Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
... Azimuthal or orbital or angular or subsidary quantum number: It denotes the sub level to which an electron belongs and also tells about its shape. It is denoted by 'l'. The permitted values of 'l' are 0, 1, 2, etc., upto n-1. 'l' can have zero value unlike 'n'. The maximum value of 'l' is equal to n ...
... Azimuthal or orbital or angular or subsidary quantum number: It denotes the sub level to which an electron belongs and also tells about its shape. It is denoted by 'l'. The permitted values of 'l' are 0, 1, 2, etc., upto n-1. 'l' can have zero value unlike 'n'. The maximum value of 'l' is equal to n ...
n = 2. - Cloudfront.net
... that a photon is emitted only when an electron moves from a higher energy orbit to a lower energy one. ...
... that a photon is emitted only when an electron moves from a higher energy orbit to a lower energy one. ...
Chapter Summary
... Finally, the spin angular momentum can take on one of only two values, conventionally referred to as “spin up” and “spin down.” The spin angular momentum is characterized by the spin quantum number, which can take on values of +1/2 or –1/2. Understanding the periodic table of elements One key to und ...
... Finally, the spin angular momentum can take on one of only two values, conventionally referred to as “spin up” and “spin down.” The spin angular momentum is characterized by the spin quantum number, which can take on values of +1/2 or –1/2. Understanding the periodic table of elements One key to und ...
chapter-27-1-with
... Max Planck found he could explain these curves if he assumed that electromagnetic energy was radiated in ...
... Max Planck found he could explain these curves if he assumed that electromagnetic energy was radiated in ...
The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this
... Together we form an ionic bond Though we are opposite charged ions I am drawn towards you Our love is unique as an orbital For only two electrons can fill this space As my love for you increases My energy level rises I am in this excited state Increasing the tendency to form a chemical bond I was an ...
... Together we form an ionic bond Though we are opposite charged ions I am drawn towards you Our love is unique as an orbital For only two electrons can fill this space As my love for you increases My energy level rises I am in this excited state Increasing the tendency to form a chemical bond I was an ...
Physics 124 : Particles and Waves
... and positron the newly formed particles won’t move. Any ‘excess’ energy will be converted into kinetic energy. Pair production requires the presence of another photon or nucleus which can absorb the photon’s momentum and for conservation of momentum not to be violated. ...
... and positron the newly formed particles won’t move. Any ‘excess’ energy will be converted into kinetic energy. Pair production requires the presence of another photon or nucleus which can absorb the photon’s momentum and for conservation of momentum not to be violated. ...
Objective 6: TSW explain how the quantum
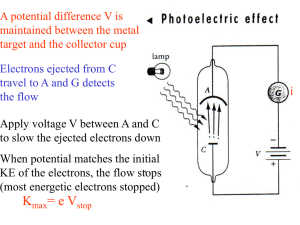
... reflect off of surfaces and that it has a speed • Photoelectric effect: the ejection of electrons from a metal surface when that surface is exposed to electromagnetic radiation of sufficiently high frequency • In 1905 Einstein was able to explain the photoelectric effect by using Planck’s quantum th ...
... reflect off of surfaces and that it has a speed • Photoelectric effect: the ejection of electrons from a metal surface when that surface is exposed to electromagnetic radiation of sufficiently high frequency • In 1905 Einstein was able to explain the photoelectric effect by using Planck’s quantum th ...
MYP Chemistry: Final Review
... What is the difference between a bright line spectrum and a continuous spectrum? Continuous spectrum contains all wavelengths (ROYGBV) like a rainbow. Bright line spectrum shows discrete wavelengths like red or blue or green, but not all the colors ...
... What is the difference between a bright line spectrum and a continuous spectrum? Continuous spectrum contains all wavelengths (ROYGBV) like a rainbow. Bright line spectrum shows discrete wavelengths like red or blue or green, but not all the colors ...
PH469 Fall 2002
... 7) In a Stern-Gerlach type of experiment, the magnetic field varies with distance in the z direction according to dBz/dz = 1.4 T/m. The silver atoms travel a distance x = 3.5 cm. The most probable speed of the atoms emerging from the oven is v = 750 m/s. Find the separation of the two beams as they ...
... 7) In a Stern-Gerlach type of experiment, the magnetic field varies with distance in the z direction according to dBz/dz = 1.4 T/m. The silver atoms travel a distance x = 3.5 cm. The most probable speed of the atoms emerging from the oven is v = 750 m/s. Find the separation of the two beams as they ...
Ch. 5 PPT Part 2
... The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom • The wave function predicts a threedimensional region around the nucleus called the atomic orbital. ...
... The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom • The wave function predicts a threedimensional region around the nucleus called the atomic orbital. ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.