General Chemistry
... A (monatomic) anion is named by placing -ide at the end of the root of the element’s name. ...
... A (monatomic) anion is named by placing -ide at the end of the root of the element’s name. ...
Chapter 4 - Mr. Fischer.com
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. A. Early philosophers believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. B. Dalton’s Atomic theory. Dalton used experimental methods, to transform Democritus’s ideas on atoms into scientific theory ...
... An atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains its identity in a chemical reaction. A. Early philosophers believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible. B. Dalton’s Atomic theory. Dalton used experimental methods, to transform Democritus’s ideas on atoms into scientific theory ...
Bohr`s Theory of the Atom
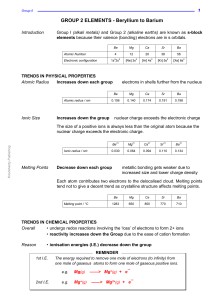
... Periodic Table it is found in. First-row elements have electrons in the first shell. Second-row elements have electrons in the first and second shells. Third-row elements have electrons in the first, second, and third shells, and so on. For the first 20 elements, the third shell can only contain a m ...
... Periodic Table it is found in. First-row elements have electrons in the first shell. Second-row elements have electrons in the first and second shells. Third-row elements have electrons in the first, second, and third shells, and so on. For the first 20 elements, the third shell can only contain a m ...
Notes
... Mg loses two electrons to become Mg2+ Nitrogen gains three electrons to become N3–. For a neutral species, the number of electrons lost and gained must be equal. However, Mg can only lose electrons in twos and N can only accept electrons in threes. Therefore, Mg needs to lose six electrons ( ...
... Mg loses two electrons to become Mg2+ Nitrogen gains three electrons to become N3–. For a neutral species, the number of electrons lost and gained must be equal. However, Mg can only lose electrons in twos and N can only accept electrons in threes. Therefore, Mg needs to lose six electrons ( ...
Atoms Molecules and Ions Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements l differ diff in i size, i mass, and d other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemi ...
... identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements l differ diff in i size, i mass, and d other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds In chemi ...
Atomic Structure
... What does all this have to do with Electricity? The number of valence electrons in an atom will determine if an element will allow electricity to flow. The ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself (away from its neighbors) is called Electronegativity. ...
... What does all this have to do with Electricity? The number of valence electrons in an atom will determine if an element will allow electricity to flow. The ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself (away from its neighbors) is called Electronegativity. ...
File
... Bohr’s model, electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, much like planets orbit a sun. The possible energies that electrons have in an atom are called energy levels. If an atom gains or loses energy, the energy of an electron can change. ...
... Bohr’s model, electrons move with constant speed in fixed orbits around the nucleus, much like planets orbit a sun. The possible energies that electrons have in an atom are called energy levels. If an atom gains or loses energy, the energy of an electron can change. ...
Section 1 Slides - St. John`s College HS
... called atoms. Atoms can be broken down into even smaller, more fundamental particles. ...
... called atoms. Atoms can be broken down into even smaller, more fundamental particles. ...
2.1 Modern Atomic Theory ppt
... A student in the lab wanted to classify an unknown substance as an element, compound, homogeneous mixture, or heterogeneous mixture. The student took the liquid substance and put it on top of a Bunsen burner. As the liquid heated up, she was able to separate two substances from each other through e ...
... A student in the lab wanted to classify an unknown substance as an element, compound, homogeneous mixture, or heterogeneous mixture. The student took the liquid substance and put it on top of a Bunsen burner. As the liquid heated up, she was able to separate two substances from each other through e ...
Export To Word
... student with that element's data from the Periodic Table of Elements. They will use that information to answer the question that the computer asks about the number of protons, neutrons, electrons or nucleons (particles in the nucleus) that an atom of that element contains. ...
... student with that element's data from the Periodic Table of Elements. They will use that information to answer the question that the computer asks about the number of protons, neutrons, electrons or nucleons (particles in the nucleus) that an atom of that element contains. ...
atomic number
... The Atomic Number = # of protons in the nucleus. The Atomic Mass = # of Protons + Neutrons The number of Protons = Number of Electrons. Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels or electron shells. ...
... The Atomic Number = # of protons in the nucleus. The Atomic Mass = # of Protons + Neutrons The number of Protons = Number of Electrons. Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels or electron shells. ...
File
... 60. In Period 2 of the Periodic Table, which Group contains the element with the highest first ionization energy? A) alkali metals B) alkaline earth metals C) halogens D) noble gases 61. Which statement is true about the properties of the elements in any one period of the Periodic Table? A) They are ...
... 60. In Period 2 of the Periodic Table, which Group contains the element with the highest first ionization energy? A) alkali metals B) alkaline earth metals C) halogens D) noble gases 61. Which statement is true about the properties of the elements in any one period of the Periodic Table? A) They are ...
The Modern Atomic Model
... • Every atom of an element will always have the same number of protons • Carbon will always have 6 protons, oxygen will always have 8 protons, and iron will always have 26 protons. ...
... • Every atom of an element will always have the same number of protons • Carbon will always have 6 protons, oxygen will always have 8 protons, and iron will always have 26 protons. ...
Atom notes
... 1. All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. ...
... 1. All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. ...
File
... • The protons have a positive charge, are found in the nucleus of the atom and contribute to the mass of the atom. • The neutrons have no charge – they are neutral. They are also found in the nucleus and contribute to the mass of the atom. • The electrons are found around the nucleus on orbitals. Th ...
... • The protons have a positive charge, are found in the nucleus of the atom and contribute to the mass of the atom. • The neutrons have no charge – they are neutral. They are also found in the nucleus and contribute to the mass of the atom. • The electrons are found around the nucleus on orbitals. Th ...
The Atomic Theory
... gas which in turn is equal to the ratio of their densities. Therefore molecular weight is proportional to density and so relative molecular and atomic weights can be determined from density measurements. Because nearly all the elements form stable compounds with it oxygen was chosen as the standard ...
... gas which in turn is equal to the ratio of their densities. Therefore molecular weight is proportional to density and so relative molecular and atomic weights can be determined from density measurements. Because nearly all the elements form stable compounds with it oxygen was chosen as the standard ...
A or `Mass Number` - Uplift Pinnacle Prep
... The US mint estimates that of all the pennies currently in circulation 66.5% of them are “new” (post-1982) pennies and 33.5% are ‘old’ pennies. A ‘new’ penny weighs 2.5g and an old penny weighs 3.1 g. Use this information to determine the average mass of a penny. ...
... The US mint estimates that of all the pennies currently in circulation 66.5% of them are “new” (post-1982) pennies and 33.5% are ‘old’ pennies. A ‘new’ penny weighs 2.5g and an old penny weighs 3.1 g. Use this information to determine the average mass of a penny. ...