chapter 21
... Strategy: We are given information as to how the concentrations of X2, Y, and Z affect the rate of the reaction and are asked to determine the rate law. We assume that the rate law takes the form rate k[X2]x[Y]y[Z]z How do we use the information to determine x, y, and z? Solution: Since the reacti ...
... Strategy: We are given information as to how the concentrations of X2, Y, and Z affect the rate of the reaction and are asked to determine the rate law. We assume that the rate law takes the form rate k[X2]x[Y]y[Z]z How do we use the information to determine x, y, and z? Solution: Since the reacti ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... This endothermic reaction proceeds toward the right with increasing temperature and the PS abundance increases. According to LeChâtelier’s principle, this reaction also proceeds toward the right with decreasing pressure, because there are 2 gas molecules on the left and 3.5 gas molecules on the rig ...
... This endothermic reaction proceeds toward the right with increasing temperature and the PS abundance increases. According to LeChâtelier’s principle, this reaction also proceeds toward the right with decreasing pressure, because there are 2 gas molecules on the left and 3.5 gas molecules on the rig ...
Chemistry 2008 Multiple Choice
... Kp = PCO2/PCO2 = (6.74 atm)2/1.63 atm = 27.9 d. Equal to because the catalyst would increase the forward and reverse reaction rates, which would decrease the time to reach equilibrium, but the not the equilibrium position. e. Decrease because Qp = PCO2/PCO2 = (2.00 atm)2/2.00 atm = 2.00 < Kp the r ...
... Kp = PCO2/PCO2 = (6.74 atm)2/1.63 atm = 27.9 d. Equal to because the catalyst would increase the forward and reverse reaction rates, which would decrease the time to reach equilibrium, but the not the equilibrium position. e. Decrease because Qp = PCO2/PCO2 = (2.00 atm)2/2.00 atm = 2.00 < Kp the r ...
CHAPTER 14 CHEMICAL KINETICS
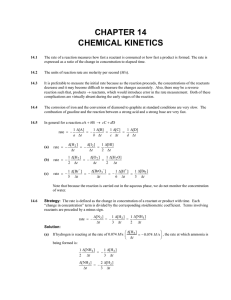
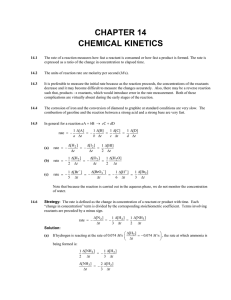
... Strategy: The relationship between the concentration of a reactant at different times in a first-order reaction is given by Equations (14.3) and (14.4) of the text. We are asked to determine the time required for 95% of the phosphine to decompose. If we initially have 100% of the compound and 95% ha ...
... Strategy: The relationship between the concentration of a reactant at different times in a first-order reaction is given by Equations (14.3) and (14.4) of the text. We are asked to determine the time required for 95% of the phosphine to decompose. If we initially have 100% of the compound and 95% ha ...
QualGroupD
... The Group D cations are characterized as having hydroxides, oxides and oxalates that are soluble in an ammonia/ammonium ion buffer solution. Three of the Group D cations, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+, form complex ions with ammonia. These complexes ions are very stable and prevent the cations from precipitat ...
... The Group D cations are characterized as having hydroxides, oxides and oxalates that are soluble in an ammonia/ammonium ion buffer solution. Three of the Group D cations, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+, form complex ions with ammonia. These complexes ions are very stable and prevent the cations from precipitat ...
Review - gbschemphys
... produced if a given amount of moles of reactant was reacted. Which quantities would be essential in order to solve such a problem? Bubble in all that apply - but only those that are essential to this calculation. a. The molar mass of the reactant b. The molar mass of the product c. The coefficients ...
... produced if a given amount of moles of reactant was reacted. Which quantities would be essential in order to solve such a problem? Bubble in all that apply - but only those that are essential to this calculation. a. The molar mass of the reactant b. The molar mass of the product c. The coefficients ...
g - Haiku
... Sample Exercise 5.1 Describing and Calculating Energy Changes A bowler lifts a 5.4-kg (12-lb) bowling ball from ground level to a height of 1.6 m (5.2 ft) and then drops it. (a) What happens to the potential energy of the ball as it is raised? (b) What quantity of work, in J, is used to raise the ba ...
... Sample Exercise 5.1 Describing and Calculating Energy Changes A bowler lifts a 5.4-kg (12-lb) bowling ball from ground level to a height of 1.6 m (5.2 ft) and then drops it. (a) What happens to the potential energy of the ball as it is raised? (b) What quantity of work, in J, is used to raise the ba ...
Acidic Environment
... This reaction from LEFT-to-RIGHT is called the forward reaction, and the reaction from RIGHT-to-LEFT is called the backward reaction. These are known as reversible reactions. ...
... This reaction from LEFT-to-RIGHT is called the forward reaction, and the reaction from RIGHT-to-LEFT is called the backward reaction. These are known as reversible reactions. ...
Acknowledgements - HAL
... The complexation reaction was quantified indirectly by either separating free and PAA bound metal ions [2] or by using displacement methods in the liquid/liquid [1] or solid/liquid [3] system. The description was done with empirical models. The data could be well described at a given pH value consid ...
... The complexation reaction was quantified indirectly by either separating free and PAA bound metal ions [2] or by using displacement methods in the liquid/liquid [1] or solid/liquid [3] system. The description was done with empirical models. The data could be well described at a given pH value consid ...
Atomic Structure
... Bond order is a concept in the molecular orbital theory. It depends on the number of electrons in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Which of the following statements is true about it? The bond order (a) Cannot be a negative quantity (b) Always has an integral value (c) Can assume any value, posi ...
... Bond order is a concept in the molecular orbital theory. It depends on the number of electrons in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Which of the following statements is true about it? The bond order (a) Cannot be a negative quantity (b) Always has an integral value (c) Can assume any value, posi ...
Chapter 4 Student Presentation
... complete ionic equation and net ionic equation for the following: a) FeCl2 (aq) + K2S (aq) b) AlBr3 (aq) + NaOH (aq) c) (NH4)3PO4 (aq) + Ca(NO3)2 (aq) d) Aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and sodium carbonate react. e) Aqueous solutions of barium chloride and potassium sulfate react. ...
... complete ionic equation and net ionic equation for the following: a) FeCl2 (aq) + K2S (aq) b) AlBr3 (aq) + NaOH (aq) c) (NH4)3PO4 (aq) + Ca(NO3)2 (aq) d) Aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and sodium carbonate react. e) Aqueous solutions of barium chloride and potassium sulfate react. ...
Unit 6 Review Answers
... considered a modernized Arrhenius acid, however.) Ammonia can’t be an Arrhenius base, because it does not contain hydroxide ions. (Ammonia could be considered a modernized Arrhenius base, however.) Students should disagree. A solution with a pH of 4 has [H3O+] = 0.0001 mol/L, whereas a solution with ...
... considered a modernized Arrhenius acid, however.) Ammonia can’t be an Arrhenius base, because it does not contain hydroxide ions. (Ammonia could be considered a modernized Arrhenius base, however.) Students should disagree. A solution with a pH of 4 has [H3O+] = 0.0001 mol/L, whereas a solution with ...
What is a solution
... The other concentration units are less frequently used:Ideal Solution: A solution of two or more constituents is said to be ideal if it obeys Raoult’s law under all conditions of temperature and concentration. We are considering a solution composed of a volatile solvent and one or more involatile so ...
... The other concentration units are less frequently used:Ideal Solution: A solution of two or more constituents is said to be ideal if it obeys Raoult’s law under all conditions of temperature and concentration. We are considering a solution composed of a volatile solvent and one or more involatile so ...
1 AM SYLLABUS (2015) CHEMISTRY AM 06 SYLLABUS
... namely, G = H - TS. Kinetic versus thermodynamic stability. ...
... namely, G = H - TS. Kinetic versus thermodynamic stability. ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.