P403H Atomic Systems
... By the end of the course, students will be able to demonstrate a knowledge and broad understanding of quantum mechanics applied to atoms. They should be able to solve the Schröding ...
... By the end of the course, students will be able to demonstrate a knowledge and broad understanding of quantum mechanics applied to atoms. They should be able to solve the Schröding ...
AMU File
... There is also an energy unit that is associated with the amu. The unit is the electron volt (eV). ...
... There is also an energy unit that is associated with the amu. The unit is the electron volt (eV). ...
The Egyptian American International School
... Characterized by its wavelength and frequency Can be thought of as a stream of packets of energy called photons Atoms can gain energy by absorbing a photon or lose energy by emitting a photon. The photoelectric effect. 11.2 The Hydrogen Atom The hydrogen atom can emit only certain energies as it ...
... Characterized by its wavelength and frequency Can be thought of as a stream of packets of energy called photons Atoms can gain energy by absorbing a photon or lose energy by emitting a photon. The photoelectric effect. 11.2 The Hydrogen Atom The hydrogen atom can emit only certain energies as it ...
Environmental Physics for Freshman Geography Students
... where q1 and q2 are the amounts of electric charge (measured in coulombs, C), r is the distance between them (measured in m), and K is Coulomb’s electrostatic constant (= 8.99 x 109 kg m3 s-2 C-2). The introduction of electric charges into the simple world of mechanics requires the use of a new dime ...
... where q1 and q2 are the amounts of electric charge (measured in coulombs, C), r is the distance between them (measured in m), and K is Coulomb’s electrostatic constant (= 8.99 x 109 kg m3 s-2 C-2). The introduction of electric charges into the simple world of mechanics requires the use of a new dime ...
Lecture9,ch4
... maximum photon energy where we neglect the work function because it is normally so small compared to the potential energy of the electron. This yields the Duane-Hunt limit which was first found experimentally. The photon wavelength depends only on the accelerating voltage and is the same for all tar ...
... maximum photon energy where we neglect the work function because it is normally so small compared to the potential energy of the electron. This yields the Duane-Hunt limit which was first found experimentally. The photon wavelength depends only on the accelerating voltage and is the same for all tar ...
What is Light?
... • Emission Spectrum - Bunsen and Kirchoff (1859) • Gas is stimulated (by heating or high voltage) to emit light • Spectroscopic pattern is opposite of absorption spectrum • Matched spectra of earth’s elements to Fraunhofer lines (He) ...
... • Emission Spectrum - Bunsen and Kirchoff (1859) • Gas is stimulated (by heating or high voltage) to emit light • Spectroscopic pattern is opposite of absorption spectrum • Matched spectra of earth’s elements to Fraunhofer lines (He) ...
Random Laser - Department of Physics
... Cathodoluminescence (CL) is an important physical phenomena used to characterize semiconductors which depicts a sample’s energy structure while possibly revealing other important material features. In brief, CL occurs when a sample absorbs electrons and emits light at a specific frequency correspond ...
... Cathodoluminescence (CL) is an important physical phenomena used to characterize semiconductors which depicts a sample’s energy structure while possibly revealing other important material features. In brief, CL occurs when a sample absorbs electrons and emits light at a specific frequency correspond ...
Chapter 7 - Gordon State College
... Energy Levels • The electrons are found at a certain distance from nucleus in their shell(s). • energy level = shell (interchangeable ...
... Energy Levels • The electrons are found at a certain distance from nucleus in their shell(s). • energy level = shell (interchangeable ...
CHAPTER 10 - NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... Since group 8 elements have 8 electrons in the outer shell, they neither gain nor lose electrons and do not form chemical bonds with anything. They can be artificially forced to. When chemical bonds form, the number of electrons lost by one element must equal the number of electrons gained by the ...
... Since group 8 elements have 8 electrons in the outer shell, they neither gain nor lose electrons and do not form chemical bonds with anything. They can be artificially forced to. When chemical bonds form, the number of electrons lost by one element must equal the number of electrons gained by the ...
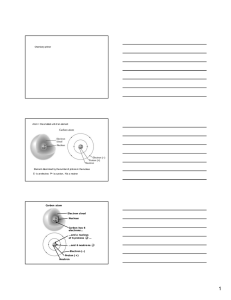
Matter is made of atoms The atom of each element is characterized
... The spectral lines can be resolved with a prism or a diffraction grating. Multi-electron atoms are complicated. Rules to be learned about later limit the number of electrons in any one state. Thus the electrons in an atom are arranged in concentric shells. The shells are labelled K, L, M, N, etc., s ...
... The spectral lines can be resolved with a prism or a diffraction grating. Multi-electron atoms are complicated. Rules to be learned about later limit the number of electrons in any one state. Thus the electrons in an atom are arranged in concentric shells. The shells are labelled K, L, M, N, etc., s ...
Review of Definitions
... 12. Bond Rupture Strength. Binding energy needed to break a bond. 13.Ionization. Any process by which an electrically neutral atom or molecule is converted into an electrically charged atom or molecule 14. Dielectric material. An insulating material or a very poor conductor of electric current. When ...
... 12. Bond Rupture Strength. Binding energy needed to break a bond. 13.Ionization. Any process by which an electrically neutral atom or molecule is converted into an electrically charged atom or molecule 14. Dielectric material. An insulating material or a very poor conductor of electric current. When ...
PHYS150-Ch28
... Wave Functions for a Confined Particle A particle confined to a region of space will have quantized energy levels. Consider a particle in a box of width L that has impenetrable walls, that is, the particle can never leave the box. Since the particle can ...
... Wave Functions for a Confined Particle A particle confined to a region of space will have quantized energy levels. Consider a particle in a box of width L that has impenetrable walls, that is, the particle can never leave the box. Since the particle can ...
Chapter 8 - Chemistry
... - energy depends primarily on n, increasing with its value - energies of orbitals with same n increase with the l quantum number - that is, 3p orbital has slightly greater energy than 3s orbital - exception: when subshells have nearly same energy, building- up order is not strictly determined by ord ...
... - energy depends primarily on n, increasing with its value - energies of orbitals with same n increase with the l quantum number - that is, 3p orbital has slightly greater energy than 3s orbital - exception: when subshells have nearly same energy, building- up order is not strictly determined by ord ...
ECE692_3_1008
... Hint: Fermi-Dirac distribution approximated by Boltzmann distribution. Results for n and p are given. ...
... Hint: Fermi-Dirac distribution approximated by Boltzmann distribution. Results for n and p are given. ...
TEST REVIEW S Valence Electrons TEST REVIEW SHEET 2017
... ionic bond and become a positive ion. If >4, it will take them and become a negative ion For the most part…. metals will give away their valence electrons and nonmetals will take enough valence electrons to fill their outer shell. Determine the charge (ionization number) for the following elements w ...
... ionic bond and become a positive ion. If >4, it will take them and become a negative ion For the most part…. metals will give away their valence electrons and nonmetals will take enough valence electrons to fill their outer shell. Determine the charge (ionization number) for the following elements w ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.























