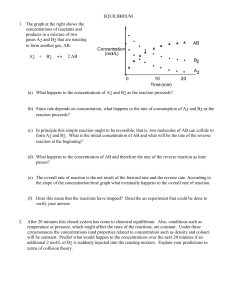
CHEM230P1_06_2014_Y_P1
... The pressure in the container is now increased by decreasing the volume of the container. Explain how the composition of A and B will change during this process and also state whether the equilibrium constant, KP, will increase, decrease or stay the same. ...
... The pressure in the container is now increased by decreasing the volume of the container. Explain how the composition of A and B will change during this process and also state whether the equilibrium constant, KP, will increase, decrease or stay the same. ...
Chapter 19 - public.asu.edu
... CO(g) + H2O(g) ! CO2 (g) + H2(g) Q = PCO2PH2/PCOPH2O Initially, Q = 0, but then it increases As the reaction progresses, DG decreases until a minimum value of G is reached; at this point, DG = 0 and net reaction ceases (though the forward and reverse reactions still occur, but they offset one anothe ...
... CO(g) + H2O(g) ! CO2 (g) + H2(g) Q = PCO2PH2/PCOPH2O Initially, Q = 0, but then it increases As the reaction progresses, DG decreases until a minimum value of G is reached; at this point, DG = 0 and net reaction ceases (though the forward and reverse reactions still occur, but they offset one anothe ...
Title Thermodynamic Analysis of Polymer
... Equation (33) is the virial expansion for the osmotic pressure in the constant pp system, and the coefficientsA2 and A3 may be called the, second and the third virial coefficients,respectively. The above equations (33) to (35) are formallyidentical with the correspondingequations for solutionsin sin ...
... Equation (33) is the virial expansion for the osmotic pressure in the constant pp system, and the coefficientsA2 and A3 may be called the, second and the third virial coefficients,respectively. The above equations (33) to (35) are formallyidentical with the correspondingequations for solutionsin sin ...
Chapter 6 - Department of Chemical Engineering
... activity coefficients using Modified Raoult’s law for each equilibrium point. Use these values to calculate GE/RTx1x2 for all equilibrium points. 4. Find Margules equation parameters using graphical data reduction method. 5. Calculate the activity coefficients for your experimental VLE data, using t ...
... activity coefficients using Modified Raoult’s law for each equilibrium point. Use these values to calculate GE/RTx1x2 for all equilibrium points. 4. Find Margules equation parameters using graphical data reduction method. 5. Calculate the activity coefficients for your experimental VLE data, using t ...
Unit 3 Notes
... Increasing the pressure will cause the equilibrium to move to ............................. the pressure. The equilibrium will move to .............................. the number of gas particles. The equilibrium moves to the .................. producing more ........................ and less ........ ...
... Increasing the pressure will cause the equilibrium to move to ............................. the pressure. The equilibrium will move to .............................. the number of gas particles. The equilibrium moves to the .................. producing more ........................ and less ........ ...
Advanced Chemical Reactions
... 2. Reversible reactions – products can re-form original reactants Reversible reactions often use 2 arrows b/c reactions occur at the same time ...
... 2. Reversible reactions – products can re-form original reactants Reversible reactions often use 2 arrows b/c reactions occur at the same time ...
Name AP Chemistry Take Home Quiz – Due Thursday, 1/9/2014
... 46. 6.0 moles of chlorine gas are placed in a 3.0 L flask at 1250 K. At this temperature, the chlorine molecules begin to dissociate into chlorine atoms. What is the value of Kc, if 50.% of the chlorine molecules dissociate when equilibrium has been achieved? a. 1.0 b. 3.0 c. 4.0 d. 6.0 e. 12.0 47. ...
... 46. 6.0 moles of chlorine gas are placed in a 3.0 L flask at 1250 K. At this temperature, the chlorine molecules begin to dissociate into chlorine atoms. What is the value of Kc, if 50.% of the chlorine molecules dissociate when equilibrium has been achieved? a. 1.0 b. 3.0 c. 4.0 d. 6.0 e. 12.0 47. ...
honors chem 6 day review packet
... the element that has 2 electrons in the p sublevel in its second main energy level 4s24p5 Be able to locate s, p, d, and f blocks on the periodic table The ___________ ____________ _____________ is the same as the period number. There are ________ main energy levels. The ____________ ___________ ___ ...
... the element that has 2 electrons in the p sublevel in its second main energy level 4s24p5 Be able to locate s, p, d, and f blocks on the periodic table The ___________ ____________ _____________ is the same as the period number. There are ________ main energy levels. The ____________ ___________ ___ ...
Curriculum Plan
... activated complex, Define entropy, Describe an increase in the entropy of the universe as a driving force (2nd law of thermodynamics), Create and recognize an energy diagram for an exothermic or endothermic reaction, including EA, Ho, enthalpy of products and enthalpy of reactants, Use the Gibbs fr ...
... activated complex, Define entropy, Describe an increase in the entropy of the universe as a driving force (2nd law of thermodynamics), Create and recognize an energy diagram for an exothermic or endothermic reaction, including EA, Ho, enthalpy of products and enthalpy of reactants, Use the Gibbs fr ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.























