Chapter 4
... present in the solution. As in NaCl(s), there are no NaCl molecules in NaCl(aq), but only separate Na + and Cl- ions. We say that NaCl(aq) is a strong electrolyte. A strong electrolyte is a solute that is present in solution almost exclusively as ions. A solution of a strong electrolyte is a good el ...
... present in the solution. As in NaCl(s), there are no NaCl molecules in NaCl(aq), but only separate Na + and Cl- ions. We say that NaCl(aq) is a strong electrolyte. A strong electrolyte is a solute that is present in solution almost exclusively as ions. A solution of a strong electrolyte is a good el ...
Chapter 14: Chemical Kinetics
... Collision theory tells us that while collisions between reacting species are occurring all of the time, only some fraction—not all—of those collisions will lead to conversion of reactants to products. Using this theory, we can understand how physical state of reactants, temperature, and molecular o ...
... Collision theory tells us that while collisions between reacting species are occurring all of the time, only some fraction—not all—of those collisions will lead to conversion of reactants to products. Using this theory, we can understand how physical state of reactants, temperature, and molecular o ...
word - My eCoach
... matter and the ability to calculate the mass of products and reactants. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to describe chemical reactions by writing balanced equations. b. Students know the quantity one mole is set by defining one mole of carbon 12 atoms to have a mass o ...
... matter and the ability to calculate the mass of products and reactants. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to describe chemical reactions by writing balanced equations. b. Students know the quantity one mole is set by defining one mole of carbon 12 atoms to have a mass o ...
Student Solutions Manual Errata
... The relative atomic mass of boron is 10.81 amu. Since boron exists as either boron-10 or boron-11, the relative abundance of boron-11 will be much higher. Of the choices given only two make sense: 20% boron-10 and 80% boron-11 (correct answer) 5.0% boron-10 and 95.0% boron-11 The best answer can be ...
... The relative atomic mass of boron is 10.81 amu. Since boron exists as either boron-10 or boron-11, the relative abundance of boron-11 will be much higher. Of the choices given only two make sense: 20% boron-10 and 80% boron-11 (correct answer) 5.0% boron-10 and 95.0% boron-11 The best answer can be ...
IIT-JEE - Brilliant Public School Sitamarhi
... Q.12 In a cubic crystal of CsCl (density = 3.97 gm/cm3) the eight corners are occupied by Cl– ions with Cs+ ions at the centre. Calculate the distance between the neighbouring Cs+ and Cl– ions. Q.13 KF has NaCl structure. What is the distance between K+ and F– in KF if density of KF is 2.48 gm/cm3. ...
... Q.12 In a cubic crystal of CsCl (density = 3.97 gm/cm3) the eight corners are occupied by Cl– ions with Cs+ ions at the centre. Calculate the distance between the neighbouring Cs+ and Cl– ions. Q.13 KF has NaCl structure. What is the distance between K+ and F– in KF if density of KF is 2.48 gm/cm3. ...
Development of Novel Catalytic Asymmetric Reactions using
... Metal enolates of carbonyl compounds are highly versatile nucleophilic reagents that can be used in reactions with various electrophilic agents. They are regarded as essential synthetic intermediates in organic chemistry. 1 Conventionally, two main approaches have been directed to develop asymmetric ...
... Metal enolates of carbonyl compounds are highly versatile nucleophilic reagents that can be used in reactions with various electrophilic agents. They are regarded as essential synthetic intermediates in organic chemistry. 1 Conventionally, two main approaches have been directed to develop asymmetric ...
File
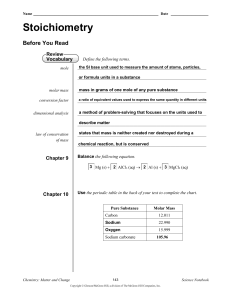
... a ratio between the numbers of moles of any two substances in a ______________________________________________________________ balanced chemical equation ______________________________________________________________ ...
... a ratio between the numbers of moles of any two substances in a ______________________________________________________________ balanced chemical equation ______________________________________________________________ ...
04 Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The ions crossed out are called spectator ions, K+ and NO3−, in this example. • The remaining ions are the reactants that form the product—an insoluble salt in a precipitation ...
... • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The ions crossed out are called spectator ions, K+ and NO3−, in this example. • The remaining ions are the reactants that form the product—an insoluble salt in a precipitation ...
redox reaction - Seattle Central College
... Earlier in the quarter we defined a solution as a homogeneous mixture; a random combination of two or more things. The part of the solution we have the most of is the solvent and the minor components of a solution are referred to as the solutes. Water is the most common solvent and a good one for io ...
... Earlier in the quarter we defined a solution as a homogeneous mixture; a random combination of two or more things. The part of the solution we have the most of is the solvent and the minor components of a solution are referred to as the solutes. Water is the most common solvent and a good one for io ...
Practice Exam 4
... R = 8.314 J · mol−1 · K−1 Assume 1 mol in each case. Entropy decreases if ∆S is negative. For the oxygen gas pressure doubling ...
... R = 8.314 J · mol−1 · K−1 Assume 1 mol in each case. Entropy decreases if ∆S is negative. For the oxygen gas pressure doubling ...
2 - Scheikundeolympiade
... Hungary. Its preparation relies on a natural precursor, (+)-vincamine (C21H26 N2O3), which is isolated from the vine plant, vinca minor. The transformation of (+)-vincamine to vinpocetine is achieved in two steps depicted below. ...
... Hungary. Its preparation relies on a natural precursor, (+)-vincamine (C21H26 N2O3), which is isolated from the vine plant, vinca minor. The transformation of (+)-vincamine to vinpocetine is achieved in two steps depicted below. ...
NO - Blue Devil Chem
... Sucrose or common table sugar was mixed with concentrated sulfuric acid. Soon an exothermic reaction takes places during which a column of carbon rises from the beaker and a cloud of steam is produced. Concentrated sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst to dehydrate sucrose to produce carbon and water. Th ...
... Sucrose or common table sugar was mixed with concentrated sulfuric acid. Soon an exothermic reaction takes places during which a column of carbon rises from the beaker and a cloud of steam is produced. Concentrated sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst to dehydrate sucrose to produce carbon and water. Th ...
Slide 1 / 55 Slide 2 / 55 Slide 3 / 55
... to a temperature above the boiling point of the liquid. Which of the following processes produces the greatest increase in the entropy of the substance? A ...
... to a temperature above the boiling point of the liquid. Which of the following processes produces the greatest increase in the entropy of the substance? A ...
PX312-1718
... 22. What is the maximum concentration of carbonate ions that will precipitate BaCO3 but not MgCO3 from a solution that is 2.7 10 3 M each in Mg2+ and Ba2+? For MgCO3, Ksp = 1.0 10–5 and for BaCO3, Ksp = 2.6 10–9. A) 3.7 10 3 M B) 9.6 10 7 M C) 2.7 10 8 M D) 7.0 10 12 M E) 2.6 10 ...
... 22. What is the maximum concentration of carbonate ions that will precipitate BaCO3 but not MgCO3 from a solution that is 2.7 10 3 M each in Mg2+ and Ba2+? For MgCO3, Ksp = 1.0 10–5 and for BaCO3, Ksp = 2.6 10–9. A) 3.7 10 3 M B) 9.6 10 7 M C) 2.7 10 8 M D) 7.0 10 12 M E) 2.6 10 ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.