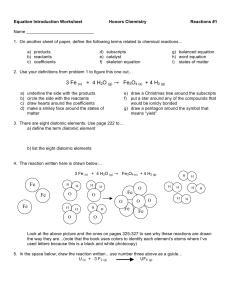
types of reactions
... ex: 4 NH3 + 2 O2 4 NO3 + 6 H2O (all divisible by 2, so simplify) 2 NH3 + O2 2 NO3 + 3 H2O ...
... ex: 4 NH3 + 2 O2 4 NO3 + 6 H2O (all divisible by 2, so simplify) 2 NH3 + O2 2 NO3 + 3 H2O ...
Document
... • A catalyst changes the mechanism of a reaction to one with a lower activation energy. • A catalyst has no effect on the equilibrium concentrations and constant. – But does affect the rate at which equilibrium is attained! ...
... • A catalyst changes the mechanism of a reaction to one with a lower activation energy. • A catalyst has no effect on the equilibrium concentrations and constant. – But does affect the rate at which equilibrium is attained! ...
Unit 8 Student Notes
... Solubility Equilibria: When the process of dissolution and precipitation are occurring at the same time and at the same rate, equilibrium is established. The equilibrium can be shown by an equation with two arrows or a double arrow: CaCl2 (s) Ca2+ (aq) + 2Cl- (aq) Note that the equation must be ba ...
... Solubility Equilibria: When the process of dissolution and precipitation are occurring at the same time and at the same rate, equilibrium is established. The equilibrium can be shown by an equation with two arrows or a double arrow: CaCl2 (s) Ca2+ (aq) + 2Cl- (aq) Note that the equation must be ba ...
AP® Chemistry 2009 Free-Response Questions Form B
... switch is closed in the cell represented above, the voltage reading is +1.14 V. (a) Write the reduction half-reaction that occurs in the cell. (b) Write the equation for the overall reaction that occurs in the cell. (c) Identify the anode in the cell. Justify your answer. (d) On the diagram above, u ...
... switch is closed in the cell represented above, the voltage reading is +1.14 V. (a) Write the reduction half-reaction that occurs in the cell. (b) Write the equation for the overall reaction that occurs in the cell. (c) Identify the anode in the cell. Justify your answer. (d) On the diagram above, u ...
Slide 1
... Some chemical and physical changes take place by themselves, given enough time. A spontaneous chemical reaction is one that, given sufficient time, will achieve chemical equilibrium, with an equilibrium constant greater than 1, by reacting from left to right. ...
... Some chemical and physical changes take place by themselves, given enough time. A spontaneous chemical reaction is one that, given sufficient time, will achieve chemical equilibrium, with an equilibrium constant greater than 1, by reacting from left to right. ...
ap chemistry – 2013-2014
... AP CHEMISTRY – 2013-2014 Course Description: This AP Chemistry course is designed to be the equivalent of the general chemistry course usually taken during the first year of college. This course is structured around six big ideas that include: Structure of matter, properties of matter-characteristic ...
... AP CHEMISTRY – 2013-2014 Course Description: This AP Chemistry course is designed to be the equivalent of the general chemistry course usually taken during the first year of college. This course is structured around six big ideas that include: Structure of matter, properties of matter-characteristic ...
Equilibrium
... *First, write the equation for the dissolving of lead(II) chloride; then, write the equilibrium law expression for the dissolving process. (i.e. the Ksp expression) ...
... *First, write the equation for the dissolving of lead(II) chloride; then, write the equilibrium law expression for the dissolving process. (i.e. the Ksp expression) ...
Chemical Equations Balancing Chemical Equations Try One…
... BALANCE IT -by adding coefficients-DO NOT CHANGE SUBSCRIPTS 1. start at the formula with the highest subscript values 2. put a “1” in front, if that doesn’t work try a “2”, etc. 3. go back and forth adding coefficients, until it’s ...
... BALANCE IT -by adding coefficients-DO NOT CHANGE SUBSCRIPTS 1. start at the formula with the highest subscript values 2. put a “1” in front, if that doesn’t work try a “2”, etc. 3. go back and forth adding coefficients, until it’s ...
A.P. Chemistry Complexation Reactions
... O2 gas reacts with a flammable carbon compound to produce CO2 and H2O ...
... O2 gas reacts with a flammable carbon compound to produce CO2 and H2O ...
Lecture 2 - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Step 2: Using the Solubility rules, determine if either product is insoluble – If all products are insoluble, then no reaction occurs ...
... Step 2: Using the Solubility rules, determine if either product is insoluble – If all products are insoluble, then no reaction occurs ...
Solution
... You dissolve 0.10 moles of an unknown acid in water and the resulting solution has a volume of 1.0 L. You measure the concentration of H3O+ in this solution and the pH is 3.0. Which of the following statements is true for this unknown acid? A.) It is a strong acid because the relative Gibbs free ene ...
... You dissolve 0.10 moles of an unknown acid in water and the resulting solution has a volume of 1.0 L. You measure the concentration of H3O+ in this solution and the pH is 3.0. Which of the following statements is true for this unknown acid? A.) It is a strong acid because the relative Gibbs free ene ...
Section 2-4 “Chemical Reactions and Enzymes”
... reaction started. Once the bonds are broken, the atoms are freed up and can make new molecules. When bonds form between the atoms to make new molecules, energy is released. The specific amount of energy that is needed to break a bond, or is releases when that same bond forms, is called bond energy. ...
... reaction started. Once the bonds are broken, the atoms are freed up and can make new molecules. When bonds form between the atoms to make new molecules, energy is released. The specific amount of energy that is needed to break a bond, or is releases when that same bond forms, is called bond energy. ...
Chapter 5 auxiliary functions
... * From the second law of thermodynamics : q ≤ T(S2 –S1) ≤ – ΔGَw therefore for reversible processes that occur at constant temperature and pressure ; the maximum amount of work , other than the p – v work is given by equation : max = – ΔGَw * again the pervious inequality can b written as ; = – (ΔG ...
... * From the second law of thermodynamics : q ≤ T(S2 –S1) ≤ – ΔGَw therefore for reversible processes that occur at constant temperature and pressure ; the maximum amount of work , other than the p – v work is given by equation : max = – ΔGَw * again the pervious inequality can b written as ; = – (ΔG ...
Chemistry 12 is an intensive course, covering a great deal of
... • performing calculations involving Keq, initial concentrations, and equilibrium concentration Prescribed Learning Outcomes B1 explain the concept of chemical equilibrium with reference to reacting systems 1. describe the reversible nature of most chemical reactions and how it can be represented on ...
... • performing calculations involving Keq, initial concentrations, and equilibrium concentration Prescribed Learning Outcomes B1 explain the concept of chemical equilibrium with reference to reacting systems 1. describe the reversible nature of most chemical reactions and how it can be represented on ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.