* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
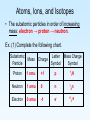
Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • All matter is composed of particles called atoms. • An atom is the smallest unit of an element that carries the general properties of that element. • Atoms are composed of subatomic particles. • The three most important subatomic particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • A proton is a subatomic particle that has a charge of +1. • A proton is a subatomic particle that has a mass of ≈1 amu (amu = atomic mass unit). • A proton can be symbolized two different ways! letter symbol: p or the mass-charge symbol: 1 H 1 (the superscript = mass & the subscript = charge). Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • A neutron is a subatomic particle that has a charge of 0 (zero). • A neutron is a subatomic particle that has a mass of ≈1 amu (In reality, a neutron is slightly more massive than a proton). • A neutron can be symbolized two different ways! letter symbol: n or the mass-charge symbol: 10n (the superscript = mass & the subscript = charge). Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • An electron is a subatomic particle that has a charge of -1. • An electron is a subatomic particle that has a mass of ≈0 amu (In reality, an electron does have a very very very very small mass). • An electron can be symbolized two different ways! letter symbol: eor the mass-charge symbol: 0 -1e (the superscript = mass & the subscript = charge). Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • The subatomic particles in order of increasing mass: electron → proton → neutron. Ex. (1) Complete the following chart. Subatomic Particle Letter Mass Charge Charge Symbol Symbol Mass Proton 1 amu +1 p 1 H 1 Neutron 1 amu 0 n 1 0n Electron 0 amu -1 e- 0 -1e Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes Ex. (2) Rank the subatomic particles from highest to lowest mass. ______ > ______ n p > ______ e• An atom’s atomic number (symbolized by the letter “Z”) is equal to its number of protons. • An atom’s mass number (symbolized by the letter “A”) is equal to the sum of its number of protons and neutrons. • Caution: mass number is not the same as atomic mass, which will be explained later. mass number ≠ atomic mass Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • An ion is a charged atom or group of atoms. • An ion composed of a single atom is called a monoatomic ion. Na1+ Cu2+ Al3+ Cl1- O2- As3- • An ion composed of two or more atoms is called a polyatomic ion (see Reference Table E). NO31- NH41+ SO42- H3O1+ PO43- Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • A positively charged ion (one that has more protons than electrons) is called a cation. Na1+ Cu2+ Al3+ NH41+ H3O1+ • A negatively charged ion (one that has more electrons than protons) is called an anion. Cl1- O2- As3- NO31- SO42- PO43- • In a atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • Dalton proposed, in his atomic theory, that atoms of the same element were exactly the same. • Isotopes of the same element exist because not all atoms of the same element are completely identical. Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • Isotopes can be defined in several ways that actually say the same thing. – Isotopes are two atoms of the same element that have different masses. – Isotopes are two atoms that have the same atomic number but that have different mass numbers. – Isotopes are two atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes • Isotopes are identified by their isotope number which is the same as the mass number (the number of protons and neutrons)! Hydrogen-1 has 1 proton and 0 neutrons. Hydrogen-2 has 1 proton and 1 neutron. Carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes Ex. (1) K-39: #p = _____ 20 19 and # n = _____ Ex. (2) Ni-59: #p = _____ 28 and # n = _____ 31 7 and # n = _____ 7 Ex. (3) N-14: #p = _____ Ba 137 Ex. (4) 56 p and 81 n : _____-_____ Si Ex. (5) 14 p and 15 n : _____-_____ 29 Ex. (6) 43 p and 56 n : _____-_____ Tc 99