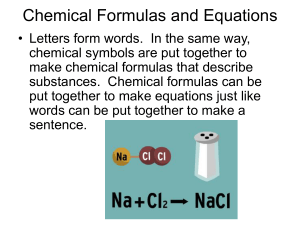
... Key Concept 2: A chemical formula is the combination of all of the elemental symbols found within a substance. The atom numbers of each element are identified by subscripts to the right of the elemental symbol. Key Concept 3: A chemical equation shows the atom numbers and molecules making up the rea ...
... Key Concept 2: A chemical formula is the combination of all of the elemental symbols found within a substance. The atom numbers of each element are identified by subscripts to the right of the elemental symbol. Key Concept 3: A chemical equation shows the atom numbers and molecules making up the rea ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
... C) the same atomic numbers but different numbers of electrons. D) the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons. E) the same atomic mass but different numbers of protons. 47) A sample of chlorine has two naturally occurring isotopes. The isotope Cl-35 (mass 35.0 amu) makes up 75.8% of the ...
... C) the same atomic numbers but different numbers of electrons. D) the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons. E) the same atomic mass but different numbers of protons. 47) A sample of chlorine has two naturally occurring isotopes. The isotope Cl-35 (mass 35.0 amu) makes up 75.8% of the ...
(p. 522)
... d. The alcohol will have the higher boiling point; it will have hydrogen bonding while the ether does not. 4. You are required to determine the energy of activation (Ea) of a reaction. Briefly describe the experimental measurements you would make and how you would obtain the activation energy from a ...
... d. The alcohol will have the higher boiling point; it will have hydrogen bonding while the ether does not. 4. You are required to determine the energy of activation (Ea) of a reaction. Briefly describe the experimental measurements you would make and how you would obtain the activation energy from a ...
1 2016-17 Honors Chemistry Review for the Final Exam Each unit
... (b) How many moles of magnesium chloride are found in a sample containing 4.50 x 1022 formula units of magnesium chloride? ...
... (b) How many moles of magnesium chloride are found in a sample containing 4.50 x 1022 formula units of magnesium chloride? ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... Generation of heat/cold, light, solid from liquid, smoke, odor 2. Use the word bank to match the correct term with its definition. decomposition reaction Law of Conservation of Mass double replacement reactions neutralization reaction ...
... Generation of heat/cold, light, solid from liquid, smoke, odor 2. Use the word bank to match the correct term with its definition. decomposition reaction Law of Conservation of Mass double replacement reactions neutralization reaction ...
L1 – CHEMISTRY FINAL REVIEW
... c. HBr- Polar molecule; dipole-dipole interactions between the molecules; medium strength interactions. 28. What are some major differences between the following types of solids? In terms of Mpt/Bpt, solubility, and conductivity. Metallic, Ionic, Polar Molecular, and Nonpolar Molecular. Give an exam ...
... c. HBr- Polar molecule; dipole-dipole interactions between the molecules; medium strength interactions. 28. What are some major differences between the following types of solids? In terms of Mpt/Bpt, solubility, and conductivity. Metallic, Ionic, Polar Molecular, and Nonpolar Molecular. Give an exam ...
(1/V m C) +
... R is the gas constant, and T is the absolute temperatures. The Gibbs adsorption equation allows one to determine the amount of surfactant adsorption Γ (moles m−2) from a plot of log γ (the surface tension at the air/water interface or interfacial tension at the liquid/liquid interface) versus log ...
... R is the gas constant, and T is the absolute temperatures. The Gibbs adsorption equation allows one to determine the amount of surfactant adsorption Γ (moles m−2) from a plot of log γ (the surface tension at the air/water interface or interfacial tension at the liquid/liquid interface) versus log ...
Chemistry Unit Summaries - Oak Park Unified School District
... as we carry measurements through calculations. The given units absorbed by matter. are multiplied by a series of conversion factors, which are ratios Equations for radiant energy, Ephoton = hf and speed of light, of equivalent quantities. After canceling out units algebraically, c = f are combined ...
... as we carry measurements through calculations. The given units absorbed by matter. are multiplied by a series of conversion factors, which are ratios Equations for radiant energy, Ephoton = hf and speed of light, of equivalent quantities. After canceling out units algebraically, c = f are combined ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... Generation of heat/cold, light, solid from liquid, smoke, odor 2. Use the word bank to match the correct term with its definition. decomposition reaction Law of Conservation of Mass double replacement reactions neutralization reaction ...
... Generation of heat/cold, light, solid from liquid, smoke, odor 2. Use the word bank to match the correct term with its definition. decomposition reaction Law of Conservation of Mass double replacement reactions neutralization reaction ...
File
... 16. Compared to an electron in the first electron shell of an atom, an electron in the third shell of the same atom has A) methane B) mercury C) ethanol D) ammonia A) less mass B) less energy 26. Which element is classified as a nonmetal? C) more mass D) more energy 17. Which electron configuration ...
... 16. Compared to an electron in the first electron shell of an atom, an electron in the third shell of the same atom has A) methane B) mercury C) ethanol D) ammonia A) less mass B) less energy 26. Which element is classified as a nonmetal? C) more mass D) more energy 17. Which electron configuration ...
NC Exam Questions - Rosshall Academy
... What name is given to the change in protein structure which occurs when ordinary cheddar is grilled? (1) (b) To make cheese for burgers, grated cheddar cheese, soluble milk proteins and some water are mixed and heated to no more than 82 °C. As the cheese begins to melt an emulsifying agent is added ...
... What name is given to the change in protein structure which occurs when ordinary cheddar is grilled? (1) (b) To make cheese for burgers, grated cheddar cheese, soluble milk proteins and some water are mixed and heated to no more than 82 °C. As the cheese begins to melt an emulsifying agent is added ...
Chemistry MSL Practical Style Review 1. What is the nuclear
... 17. In a titration experiment, if 30.0 mL of an HCl solution reacts with 24.6 mL of a 0.50-M NaOH solution, what is the concentration of the HCl solution? A B C D ...
... 17. In a titration experiment, if 30.0 mL of an HCl solution reacts with 24.6 mL of a 0.50-M NaOH solution, what is the concentration of the HCl solution? A B C D ...
Chemical Equations
... The reactants are listed on the left side and show what went into the reaction. The products are on the right side and show what was produced by the reaction. The arrow is like an = sign, but shows the direction of the reaction. The coefficients show the ratio in which the substances reacted/were pr ...
... The reactants are listed on the left side and show what went into the reaction. The products are on the right side and show what was produced by the reaction. The arrow is like an = sign, but shows the direction of the reaction. The coefficients show the ratio in which the substances reacted/were pr ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.