Chapter 6 HEAT CAPACITY, ENTHALPY, ENTROPY, AND
... in 1819 which states that the molar heat capacities of all solid elements have the value 3R(=24.9 J/K), and, in 1865, Kopp introduced a rule which states that, at ordinary temperatures, the molar heat capacity of a solid chemical compound is approximately equal to the sum of molar heat capacities of ...
... in 1819 which states that the molar heat capacities of all solid elements have the value 3R(=24.9 J/K), and, in 1865, Kopp introduced a rule which states that, at ordinary temperatures, the molar heat capacity of a solid chemical compound is approximately equal to the sum of molar heat capacities of ...
Exam
... 51) A solution is prepared by dissolving 2 g of KCl in 100 g of H2 O. In this solution, H2 O is the A) solute. B) solvent. C) solution. D) solid. E) ionic compound. 52) Oil does not dissolve in water because A) oil is polar. B) oil is nonpolar. C) water is nonpolar. D) water is saturated. E) oil is ...
... 51) A solution is prepared by dissolving 2 g of KCl in 100 g of H2 O. In this solution, H2 O is the A) solute. B) solvent. C) solution. D) solid. E) ionic compound. 52) Oil does not dissolve in water because A) oil is polar. B) oil is nonpolar. C) water is nonpolar. D) water is saturated. E) oil is ...
1 3. Molecular mass transport 3.1 Introduction to mass transfer 3.2
... [ from Ideal gas law PV = nRT] ...
... [ from Ideal gas law PV = nRT] ...
1. Define the following term: system. A) The part of the universe that
... A) State functions: P,V; Not: work, energy B) State functions: energy, P; Not: T, heat C) State functions: energy, V; Not: work, heat D) State functions: energy, work; Not: T, heat ...
... A) State functions: P,V; Not: work, energy B) State functions: energy, P; Not: T, heat C) State functions: energy, V; Not: work, heat D) State functions: energy, work; Not: T, heat ...
ELECTROLYTE CONDUCTANCE
... upon the degree of dissociation with dilution. Higher the degree of dissociation, larger is the molar conductance. With increase in dilution Degree of dissociation increases as a result molar conductivity increases. At infinite dilution, the electrolyte is completely dissociated so that the ...
... upon the degree of dissociation with dilution. Higher the degree of dissociation, larger is the molar conductance. With increase in dilution Degree of dissociation increases as a result molar conductivity increases. At infinite dilution, the electrolyte is completely dissociated so that the ...
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Front Nucleation in a Bistable
... on a Pt( 100) surface.l.2 Propagating reaction fronts, spiral waves, and turbulent patterns have been observed a t temperatures between about 420 and 440 K.3-5 In this parameter range the surface reaction rate oscillates only on a local scale, but macroscopic rate oscillations can be excited by a sm ...
... on a Pt( 100) surface.l.2 Propagating reaction fronts, spiral waves, and turbulent patterns have been observed a t temperatures between about 420 and 440 K.3-5 In this parameter range the surface reaction rate oscillates only on a local scale, but macroscopic rate oscillations can be excited by a sm ...
Experimental Study of Closed System in the Chlorine Dioxide
... When the mole ratio r is below or equal to 1.00 (see curves 1 and 2), the absorbance decreases along with the extension of reaction time at 350 nm and then does not change with the reaction time afterwards. Under the condition that r is greater than 1.00 (see curve 3 to curve 7), the absorbance incr ...
... When the mole ratio r is below or equal to 1.00 (see curves 1 and 2), the absorbance decreases along with the extension of reaction time at 350 nm and then does not change with the reaction time afterwards. Under the condition that r is greater than 1.00 (see curve 3 to curve 7), the absorbance incr ...
Effect of an industrial chemical waste on the uptake
... acids, as fractions of humic substances, are the most important HS components that, due to their high structural complexity, contribute to the overall fate of trace metal cations, such as Pb(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) and Cd(II), in environment. 5–7 They contain a variety of functional groups which may rea ...
... acids, as fractions of humic substances, are the most important HS components that, due to their high structural complexity, contribute to the overall fate of trace metal cations, such as Pb(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) and Cd(II), in environment. 5–7 They contain a variety of functional groups which may rea ...
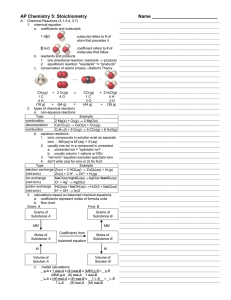
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... convert 9.0 g of glucose into moles (MM 180) convert moles of glucose into moles of water convert moles of water into grams (MM 18.02) convert grams of water into mL a) How? what is the relationship between mass and volume? density of water = 1.00 g/mL ...
... convert 9.0 g of glucose into moles (MM 180) convert moles of glucose into moles of water convert moles of water into grams (MM 18.02) convert grams of water into mL a) How? what is the relationship between mass and volume? density of water = 1.00 g/mL ...
A Low-Fluorine Solution with the F/Ba Mole Ratio of 2 for the
... deionized water, and propionic acid were mixed directly. The quantity of TFA was 10.3 mol.% of the total CH3 COO− anion with a uncertainty estimated to be 0.5%. After stirring for 1 h, the obtained solution was refined in a BUCHI Rotavapor R210 rotary evaporator under decompression for 2 h. Methanol ...
... deionized water, and propionic acid were mixed directly. The quantity of TFA was 10.3 mol.% of the total CH3 COO− anion with a uncertainty estimated to be 0.5%. After stirring for 1 h, the obtained solution was refined in a BUCHI Rotavapor R210 rotary evaporator under decompression for 2 h. Methanol ...
1. Potentiometric determination of the dissociation constant of week
... treatment will refer particularly to solutions which are liquid, although the dissolved substance may originally be a solid. It has been known for many years that when a non-volatile solute is dissolved in a liquid, the vapor pressure of the solution is lower than that of the pure liquid (solvent). ...
... treatment will refer particularly to solutions which are liquid, although the dissolved substance may originally be a solid. It has been known for many years that when a non-volatile solute is dissolved in a liquid, the vapor pressure of the solution is lower than that of the pure liquid (solvent). ...
Hydrogen Peroxide Formation Rates in a PEMFC Anode and Cathode
... Effect of oxygen concentration.— The effect of oxygen concentration on ORR and H2O2 formation kinetics was studied by varying the concentration of oxygen in the solution. The following three gases were used: oxygen 共UHP grade, Praxair兲, air 共Industrial, Praxair兲 and 10.01% oxygen in nitrogen 共Airgas ...
... Effect of oxygen concentration.— The effect of oxygen concentration on ORR and H2O2 formation kinetics was studied by varying the concentration of oxygen in the solution. The following three gases were used: oxygen 共UHP grade, Praxair兲, air 共Industrial, Praxair兲 and 10.01% oxygen in nitrogen 共Airgas ...
Ch 12 Solutions
... - Hydration is the attraction of ions for dipoles on H2O. It is the result of ion-dipole forces. The + H atom is attracted to anions (–), while the – O atom is attracted to cations (+). - Lattice energy is the attraction of oppositely charged ions to each other to form the ionic crystal. It is the ...
... - Hydration is the attraction of ions for dipoles on H2O. It is the result of ion-dipole forces. The + H atom is attracted to anions (–), while the – O atom is attracted to cations (+). - Lattice energy is the attraction of oppositely charged ions to each other to form the ionic crystal. It is the ...
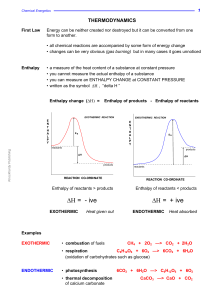
Topic 5 Energetics File
... Entropy: A measure of the disorder of a system. Things causing entropy to increase: 1) increase of number of moles of gaseous molecules; 2) change of state from solid to liquid or liquid to gas; 3) increase of temperature Exothermic: A reaction in which energy is evolved. ΔH is –. Products more stab ...
... Entropy: A measure of the disorder of a system. Things causing entropy to increase: 1) increase of number of moles of gaseous molecules; 2) change of state from solid to liquid or liquid to gas; 3) increase of temperature Exothermic: A reaction in which energy is evolved. ΔH is –. Products more stab ...
aq - Byron High School
... If you were to draw diagrams (such as that shown below) representing aqueous solutions of each of the following ionic compounds, how many anions would you show if the diagram contained six cations? (a) NiSO4, (b) Ca(NO3)2 , (c) Na3PO4, (d) ...
... If you were to draw diagrams (such as that shown below) representing aqueous solutions of each of the following ionic compounds, how many anions would you show if the diagram contained six cations? (a) NiSO4, (b) Ca(NO3)2 , (c) Na3PO4, (d) ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.