Word - chemmybear.com
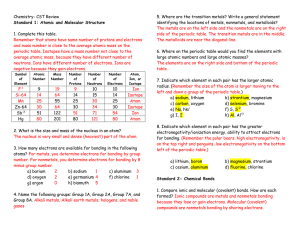
... a) all salts containing NH4+ are soluble. b) all salts containing NO3– are soluble. c) all fluorides are soluble. d) all sulfates (except those of Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, and Pb2+) are soluble. e) most hydroxides are insoluble, except those of Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, the alkali metals and NH4+. ...
... a) all salts containing NH4+ are soluble. b) all salts containing NO3– are soluble. c) all fluorides are soluble. d) all sulfates (except those of Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, and Pb2+) are soluble. e) most hydroxides are insoluble, except those of Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, the alkali metals and NH4+. ...
calculations of mechanical work in 1, 2 and 3 dimensions
... A chemical reaction with methanol creates heat in the NiTi alloy wire. At a higher temperature, the wire’s length shrinks - thus lifting a weight and doing work on the surroundings. V.H. Ebron et al., Science (2006) 311, 1580 ...
... A chemical reaction with methanol creates heat in the NiTi alloy wire. At a higher temperature, the wire’s length shrinks - thus lifting a weight and doing work on the surroundings. V.H. Ebron et al., Science (2006) 311, 1580 ...
Matter and Its Changes
... atoms together Chemical REACTIONS occur when chemical bonds are formed or broken. ...
... atoms together Chemical REACTIONS occur when chemical bonds are formed or broken. ...
Partial Pressures of Gases
... First, balance atoms that are not in polyatomic ions, and are not O or H. (Oxygen and hydrogen atoms may be constituents of many compounds in a reaction. Balancing O and H early could be a waste of time, because they might need to be rebalanced again at a later stage.) In this case, we can start wit ...
... First, balance atoms that are not in polyatomic ions, and are not O or H. (Oxygen and hydrogen atoms may be constituents of many compounds in a reaction. Balancing O and H early could be a waste of time, because they might need to be rebalanced again at a later stage.) In this case, we can start wit ...
Final Review
... a. Gases are compressible b. Gases can expand c. Gases can spontaneously diffuse d. Gases are very dense e. Gases have high fluidity 2. When 45.3 grams of C3H8 reacts with oxygen gas, how many liters of CO2 are produced if the reaction is carried out at 56°C and a pressure of 780 mmHg? A. 3.1 B. 81 ...
... a. Gases are compressible b. Gases can expand c. Gases can spontaneously diffuse d. Gases are very dense e. Gases have high fluidity 2. When 45.3 grams of C3H8 reacts with oxygen gas, how many liters of CO2 are produced if the reaction is carried out at 56°C and a pressure of 780 mmHg? A. 3.1 B. 81 ...
Chemistry Review
... Barometer- a manometer used to measure atmospheric pressure Capillary Action - the attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid Condensation- change in state from a gas to a liquid Deposition – change in state directly from a gas to a solid Diffusion – mixing of 2 or more gases Ef ...
... Barometer- a manometer used to measure atmospheric pressure Capillary Action - the attraction of the surface of a liquid to the surface of a solid Condensation- change in state from a gas to a liquid Deposition – change in state directly from a gas to a solid Diffusion – mixing of 2 or more gases Ef ...
Chemical Reactions - Northside Middle School
... • Can predict the products if it is a binary compound • Made up of only two elements • Falls apart into its elements • 2H2O electricity 2H2 + O2 ...
... • Can predict the products if it is a binary compound • Made up of only two elements • Falls apart into its elements • 2H2O electricity 2H2 + O2 ...
Chemistry I Review - BarbaraElam-Rice
... If 10 liters of H2 (g) at STP is heated to a temperature of 546 K, pressure remaining constant, the new volume of the gas will be 20 liters. d. Draw the graph representing Boyle’s Law. Label the X & Y axis. e. Draw the graph representing Charles’s Law. Label the X & Y axis. f. Draw the graph represe ...
... If 10 liters of H2 (g) at STP is heated to a temperature of 546 K, pressure remaining constant, the new volume of the gas will be 20 liters. d. Draw the graph representing Boyle’s Law. Label the X & Y axis. e. Draw the graph representing Charles’s Law. Label the X & Y axis. f. Draw the graph represe ...
PDF
... are not the amounts that would be produced if the reactions were actually done in the laboratory. In each case, less product would be obtained than was calculated. There are numerous causes. Some materials are lost during transfers from one container to another and side reactions take place that are ...
... are not the amounts that would be produced if the reactions were actually done in the laboratory. In each case, less product would be obtained than was calculated. There are numerous causes. Some materials are lost during transfers from one container to another and side reactions take place that are ...
Physical and Chemical equilibrium
... Rate of forward reaction rf ∝ [A]a [B]b Rate of backward reaction rb ∝ [C]c [D]d Active mass of a substance is simply number of moles dissolved per litre of the solution. Active mass of a gas or liquid is equal to its pressure or molar concentration, where as active mass of solid is constant and is ...
... Rate of forward reaction rf ∝ [A]a [B]b Rate of backward reaction rb ∝ [C]c [D]d Active mass of a substance is simply number of moles dissolved per litre of the solution. Active mass of a gas or liquid is equal to its pressure or molar concentration, where as active mass of solid is constant and is ...
Entropy
... Positional Entropy • Positional Entropy (S) – depends upon the number of microstates a set of molecules can have in space 1. Solids have the fewest possible number of microstates in space, atoms are very ordered, crystal structures 2. Liquids have many more ways for molecules to be arranged than a ...
... Positional Entropy • Positional Entropy (S) – depends upon the number of microstates a set of molecules can have in space 1. Solids have the fewest possible number of microstates in space, atoms are very ordered, crystal structures 2. Liquids have many more ways for molecules to be arranged than a ...
PPT
... • A balanced chemical equation is one in which the number of atoms of each element in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms of that same element in the products. • A reaction can be balanced by applying the law of conservation of matter. • Coefficients (in red below) are written to the left ...
... • A balanced chemical equation is one in which the number of atoms of each element in the reactants is equal to the number of atoms of that same element in the products. • A reaction can be balanced by applying the law of conservation of matter. • Coefficients (in red below) are written to the left ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.























