E - Analytical Chemistry
... E° for dissolution of iron(II) carbonate is negative, which means that the reaction is "not spontaneous." "Not spontaneous" simply means K < 1. The reaction proceeds until the concentrations of reactants and products satisfy the equilibrium condition. From E° for the net reaction, we can compute Ksp ...
... E° for dissolution of iron(II) carbonate is negative, which means that the reaction is "not spontaneous." "Not spontaneous" simply means K < 1. The reaction proceeds until the concentrations of reactants and products satisfy the equilibrium condition. From E° for the net reaction, we can compute Ksp ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... Honors Only: c) What is the molecular formula if the empirical formula is NaO and the gram formula mass is 78 g? Objective 3.7 1. Know the 5 assumptions of the kinetic molecular theory. 2. Know the difference between an ideal gas and a real gas. What conditions does a real gas deviate from an ideal ...
... Honors Only: c) What is the molecular formula if the empirical formula is NaO and the gram formula mass is 78 g? Objective 3.7 1. Know the 5 assumptions of the kinetic molecular theory. 2. Know the difference between an ideal gas and a real gas. What conditions does a real gas deviate from an ideal ...
1. Explain electrophile and nucleophile. 2. Explain
... 51. What will be volume of a gas at 273K and 1 atm which occupied 4.6 litre volume at 542 atm and 232K? 52. Derive ideal gas equation PV=nRT 53. The reaction 25O2(g)+O2(g) 25O3 was started by taking one mole each of SO2(g) and O2 in a vessel of 5.00dm3. 54. At 450K Kp=2.0*1010/bar for the given reac ...
... 51. What will be volume of a gas at 273K and 1 atm which occupied 4.6 litre volume at 542 atm and 232K? 52. Derive ideal gas equation PV=nRT 53. The reaction 25O2(g)+O2(g) 25O3 was started by taking one mole each of SO2(g) and O2 in a vessel of 5.00dm3. 54. At 450K Kp=2.0*1010/bar for the given reac ...
Chemistry Review Fill in the blank
... 5. Qualitative data is information that _____________________________________________. 6. Quantitative data is information that _____________________________________________. 7. Exothermic reaction ___________________ energy and energy is shown on the _______________ side. 8. Endothermic reaction __ ...
... 5. Qualitative data is information that _____________________________________________. 6. Quantitative data is information that _____________________________________________. 7. Exothermic reaction ___________________ energy and energy is shown on the _______________ side. 8. Endothermic reaction __ ...
CfE HIGHER CHEMISTRY Chemistry in Society
... remember to ignore all solids and liquids in all calculations. Also remember to read information in the question about the temperature of the reaction; if the temperature of the reaction is 100oC or above, liquid water will become a gas so its volume must be included in your answer. 1 mole of any ga ...
... remember to ignore all solids and liquids in all calculations. Also remember to read information in the question about the temperature of the reaction; if the temperature of the reaction is 100oC or above, liquid water will become a gas so its volume must be included in your answer. 1 mole of any ga ...
Unit 2:
... equilibrium is represented by the equation above. (a) Write the expression for the solubility-product constant, Ksp, and calculate its value at 18ºC. (b) Calculate the equilibrium concentration of Mg2+ in 1.000 liter of saturated MgF2 solution at 18ºC to which 0.100 mole of solid KF has been added. ...
... equilibrium is represented by the equation above. (a) Write the expression for the solubility-product constant, Ksp, and calculate its value at 18ºC. (b) Calculate the equilibrium concentration of Mg2+ in 1.000 liter of saturated MgF2 solution at 18ºC to which 0.100 mole of solid KF has been added. ...
Chemistry Syllabus
... from the lab. All work must be shown with equations for credit. You will get an automatic revisit for this section if your work is not shown. 1) Write all calculations in this section. One sample calculation is needed where the same calculation is repeated. Make sure the equation is written, numbers ...
... from the lab. All work must be shown with equations for credit. You will get an automatic revisit for this section if your work is not shown. 1) Write all calculations in this section. One sample calculation is needed where the same calculation is repeated. Make sure the equation is written, numbers ...
Chemistry II Exams and Keys Corrected 2016 Season
... the interactions between the polar stationary and less-polar mobile phase. A mixture is placed on the plate at position marked X, then through capillary action solvent A moves up the plate until the point shown (solvent front). The plate is then dried, rotated 90 ᵒ to the left and the process repeat ...
... the interactions between the polar stationary and less-polar mobile phase. A mixture is placed on the plate at position marked X, then through capillary action solvent A moves up the plate until the point shown (solvent front). The plate is then dried, rotated 90 ᵒ to the left and the process repeat ...
Lecture 9. Redox chemistry
... Al(s) + Ni2+(aq) Al3+(aq) + Ni(s) – Divide reaction into two half-reactions Al(s) Al3+(aq) + 3e Ni2+(aq) + 2e Ni(s) ...
... Al(s) + Ni2+(aq) Al3+(aq) + Ni(s) – Divide reaction into two half-reactions Al(s) Al3+(aq) + 3e Ni2+(aq) + 2e Ni(s) ...
Class Notes
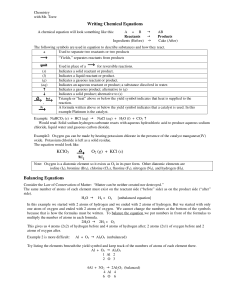
... only those particles that are directly involved in the chemical change. Net ionic equations differentiate between ions that react to form a precipitate, a gas, or water, and ions that simply remain in aqueous solution. In the example above, the NO3-1(aq) and the Na+1(aq) are both spectator ions. The ...
... only those particles that are directly involved in the chemical change. Net ionic equations differentiate between ions that react to form a precipitate, a gas, or water, and ions that simply remain in aqueous solution. In the example above, the NO3-1(aq) and the Na+1(aq) are both spectator ions. The ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... Both bases were the same concentration so they both contained the same number of molecules / units to begin with. The strong base will have dissociated completely meaning that all the OH—(aq) ions were available to react with the Fe3+(aq) ions . The weak base is only partially dissociated so less th ...
... Both bases were the same concentration so they both contained the same number of molecules / units to begin with. The strong base will have dissociated completely meaning that all the OH—(aq) ions were available to react with the Fe3+(aq) ions . The weak base is only partially dissociated so less th ...
LECTURE 6 - GENESIS OF MINERAL1
... System: - Is an arbitrarily chosen, finite volume of material (e.g. a hand specimen of a rock, or a complete geological unit). Equilibrium: - The condition of minimum energy for a system. Phase: A physically and chemically homogeneous, mechanically separable part of a physicalchemical system. Degree ...
... System: - Is an arbitrarily chosen, finite volume of material (e.g. a hand specimen of a rock, or a complete geological unit). Equilibrium: - The condition of minimum energy for a system. Phase: A physically and chemically homogeneous, mechanically separable part of a physicalchemical system. Degree ...
THE FREE ENERGIES OF FORMATION OF AQUEOUS d
... because it is probable that with aspartic acid, on account of the great tendency of its neutral molecules to form aggregates, there is a considerable heat of dilution, which would make t,he activit~y coefficient at 25” quite different from that at the freezing point. We have, nevertheless, computed ...
... because it is probable that with aspartic acid, on account of the great tendency of its neutral molecules to form aggregates, there is a considerable heat of dilution, which would make t,he activit~y coefficient at 25” quite different from that at the freezing point. We have, nevertheless, computed ...
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates of the forward and backward reactions are generally not zero, but equal. Thus, there are no net changes in the concentrations of the reactant(s) and product(s). Such a state is known as dynamic equilibrium.