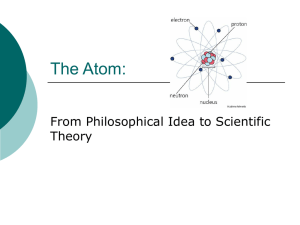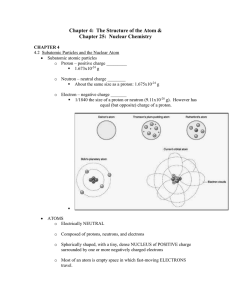
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... o Above the band of stability – too many _____________; Below the band of stability – too many _______________ or too few ______________ o BETA DECAY: For elements above the band of stability (too many neutrons) A NEUTRON will decay into a PROTON (stays in the nucleus) and an ELECTRON (leaves the ...
... o Above the band of stability – too many _____________; Below the band of stability – too many _______________ or too few ______________ o BETA DECAY: For elements above the band of stability (too many neutrons) A NEUTRON will decay into a PROTON (stays in the nucleus) and an ELECTRON (leaves the ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • All matter composed of atoms Atoms… • of same element are identical; atoms of diff. elements are diff. • cannot be divided, created, destroyed • combine in simple whole # ratios to form compounds (Law of Definite Proportions) • are combined, separated or rearranged in chem. ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • All matter composed of atoms Atoms… • of same element are identical; atoms of diff. elements are diff. • cannot be divided, created, destroyed • combine in simple whole # ratios to form compounds (Law of Definite Proportions) • are combined, separated or rearranged in chem. ...
Chapter 4
... Other Elements on the periodic table • ____________ Transition Metals - elements in Group 3 through 12. These metals are hard and shiny, good conductors of electricity, less reactive than metals in Groups 1 and 2. ________ is an Iron (Fe) example of a very important transition metal. • ____________ ...
... Other Elements on the periodic table • ____________ Transition Metals - elements in Group 3 through 12. These metals are hard and shiny, good conductors of electricity, less reactive than metals in Groups 1 and 2. ________ is an Iron (Fe) example of a very important transition metal. • ____________ ...
Chapter 1 Notes - cloudfront.net
... Chapter 1 Notes Chemistry – The study of the composition, structure, and properties of matter and the changes it undergoes. ...
... Chapter 1 Notes Chemistry – The study of the composition, structure, and properties of matter and the changes it undergoes. ...
Are You suprised ?
... 3. Give the noble gas configuration of the following elements. Try not to use the atomic number while doing so. (HINT: use the s, p, d, and f blocks we discussed). a. Cl b. Co c. Al d. I 4. What element has the following electron configuration? a. [Kr] 5s2 4d5 b. [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p4 c. [Xe] 6s2 4f14 ...
... 3. Give the noble gas configuration of the following elements. Try not to use the atomic number while doing so. (HINT: use the s, p, d, and f blocks we discussed). a. Cl b. Co c. Al d. I 4. What element has the following electron configuration? a. [Kr] 5s2 4d5 b. [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p4 c. [Xe] 6s2 4f14 ...
Atoms
... History of Atomic Theory Thomson – (discovering the electron) Proposed that atoms were made up of smaller particles. Theory that smaller negatively charged particles are spread evenly around a positively charged nucleus. His model was called the plum-pudding model. ...
... History of Atomic Theory Thomson – (discovering the electron) Proposed that atoms were made up of smaller particles. Theory that smaller negatively charged particles are spread evenly around a positively charged nucleus. His model was called the plum-pudding model. ...
Chapter 4
... four forces that account for the behavior of sub part 1. electromagnetic force *either attract or repel particles ...
... four forces that account for the behavior of sub part 1. electromagnetic force *either attract or repel particles ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... o The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is its mass number o Many elements have more than one stable kind of atom (atoms with the same number of protons but with different number of neutrons) o These are called isotopes; hydrogen has three, for example ...
... o The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom is its mass number o Many elements have more than one stable kind of atom (atoms with the same number of protons but with different number of neutrons) o These are called isotopes; hydrogen has three, for example ...
The Atom
... Atoms of a given element are identical in size and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in all these properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atom ...
... Atoms of a given element are identical in size and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in all these properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atom ...
Solid - burgess
... 3. the properties of the compound are different from the properties of the elements that make up the compound 4. can be separated only by a chemical reaction 5. two types of compounds a. ionic i. formed by the attraction between two or more elements that transfer electrons known as ions ...
... 3. the properties of the compound are different from the properties of the elements that make up the compound 4. can be separated only by a chemical reaction 5. two types of compounds a. ionic i. formed by the attraction between two or more elements that transfer electrons known as ions ...
The Atom - Williamstown Independent Schools
... Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated or rearranged. ...
... Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated or rearranged. ...
Chapter 14: Inside the Atom
... • Scientists create new elements by smashing atomic particles into a target element. • Isotope iodine131 used to diagnose ...
... • Scientists create new elements by smashing atomic particles into a target element. • Isotope iodine131 used to diagnose ...
Electron Arrangement
... An element contains only ONE type of atom. All elements are found in the Periodic Table in periods (rows) and groups (columns). All elements have a chemical symbol which has ONE capital letter and a small letter if a 2nd is needed. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties. Group 1 ...
... An element contains only ONE type of atom. All elements are found in the Periodic Table in periods (rows) and groups (columns). All elements have a chemical symbol which has ONE capital letter and a small letter if a 2nd is needed. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties. Group 1 ...
Aristotle - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... Elements are composed of submicroscopic indivisible particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different from one another. Atoms of one element can mix or chemically combine with atoms of other elements, creating compounds with simple whole-nu ...
... Elements are composed of submicroscopic indivisible particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different from one another. Atoms of one element can mix or chemically combine with atoms of other elements, creating compounds with simple whole-nu ...
Chapter 4 and 5 Powerpoint - School District of La Crosse
... points that the group 1 metals. 2.These metals are less reactive than group 1 because they have 2 electrons in the outer shell. 3. In order for them to have a full outer shell they must loose two electrons. 4.Magnesium is used in construction because of its strength and lightness. 5.Calcium is the b ...
... points that the group 1 metals. 2.These metals are less reactive than group 1 because they have 2 electrons in the outer shell. 3. In order for them to have a full outer shell they must loose two electrons. 4.Magnesium is used in construction because of its strength and lightness. 5.Calcium is the b ...
Atomic History powerpoint
... 1. All elements are composed of submicroscopic, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one elements are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine with one a ...
... 1. All elements are composed of submicroscopic, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one elements are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine with one a ...
PowerPoint - De Anza College
... Configuration of an Atom Rule [2] Each orbital holds a maximum of 2 electrons. Rule [3] When orbitals are equal in energy: •1 electron is added to each orbital until all of the orbitals are half-filled. •Then, the orbitals can be completely filled. ...
... Configuration of an Atom Rule [2] Each orbital holds a maximum of 2 electrons. Rule [3] When orbitals are equal in energy: •1 electron is added to each orbital until all of the orbitals are half-filled. •Then, the orbitals can be completely filled. ...
The Atomic Theory of Matter
... • The rest of the subatomic particles were found when scientists made theories on where the electrons were in an atom. In 1910, a scientist named Rutherford examined the effects of passing alpha rays through a gold foil a few thousand atoms thick. He found that most passed right through the gold foi ...
... • The rest of the subatomic particles were found when scientists made theories on where the electrons were in an atom. In 1910, a scientist named Rutherford examined the effects of passing alpha rays through a gold foil a few thousand atoms thick. He found that most passed right through the gold foi ...
Atomic Theory
... Configuration: the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom *The most stable electron configuration is the one in which the electrons are in orbitals with the lowest possible energies (we call this the ground state) *If an electron absorbs energy it is said to be in an excited state which ...
... Configuration: the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom *The most stable electron configuration is the one in which the electrons are in orbitals with the lowest possible energies (we call this the ground state) *If an electron absorbs energy it is said to be in an excited state which ...