Sub-atomic particles - Southwest High School
... where F is the force q1 and q2 are two charges and r is the distance between them. The electrical force is the chief force involved in atomic reactions. This force is attractive when charges q1 and q2 have opposite signs and repulsive when the charges have the same sign. (1803) John Dalton (Englan ...
... where F is the force q1 and q2 are two charges and r is the distance between them. The electrical force is the chief force involved in atomic reactions. This force is attractive when charges q1 and q2 have opposite signs and repulsive when the charges have the same sign. (1803) John Dalton (Englan ...
Oxidation numbers
... oxidation states, forming cations with different positive charges. This is due to the fact that many Transition Metals are characterized by a partially filled inner electron level, inside the valence shell. Electrons within this inner shell may sometimes behave as valence electrons and are lost alon ...
... oxidation states, forming cations with different positive charges. This is due to the fact that many Transition Metals are characterized by a partially filled inner electron level, inside the valence shell. Electrons within this inner shell may sometimes behave as valence electrons and are lost alon ...
Chemistry - Gorman Learning Center
... c. how to use the Periodic Table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, and trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and the relative sizes of ions and atoms. d. how to use the Periodic Table to determine the number of electrons available for bonding. e. the n ...
... c. how to use the Periodic Table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, and trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and the relative sizes of ions and atoms. d. how to use the Periodic Table to determine the number of electrons available for bonding. e. the n ...
Grades 9-12 Chemistry California Content Standards
... c. how to use the Periodic Table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, and trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and the relative sizes of ions and atoms. d. how to use the Periodic Table to determine the number of electrons available for bonding. e. the n ...
... c. how to use the Periodic Table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, and trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and the relative sizes of ions and atoms. d. how to use the Periodic Table to determine the number of electrons available for bonding. e. the n ...
Unit 1 Notes (general chem review)
... Atomic number(Z) – The number of p+ in an atom. All atoms of the same element have the same number of p+. Different elements have different atomic numbers b/c p+ are different. Atomic mass number(A) – The sum of the number of neutrons and p+ for an atom. Protons and neutrons are the only s ...
... Atomic number(Z) – The number of p+ in an atom. All atoms of the same element have the same number of p+. Different elements have different atomic numbers b/c p+ are different. Atomic mass number(A) – The sum of the number of neutrons and p+ for an atom. Protons and neutrons are the only s ...
ite and - Smithycroft Secondary School
... I can explain what an atomic number and a mass number are in an atom I can state the mass of subatomic particles Look at the periodic table on page 8 of chemistry data book. Notice that each element has a number above it - this is its unique ATOMIC NUMBER. The atomic number used to be called the pro ...
... I can explain what an atomic number and a mass number are in an atom I can state the mass of subatomic particles Look at the periodic table on page 8 of chemistry data book. Notice that each element has a number above it - this is its unique ATOMIC NUMBER. The atomic number used to be called the pro ...
Chapter 6 - Section 1-The Chemical Context of Life
... Pt. injected with glucose labeled with radioactive carbon Particles collide with electrons from chemical reactions in the body The PET detects these hot spots” Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Pt. injected with glucose labeled with radioactive carbon Particles collide with electrons from chemical reactions in the body The PET detects these hot spots” Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
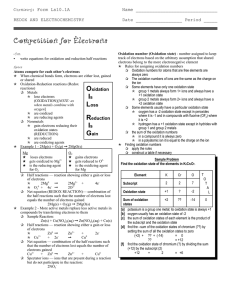
Competition for Electrons
... track of electrons based on the arbitrary assumption that shared electrons belong to the more electronegative element n Rules for assigning oxidation numbers q Oxidation numbers for atoms that are free elements are always zero q The oxidation numbers of ions are the same as the charge on the ion q S ...
... track of electrons based on the arbitrary assumption that shared electrons belong to the more electronegative element n Rules for assigning oxidation numbers q Oxidation numbers for atoms that are free elements are always zero q The oxidation numbers of ions are the same as the charge on the ion q S ...
Atoms - Learn More Chemistry
... • not all combinations of protons and neutrons create a stable nucleus • protons in the nucleus should repel each other, but there is a strong nuclear force (that is an attractive force) that holds the nucleus together • the nuclear force is only strong between subatomic particles that are extremely ...
... • not all combinations of protons and neutrons create a stable nucleus • protons in the nucleus should repel each other, but there is a strong nuclear force (that is an attractive force) that holds the nucleus together • the nuclear force is only strong between subatomic particles that are extremely ...
Chapter 2 - Bruder Chemistry
... Two regions Nucleus- protons and neutrons Electron cloud- region where you have a chance of finding an electron ...
... Two regions Nucleus- protons and neutrons Electron cloud- region where you have a chance of finding an electron ...
MATTER-Ch. 3-homogeneous vs. heterogeneous, elements
... Argon, krypton, and xenon are a. alkaline earth metals. c. actinides. b. noble gases. d. lanthanides. ___ ...
... Argon, krypton, and xenon are a. alkaline earth metals. c. actinides. b. noble gases. d. lanthanides. ___ ...
Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes
... Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • Isotopes can be defined in several ways that actually say the same thing. – Isotopes are two atoms of the same element that have different masses. – Isotopes are two atoms that have the same atomic number but that have different mass numbers. – Isotopes are two atoms tha ...
... Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • Isotopes can be defined in several ways that actually say the same thing. – Isotopes are two atoms of the same element that have different masses. – Isotopes are two atoms that have the same atomic number but that have different mass numbers. – Isotopes are two atoms tha ...
Topic 2
... Answer the following questions for species below: ionic or molecular substance; formula unit or molecule; ionic or covalent bonds involved? ...
... Answer the following questions for species below: ionic or molecular substance; formula unit or molecule; ionic or covalent bonds involved? ...
Unit 2 Review Game
... • During a chemical reaction, a group combines 5.00 grams of sodium and 7.72 grams of chlorine. The result of the reaction was 12.72 grams of sodium chloride. Which law does this support? ...
... • During a chemical reaction, a group combines 5.00 grams of sodium and 7.72 grams of chlorine. The result of the reaction was 12.72 grams of sodium chloride. Which law does this support? ...
Laws
... • During a chemical reaction, a group combines 5.00 grams of sodium and 7.72 grams of chlorine. The result of the reaction was 12.72 grams of sodium chloride. Which law does this support? ...
... • During a chemical reaction, a group combines 5.00 grams of sodium and 7.72 grams of chlorine. The result of the reaction was 12.72 grams of sodium chloride. Which law does this support? ...
Balancing RedOx reactions handout
... 1. Determine the oxidation numbers for all atoms in the reaction. 2. Determine which atom is being oxidized and which is being reduced. 3. Write a half reaction for the reduction process (addition of electrons…electrons added to the left side). 4. Write a half reaction for the oxidation process (los ...
... 1. Determine the oxidation numbers for all atoms in the reaction. 2. Determine which atom is being oxidized and which is being reduced. 3. Write a half reaction for the reduction process (addition of electrons…electrons added to the left side). 4. Write a half reaction for the oxidation process (los ...
The Mighty Electron - MVUSD Haiku Learning
... minus sign, its an ion! If there is no sign, its neutral. • P = neutral atom of phosphorous • O-2 = ion of oxygen w/a -2 charge • Li+ = ion of lithium w/a +1 charge ...
... minus sign, its an ion! If there is no sign, its neutral. • P = neutral atom of phosphorous • O-2 = ion of oxygen w/a -2 charge • Li+ = ion of lithium w/a +1 charge ...
Chem-130 Test Lecture
... Atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus. All atoms of the same element have the same atomic number. Mass number is the sum of the number of protons & neutrons The number of neutrons in the nucleus is given by the mass number minus the atomic number. Isotopes are atoms of the same ...
... Atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus. All atoms of the same element have the same atomic number. Mass number is the sum of the number of protons & neutrons The number of neutrons in the nucleus is given by the mass number minus the atomic number. Isotopes are atoms of the same ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Binary Ionic Compounds Type II Metals -have multiple charges in ionic compounds (Variable Oxidation #’s) ...
... Binary Ionic Compounds Type II Metals -have multiple charges in ionic compounds (Variable Oxidation #’s) ...
Electron Configurations
... The electron behaves as if it were spinning about an axis through its center. This electron spin generates a magnetic field, the direction of which depends on the direction of the spin. ...
... The electron behaves as if it were spinning about an axis through its center. This electron spin generates a magnetic field, the direction of which depends on the direction of the spin. ...
Chapter 11
... B) A large atom can be photographed with the aid of an ordinary microscope. C) An atom is the smallest particle known to exist. D) There are only about 100 different kinds of atoms that combine to form all ...
... B) A large atom can be photographed with the aid of an ordinary microscope. C) An atom is the smallest particle known to exist. D) There are only about 100 different kinds of atoms that combine to form all ...