- Te Kura
... expected to complete the teacher-marked assignment CH3001A. The theme of this resource is how chemists use the Periodic Table as a tool to help them make sense of chemistry. If you have difficulty with these concepts, it is advisable to enrol in CH2000 first, before continuing with CH3000. Keep this ...
... expected to complete the teacher-marked assignment CH3001A. The theme of this resource is how chemists use the Periodic Table as a tool to help them make sense of chemistry. If you have difficulty with these concepts, it is advisable to enrol in CH2000 first, before continuing with CH3000. Keep this ...
Practice Test Material - Directorate of Education
... Write the balanced ionic equation for the reaction of potassium dichromate with sodium sulphite to give Cr(III) and sulphate ions. ...
... Write the balanced ionic equation for the reaction of potassium dichromate with sodium sulphite to give Cr(III) and sulphate ions. ...
Principles of Chemistry: A Molecular Approach
... Since there are twice as many oxygen atoms per carbon atom in carbon dioxide than in carbon monoxide, the oxygen mass ratio ti should h ld b be 2 ...
... Since there are twice as many oxygen atoms per carbon atom in carbon dioxide than in carbon monoxide, the oxygen mass ratio ti should h ld b be 2 ...
Final
... 26. 5 pts. Identify the oxidizing agent, the reducing agent, the element being oxidized, the element being reduced, and the number of electrons transferred in this balanced chemical equation: 4 HNO3 + 3 S Æ 3 SO2 + 4 NO + 2 H2O ...
... 26. 5 pts. Identify the oxidizing agent, the reducing agent, the element being oxidized, the element being reduced, and the number of electrons transferred in this balanced chemical equation: 4 HNO3 + 3 S Æ 3 SO2 + 4 NO + 2 H2O ...
Chemistry
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The microscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been intr ...
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The microscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been intr ...
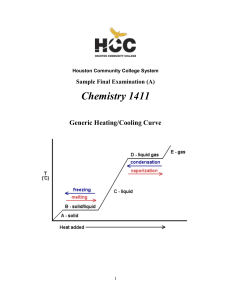
Chemistry 1411 Practice Exam 1, Chapters 1
... When an object claimed to be made of pure gold was immersed in a graduated cylinder containing water, the water level rose from 25.0 mL to 25.8 mL. The mass of the object was 7.1 g. What is the density of the object in grams per mL? (3 pts) ...
... When an object claimed to be made of pure gold was immersed in a graduated cylinder containing water, the water level rose from 25.0 mL to 25.8 mL. The mass of the object was 7.1 g. What is the density of the object in grams per mL? (3 pts) ...
REVIEW and answers
... melting point (bottom right hand side of transition metals). As electrons become less delocalized the metals become harder, more brittle and conduct less well, but their melting and boiling points increase (top left hand side of transition metals). ...
... melting point (bottom right hand side of transition metals). As electrons become less delocalized the metals become harder, more brittle and conduct less well, but their melting and boiling points increase (top left hand side of transition metals). ...
Contributions to Function in Blue Copper Proteins
... allowed), the metal L-edge and ligand K-edge can provide higher resolution probes of a metal center, and in particular, their intensities provide a very direct method to quantitate covalency of the metal d-based MOs.16-18 This is described in section 3.2. All of the above methods involve excitation ...
... allowed), the metal L-edge and ligand K-edge can provide higher resolution probes of a metal center, and in particular, their intensities provide a very direct method to quantitate covalency of the metal d-based MOs.16-18 This is described in section 3.2. All of the above methods involve excitation ...
幻灯片 1
... way different orbitals are filled is controlled by their energies (and hence their An atom consists of a very small positively charged nucleus, Electron and Nuclei different screening by other electrons) and by the Pauli exclusion principle. surrounded by negative electrons held by electrostatic att ...
... way different orbitals are filled is controlled by their energies (and hence their An atom consists of a very small positively charged nucleus, Electron and Nuclei different screening by other electrons) and by the Pauli exclusion principle. surrounded by negative electrons held by electrostatic att ...
Support Material
... Discovery of Electron, Proton and Neutron, atomic number, isotopes and isobars. Thomson’s model and its limitations. Rutherford’s model and its limitations, Bohr’s model and its limitations, concept of shells and subshells, dual nature of matter and light, cle Broglie’s relationship, Heisenberg unce ...
... Discovery of Electron, Proton and Neutron, atomic number, isotopes and isobars. Thomson’s model and its limitations. Rutherford’s model and its limitations, Bohr’s model and its limitations, concept of shells and subshells, dual nature of matter and light, cle Broglie’s relationship, Heisenberg unce ...
Electronic Structure and Exchange Integrals of Low
... The understanding of low-dimensional cuprates might be not only the key for the problem of HTSC: The main issue addressed in this work are the unusually magnetic properties of these systems (see Chapter 4) that attracted large theoretical interest in recent years. In the class of quasi one-dimension ...
... The understanding of low-dimensional cuprates might be not only the key for the problem of HTSC: The main issue addressed in this work are the unusually magnetic properties of these systems (see Chapter 4) that attracted large theoretical interest in recent years. In the class of quasi one-dimension ...
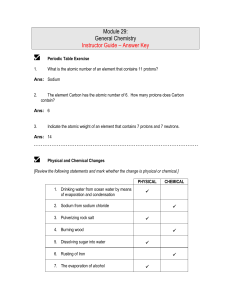
Module 29: General Chemistry Instructor Guide – Answer Key
... Ans: A physical change in matter is a change in the form of matter but not in its chemical identity. A chemical change in matter is a change in which one or more kinds of matter transform into a new kind of matter. ...
... Ans: A physical change in matter is a change in the form of matter but not in its chemical identity. A chemical change in matter is a change in which one or more kinds of matter transform into a new kind of matter. ...
Unit - 7.pmd
... covalency to four, nitrogen cannot form dπ –pπ bond as the heavier elements can e.g., R3P = O or R3P = CH2 (R = alkyl group). Phosphorus and arsenic can form dπ –dπ bond also with transition metals when their compounds like P(C2H5)3 and As(C6H5)3 act as ligands. (i) Reactivity towards hydrogen: All ...
... covalency to four, nitrogen cannot form dπ –pπ bond as the heavier elements can e.g., R3P = O or R3P = CH2 (R = alkyl group). Phosphorus and arsenic can form dπ –dπ bond also with transition metals when their compounds like P(C2H5)3 and As(C6H5)3 act as ligands. (i) Reactivity towards hydrogen: All ...
Group 1: The Alkali Metals
... boiling and melting points and are less dense than most elements. Li, Na, and K float on water because of their low densities. All of these characteristics can be attributed to the large atomic radii and weak metallic bonding these elements possess. Group 1 elements have a valence electron configura ...
... boiling and melting points and are less dense than most elements. Li, Na, and K float on water because of their low densities. All of these characteristics can be attributed to the large atomic radii and weak metallic bonding these elements possess. Group 1 elements have a valence electron configura ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... Polyatomic Ions • Polyatomic ions consist of more than one atom. • Polyatomic ions are usually groups of NONMETAL elements covalently bonded together. This group as a whole has a net charge (+ or –). The naming of ionic and molecular compounds will be covered in lab. However, you are expected to kno ...
... Polyatomic Ions • Polyatomic ions consist of more than one atom. • Polyatomic ions are usually groups of NONMETAL elements covalently bonded together. This group as a whole has a net charge (+ or –). The naming of ionic and molecular compounds will be covered in lab. However, you are expected to kno ...
Worksheet Significant Figures
... graphs are used when the data is qualitative (descriptive, based on observations or categories of data). Line graphs are used when the data is quantitative (more precise, measured with tools). **VERY IMPORTANT** When designing an experiment, you should have only one independent and one dependent var ...
... graphs are used when the data is qualitative (descriptive, based on observations or categories of data). Line graphs are used when the data is quantitative (more precise, measured with tools). **VERY IMPORTANT** When designing an experiment, you should have only one independent and one dependent var ...
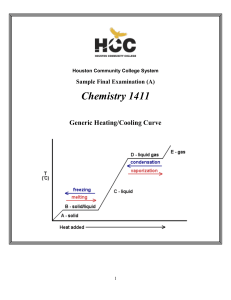
1411FINALSAMPLE+KEY - Houston Community College
... Since there are a total of four atoms plus lone pairs (four “electron domains”) around the central sulfur, the overall geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal. The hybridization of the sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not s ...
... Since there are a total of four atoms plus lone pairs (four “electron domains”) around the central sulfur, the overall geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal. The hybridization of the sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not s ...
Chemistry 2008 Multiple Choice
... [OH-] = ½(0.002 M) = 0.001 M pOH = -log(1 x 10-3) = 3 pH = 14 – 3 = 11 At the same temperature both gases have the same kinetic energy (K = 3/2RT). Amino acids: NH2–C(R)H–COOH (I hope you remember your biology). CO32- + 2 H+ CO2(g) + H2O Zn + 2 H+ H2(g) + Zn2+ Ba2+ + SO42- BaSO4(s) ...
... [OH-] = ½(0.002 M) = 0.001 M pOH = -log(1 x 10-3) = 3 pH = 14 – 3 = 11 At the same temperature both gases have the same kinetic energy (K = 3/2RT). Amino acids: NH2–C(R)H–COOH (I hope you remember your biology). CO32- + 2 H+ CO2(g) + H2O Zn + 2 H+ H2(g) + Zn2+ Ba2+ + SO42- BaSO4(s) ...
Molecular orbital diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place.