File
... 89. The ability to conduct electricity in the solid state is a characteristic of metallic bonding. This characteristic is best explained by the presence of A) high ionization energies B) high electronegativities C) mobile electrons D) mobile protons 90. Which formula represents a nonpolar molecule c ...
... 89. The ability to conduct electricity in the solid state is a characteristic of metallic bonding. This characteristic is best explained by the presence of A) high ionization energies B) high electronegativities C) mobile electrons D) mobile protons 90. Which formula represents a nonpolar molecule c ...
S90 Notes U2 Topic 6 Chemical Compounds
... Naming ionic compounds: Ex. NaCl, LiF, CaCl2 Rules are from IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) 1. Name the metallic element 1st as it is written on the periodic table. 2. Name the nonmetallic element second, changing its ending to “ide.” 3. Positive and negative charges must e ...
... Naming ionic compounds: Ex. NaCl, LiF, CaCl2 Rules are from IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) 1. Name the metallic element 1st as it is written on the periodic table. 2. Name the nonmetallic element second, changing its ending to “ide.” 3. Positive and negative charges must e ...
Chem 1411 Chapt2
... have the same composition. Example, each water molecules has 2 hydrogen atoms for every oxygen atom. Law of Conservation of matter- Matter can neither be created nor destroyed. Radioactivity- Spontaneous emission of radiation, atomic and subatomic particles. X-Rays- High energy light(photons). Gamma ...
... have the same composition. Example, each water molecules has 2 hydrogen atoms for every oxygen atom. Law of Conservation of matter- Matter can neither be created nor destroyed. Radioactivity- Spontaneous emission of radiation, atomic and subatomic particles. X-Rays- High energy light(photons). Gamma ...
Quantum Number - Career Launcher
... If the nitrogen atom had electronic configuration 1s7, it would have energy lower than that of the normal ground state configuration 1s2 2s2 2p3, because the electrons would be closer to the nucleus. Yet 1s7 is not observed because it violates (a) Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle ...
... If the nitrogen atom had electronic configuration 1s7, it would have energy lower than that of the normal ground state configuration 1s2 2s2 2p3, because the electrons would be closer to the nucleus. Yet 1s7 is not observed because it violates (a) Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle ...
video slide
... a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom in a different molecule In living cells, the electronegative partners are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms ...
... a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom in a different molecule In living cells, the electronegative partners are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms ...
End Show
... The Quantum Mechanical Model What does the quantum mechanical model determine about the electrons in an atom? The quantum mechanical model determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations Slide around the nucleus. 6 of 26 © Copyright ...
... The Quantum Mechanical Model What does the quantum mechanical model determine about the electrons in an atom? The quantum mechanical model determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations Slide around the nucleus. 6 of 26 © Copyright ...
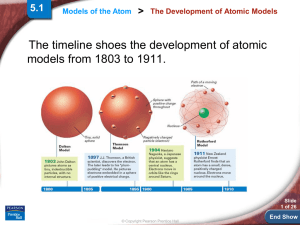
Models of the Atom > The Development of Atomic Models
... 1961) used new theoretical calculations and results to devise and solve a mathematical equation describing the behavior of the electron in a hydrogen atom. The modern description of the electrons in atoms, the quantum mechanical model, comes from the mathematical solutions to the Schrödinger equatio ...
... 1961) used new theoretical calculations and results to devise and solve a mathematical equation describing the behavior of the electron in a hydrogen atom. The modern description of the electrons in atoms, the quantum mechanical model, comes from the mathematical solutions to the Schrödinger equatio ...
Assignment 6
... e) Substitute in these forms for the integrals to get a function for the expected ground state electronic energy. Use Mathematica or whatever package you like to plot this energy function versus Z and R. Choose some appropriate energy scale to make the energy function dimensionless; make sure you st ...
... e) Substitute in these forms for the integrals to get a function for the expected ground state electronic energy. Use Mathematica or whatever package you like to plot this energy function versus Z and R. Choose some appropriate energy scale to make the energy function dimensionless; make sure you st ...
topic 3: periodicity
... As you go down: reactivity decreases; fluorine is the most reactive halogen and best oxidising agent (why does the oxidising ability decrease as you go down?) (fluorine has the highest electronegativity because of its smallest radius and little shielding); F2 oxidises Cl-, Br- and I- to Cl2, Br2 a ...
... As you go down: reactivity decreases; fluorine is the most reactive halogen and best oxidising agent (why does the oxidising ability decrease as you go down?) (fluorine has the highest electronegativity because of its smallest radius and little shielding); F2 oxidises Cl-, Br- and I- to Cl2, Br2 a ...
1 Rutherford`s Nuclear Model of the atom A is the currently accepted
... does not account for the stability of most atoms since C accelerating electrons would quickly lose energy and fall into the nucleus, causing the atom to collapse. D ...
... does not account for the stability of most atoms since C accelerating electrons would quickly lose energy and fall into the nucleus, causing the atom to collapse. D ...
Four Quantum Numbers
... • Four d orbitals have same shape but different orientations • Fifth d orbital, 3dz2 is shaped and oriented different from the other four ...
... • Four d orbitals have same shape but different orientations • Fifth d orbital, 3dz2 is shaped and oriented different from the other four ...
Is Matter Made of Light? The Transluminal Energy Quantum (TEQ
... is formed of a helical vortex or circular ring of charged filiments circulating at high speed along a common continuous path in an atom. Also known as the "toroidal ring model","magnetic electron", "plasmoid ring", "vortex ring", or "helicon ring". Parson’s magneton model for chemical bonding and el ...
... is formed of a helical vortex or circular ring of charged filiments circulating at high speed along a common continuous path in an atom. Also known as the "toroidal ring model","magnetic electron", "plasmoid ring", "vortex ring", or "helicon ring". Parson’s magneton model for chemical bonding and el ...
Bonding and Nomenclature
... • Step #4: If there are no electrons left, move electrons from a different atom to form another bond…double • Side note: When more than one Lewis structure can be drawn, the molecule or ion is said to have resonance. ...
... • Step #4: If there are no electrons left, move electrons from a different atom to form another bond…double • Side note: When more than one Lewis structure can be drawn, the molecule or ion is said to have resonance. ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.